标签:store ges middle through 对象 axis while 开始 available
1、SDL_CreateThread
/*** Create a thread.*/extern DECLSPEC SDL_Thread *SDLCALLSDL_CreateThread(SDL_ThreadFunction fn, const char *name, void *data,pfnSDL_CurrentBeginThread pfnBeginThread,pfnSDL_CurrentEndThread pfnEndThread);
| ID | 参数 | 说明 |
| 1 | SDL_ThreadFunction fn | 线程所调用的函数 |
| 2 | const char *name | 线程的名称 |
| 3 | void *data | 线程所传入的数据 |
| 4 | pfnSDL_CurrentBeginThread pfnBeginThread | 开始线程 |
| 5 | pfnSDL_CurrentEndThread pfnEndThread | 结束线程 |
/*** Create a thread.*/#if defined(SDL_CreateThread) && SDL_DYNAMIC_API#undef SDL_CreateThread#define SDL_CreateThread(fn, name, data) SDL_CreateThread_REAL(fn, name, data, (pfnSDL_CurrentBeginThread)_beginthreadex, (pfnSDL_CurrentEndThread)_endthreadex)#else#define SDL_CreateThread(fn, name, data) SDL_CreateThread(fn, name, data, (pfnSDL_CurrentBeginThread)_beginthreadex, (pfnSDL_CurrentEndThread)_endthreadex)#endif#else/*** Create a thread.** Thread naming is a little complicated: Most systems have very small* limits for the string length (Haiku has 32 bytes, Linux currently has 16,* Visual C++ 6.0 has nine!), and possibly other arbitrary rules. You‘ll* have to see what happens with your system‘s debugger. The name should be* UTF-8 (but using the naming limits of C identifiers is a better bet).* There are no requirements for thread naming conventions, so long as the* string is null-terminated UTF-8, but these guidelines are helpful in* choosing a name:** http://stackoverflow.com/questions/149932/naming-conventions-for-threads** If a system imposes requirements, SDL will try to munge the string for* it (truncate, etc), but the original string contents will be available* from SDL_GetThreadName().*/extern DECLSPEC SDL_Thread *SDLCALLSDL_CreateThread(SDL_ThreadFunction fn, const char *name, void *data);#endif
| ID | 参数 | 说明 |
| 1 | SDL_ThreadFunction fn | 线程所调用的函数 |
| 2 | const char *name | 线程的名称 |
| 3 | void *data | 线程所传入的数据 |
/*** \brief Wait a specified number of milliseconds before returning.*/extern DECLSPEC void SDLCALL SDL_Delay(Uint32 ms);
| ID | 参数 | 说明 |
| 1 | Uint32 ms | 已毫秒为单位的数值 |
/*** Wait for a thread to finish. Threads that haven‘t been detached will* remain (as a "zombie") until this function cleans them up. Not doing so* is a resource leak.** Once a thread has been cleaned up through this function, the SDL_Thread* that references it becomes invalid and should not be referenced again.* As such, only one thread may call SDL_WaitThread() on another.** The return code for the thread function is placed in the area* pointed to by \c status, if \c status is not NULL.** You may not wait on a thread that has been used in a call to* SDL_DetachThread(). Use either that function or this one, but not* both, or behavior is undefined.** It is safe to pass NULL to this function; it is a no-op.*/extern DECLSPEC void SDLCALL SDL_WaitThread(SDL_Thread * thread, int *status);
| ID | 参数 | 说明 |
| 1 | SDL_Thread * thread | 所等待的线程 |
| 2 | int *status | 返回的线程状态 |
/*** \brief Waits indefinitely for the next available event.** \return 1, or 0 if there was an error while waiting for events.** \param event If not NULL, the next event is removed from the queue and* stored in that area.*/extern DECLSPEC int SDLCALL SDL_WaitEvent(SDL_Event * event);
| ID | 参数 | 说明 |
| 1 | int | 返回参数 返回0或1,如果返回错误将继续等下一个事件 |
| 2 | SDL_Event * event | 返回SDL_EVENT事件 |
/*** \brief General event structure*/typedef union SDL_Event{Uint32 type; /**< Event type, shared with all events */SDL_CommonEvent common; /**< Common event data */SDL_WindowEvent window; /**< Window event data */SDL_KeyboardEvent key; /**< Keyboard event data */SDL_TextEditingEvent edit; /**< Text editing event data */SDL_TextInputEvent text; /**< Text input event data */SDL_MouseMotionEvent motion; /**< Mouse motion event data */SDL_MouseButtonEvent button; /**< Mouse button event data */SDL_MouseWheelEvent wheel; /**< Mouse wheel event data */SDL_JoyAxisEvent jaxis; /**< Joystick axis event data */SDL_JoyBallEvent jball; /**< Joystick ball event data */SDL_JoyHatEvent jhat; /**< Joystick hat event data */SDL_JoyButtonEvent jbutton; /**< Joystick button event data */SDL_JoyDeviceEvent jdevice; /**< Joystick device change event data */SDL_ControllerAxisEvent caxis; /**< Game Controller axis event data */SDL_ControllerButtonEvent cbutton; /**< Game Controller button event data */SDL_ControllerDeviceEvent cdevice; /**< Game Controller device event data */SDL_AudioDeviceEvent adevice; /**< Audio device event data */SDL_QuitEvent quit; /**< Quit request event data */SDL_UserEvent user; /**< Custom event data */SDL_SysWMEvent syswm; /**< System dependent window event data */SDL_TouchFingerEvent tfinger; /**< Touch finger event data */SDL_MultiGestureEvent mgesture; /**< Gesture event data */SDL_DollarGestureEvent dgesture; /**< Gesture event data */SDL_DropEvent drop; /**< Drag and drop event data *//* This is necessary for ABI compatibility between Visual C++ and GCCVisual C++ will respect the push pack pragma and use 52 bytes forthis structure, and GCC will use the alignment of the largest datatypewithin the union, which is 8 bytes.So... we‘ll add padding to force the size to be 56 bytes for both.*/Uint8 padding[56];} SDL_Event;
/* The SDL mutex structure, defined in SDL_sysmutex.c */struct SDL_mutex;typedef struct SDL_mutex SDL_mutex;
/*** Create a mutex, initialized unlocked.*/extern DECLSPEC SDL_mutex *SDLCALL SDL_CreateMutex(void);
/*** Lock the mutex.** \return 0, or -1 on error.*/#define SDL_mutexP(m) SDL_LockMutex(m)extern DECLSPEC int SDLCALL SDL_LockMutex(SDL_mutex * mutex);/*** Try to lock the mutex** \return 0, SDL_MUTEX_TIMEDOUT, or -1 on error*/extern DECLSPEC int SDLCALL SDL_TryLockMutex(SDL_mutex * mutex);
/*** Unlock the mutex.** \return 0, or -1 on error.** \warning It is an error to unlock a mutex that has not been locked by* the current thread, and doing so results in undefined behavior.*/#define SDL_mutexV(m) SDL_UnlockMutex(m)extern DECLSPEC int SDLCALL SDL_UnlockMutex(SDL_mutex * mutex);
/*** Destroy a mutex.*/extern DECLSPEC void SDLCALL SDL_DestroyMutex(SDL_mutex * mutex);
/* The SDL condition variable structure, defined in SDL_syscond.c */struct SDL_cond;typedef struct SDL_cond SDL_cond;
/*** Create a condition variable.** Typical use of condition variables:** Thread A:* SDL_LockMutex(lock);* while ( ! condition ) {* SDL_CondWait(cond, lock);* }* SDL_UnlockMutex(lock);** Thread B:* SDL_LockMutex(lock);* ...* condition = true;* ...* SDL_CondSignal(cond);* SDL_UnlockMutex(lock);** There is some discussion whether to signal the condition variable* with the mutex locked or not. There is some potential performance* benefit to unlocking first on some platforms, but there are some* potential race conditions depending on how your code is structured.** In general it‘s safer to signal the condition variable while the* mutex is locked.*/extern DECLSPEC SDL_cond *SDLCALL SDL_CreateCond(void);
/*** Destroy a condition variable.*/extern DECLSPEC void SDLCALL SDL_DestroyCond(SDL_cond * cond);
/*** Restart one of the threads that are waiting on the condition variable.** \return 0 or -1 on error.*/extern DECLSPEC int SDLCALL SDL_CondSignal(SDL_cond * cond);
/*** Restart all threads that are waiting on the condition variable.** \return 0 or -1 on error.*/extern DECLSPEC int SDLCALL SDL_CondBroadcast(SDL_cond * cond);
/*** Wait on the condition variable, unlocking the provided mutex.** \warning The mutex must be locked before entering this function!** The mutex is re-locked once the condition variable is signaled.** \return 0 when it is signaled, or -1 on error.*/extern DECLSPEC int SDLCALL SDL_CondWait(SDL_cond * cond, SDL_mutex * mutex);
| ID | 参数 | 说明 |
| 1 | SDL_cond * cond | 条件变量 |
| 2 | SDL_mutex * mutex | SDL互斥对象 |
/*** Waits for at most \c ms milliseconds, and returns 0 if the condition* variable is signaled, ::SDL_MUTEX_TIMEDOUT if the condition is not* signaled in the allotted time, and -1 on error.** \warning On some platforms this function is implemented by looping with a* delay of 1 ms, and so should be avoided if possible.*/extern DECLSPEC int SDLCALL SDL_CondWaitTimeout(SDL_cond * cond,SDL_mutex * mutex, Uint32 ms);
| ID | 参数 | 说明 |
| 1 | SDL_cond * cond | 条件变量 |
| 2 | SDL_mutex * mutex | SDL互斥对象 |
| 3 | Uint32 ms | 超时时间,单位毫秒 |
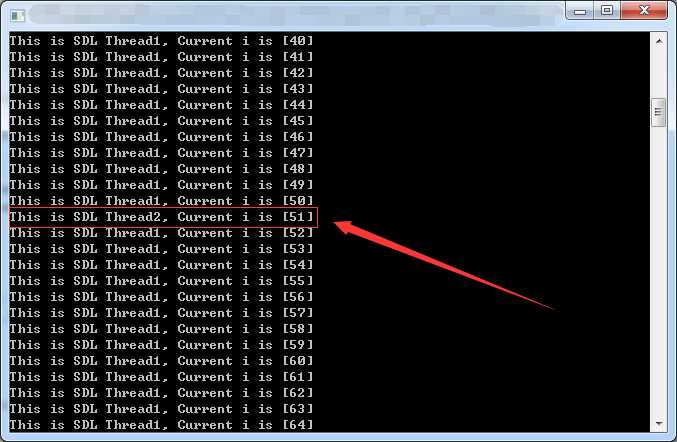
// SDL_ThreadTest.cpp : 定义控制台应用程序的入口点。//#include "stdafx.h"#define __STDC_CONSTANT_MACROS#define SDL_MAIN_HANDLED#define SDL_THREAD_FINISH (SDL_USEREVENT+1)// 导入SDL库#include "SDL.h"int i = 0;SDL_mutex* data_lock;SDL_cond * cond;SDL_Thread* pthread1;SDL_Thread* pthread2;SDL_Event event;int SDLThread1(void *data){int * pi = (int*)data;for (;;){if ((*pi) > 99){SDL_Event event;event.type = SDL_THREAD_FINISH;SDL_PushEvent(&event);break;}SDL_LockMutex(data_lock);(*pi)++;printf("This is SDL Thread1, Current i is [%d]\n", (*pi));if ((*pi)==50){SDL_CondSignal(cond);}SDL_UnlockMutex(data_lock);SDL_Delay(10);}return 0;}int SDLThread2(void *data){int * pi = (int*)data;for (;;){if ((*pi) > 99){SDL_Event event;event.type = SDL_THREAD_FINISH;SDL_PushEvent(&event);break;}SDL_LockMutex(data_lock);SDL_CondWait(cond, data_lock);(*pi)++;printf("This is SDL Thread2, Current i is [%d]\n", (*pi));SDL_UnlockMutex(data_lock);SDL_Delay(10);}return 0;}int main(){SDL_Init(SDL_INIT_EVERYTHING);data_lock = SDL_CreateMutex();cond = SDL_CreateCond();pthread1 = SDL_CreateThread(SDLThread1, "Thread1", &i);pthread2 = SDL_CreateThread(SDLThread2, "Thread2", &i);for (;;){SDL_WaitEvent(&event);if (event.type == SDL_THREAD_FINISH)break;}SDL_DestroyCond(cond);SDL_DestroyMutex(data_lock);SDL_Quit();system("pause");return 0;}
标签:store ges middle through 对象 axis while 开始 available
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/findman/p/6050589.html