标签:conf lin tty char 路由 作用 整合 action 构造
下载本文提到的完整代码示例请访问:How to authorization Angular 2 app with asp.net core web api
Angular2是对Angular1的一次彻底的,破坏性的更新。
相对于Angular1.x,借用某果的广告语,唯一的不同,就是处处都不同。
关于Angular2,强烈建议查阅官方文档:英文传送门 | 中文传送门
废话不多说,接下来的内容中,将介绍如何将 Angular2 整合到 ASP.NET Core 中,并实现一个Anguar2 和 ASP.NET Core Web API 的身份认证。
注意:本文章属于Step by step + Code Sample教程,且篇幅较长,建议下载本Sample并跟着本文进度自己重做一遍本例,下载完整代码并分析代码结构才有意义,下载地址:How to authorization Angular 2 app with asp.net core web api
在VS中新建项目,项目类型选择 ASP.NET Core Web Application(.Net Core),输入项目名称为:CSAuthorAngular2InASPNetCore,Template选择为Empty.
注:添加下面的代码时IDE会报代码错误,这是因为还没有引用对用的包,进入报错的这一行,点击灯泡,加载对应的包就可以了。
(图文无关)
在ConfigureServices中添加如下代码
services.AddMvc();
这里是添加MVC服务
在Configure中添加如下代码
app.UseStaticFiles();
app.UseMvc(routes =>
{
routes.MapRoute(
name: "default",
template: "{controller=Home}/{action=Index}");
});
第一句是启用静态文件,第二句是应用MVC模式并添加路由配置。
完整的代码应该是这个样子
public class Startup
{
// This method gets called by the runtime. Use this method to add services to the container.
// For more information on how to configure your application, visit http://go.microsoft.com/fwlink/?LinkID=398940
public void ConfigureServices(IServiceCollection services)
{
services.AddMvc();
}
// This method gets called by the runtime. Use this method to configure the HTTP request pipeline.
public void Configure(IApplicationBuilder app, IHostingEnvironment env, ILoggerFactory loggerFactory)
{
app.UseStaticFiles();
app.UseMvc(routes =>
{
routes.MapRoute(
name: "default",
template: "{controller=Home}/{action=Index}");
});
}
}
3.2.1.在项目根目录下添加Controllers目录,并在其中添加一个控制器HomeController.cs,默认代码即可。
3.2.2.在项目跟目录下创建Views目录,在Views目录中新建目录Home, 最后在Home目录中新建视图Index.cshtml,内容应该是这样:
<html>
<head>
<title>Angular QuickStart</title>
<base href="/">
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1">
<!-- 1. Load libraries -->
<!-- Polyfill(s) for older browsers -->
<script src="node_modules/core-js/client/shim.min.js"></script>
<script src="node_modules/zone.js/dist/zone.js"></script>
<script src="node_modules/reflect-metadata/Reflect.js"></script>
<script src="node_modules/systemjs/dist/system.src.js"></script>
<!-- 2. Configure SystemJS -->
<script src="systemjs.config.js"></script>
<script>
System.import(‘app‘).catch(function(err){ console.error(err); });
</script>
</head>
<!-- 3. Display the application -->
<body>
<my-app>Loading...</my-app>
</body>
</html>
现在运行项目的话你仅仅能看到一个Loading,再控制台中你还能看到错误,这是因为我们还没有配置Angular。让我们前往wwwroot目录。
3.3.1搭建Angular2基础环境
package.json
{
"name": "angular-quickstart",
"version": "1.0.0",
"scripts": {
"start": "tsc && concurrently \"tsc -w\" \"lite-server\" ",
"lite": "lite-server",
"postinstall": "typings install",
"tsc": "tsc",
"tsc:w": "tsc -w",
"typings": "typings"
},
"licenses": [
{
"type": "MIT",
"url": "https://github.com/angular/angular.io/blob/master/LICENSE"
}
],
"dependencies": {
"@angular/common": "2.0.2",
"@angular/compiler": "2.0.2",
"@angular/core": "2.0.2",
"@angular/forms": "2.0.2",
"@angular/http": "2.0.2",
"@angular/platform-browser": "2.0.2",
"@angular/platform-browser-dynamic": "2.0.2",
"@angular/router": "3.0.2",
"@angular/upgrade": "2.0.2",
"angular-in-memory-web-api": "0.1.5",
"bootstrap": "3.3.7",
"core-js": "2.4.1",
"reflect-metadata": "0.1.8",
"rxjs": "5.0.0-beta.12",
"systemjs": "0.19.39",
"zone.js": "0.6.25"
},
"devDependencies": {
"concurrently": "3.0.0",
"gulp": "^3.9.1",
"lite-server": "2.2.2",
"typescript": "2.0.3",
"typings": "1.4.0"
}
}
systemjs.config.js
(function (global) {
System.config({
paths: {
// paths serve as alias
‘npm:‘: ‘node_modules/‘
},
// map tells the System loader where to look for things
map: {
// our app is within the app folder
app: ‘app‘,
// angular bundles
‘@angular/core‘: ‘npm:@angular/core/bundles/core.umd.js‘,
‘@angular/common‘: ‘npm:@angular/common/bundles/common.umd.js‘,
‘@angular/compiler‘: ‘npm:@angular/compiler/bundles/compiler.umd.js‘,
‘@angular/platform-browser‘: ‘npm:@angular/platform-browser/bundles/platform-browser.umd.js‘,
‘@angular/platform-browser-dynamic‘: ‘npm:@angular/platform-browser-dynamic/bundles/platform-browser-dynamic.umd.js‘,
‘@angular/http‘: ‘npm:@angular/http/bundles/http.umd.js‘,
‘@angular/router‘: ‘npm:@angular/router/bundles/router.umd.js‘,
‘@angular/forms‘: ‘npm:@angular/forms/bundles/forms.umd.js‘,
‘@angular/upgrade‘: ‘npm:@angular/upgrade/bundles/upgrade.umd.js‘,
// other libraries
‘rxjs‘: ‘npm:rxjs‘,
‘angular-in-memory-web-api‘: ‘npm:angular-in-memory-web-api/bundles/in-memory-web-api.umd.js‘
},
// packages tells the System loader how to load when no filename and/or no extension
packages: {
app: {
main: ‘./main.js‘,
defaultExtension: ‘js‘
},
rxjs: {
defaultExtension: ‘js‘
}
}
});
})(this);
tsconfig.js
{
"compileOnSave": true,
"compilerOptions": {
"target": "es5",
"module": "commonjs",
"moduleResolution": "node",
"sourceMap": true,
"emitDecoratorMetadata": true,
"experimentalDecorators": true,
"removeComments": false,
"noImplicitAny": false
},
"exclude": [
"node_modules"
]
}
typings.json(注,在最新文档中typings已被npm的@types替代,参见官方文档:文档变更日志)
{
"globalDependencies": {
"core-js": "registry:dt/core-js#0.0.0+20160725163759",
"jasmine": "registry:dt/jasmine#2.2.0+20160621224255",
"node": "registry:dt/node#6.0.0+20160909174046"
}
}
右击wwwroot中的Package.json,选择Restore Packages(或者在CMD下进入wwwroot目录,并执行命令 npm install),npm会去下载需要的包,并存储于node_modules目录中。
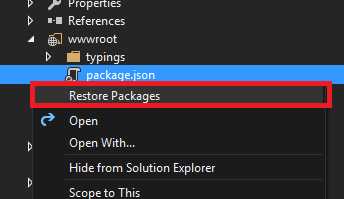
3.3.2.配置启动文件以启用Angular2
在wwwroot下新建目录app,app拥有如下文件:
app.component.ts
import { Component } from ‘@angular/core‘;
@Component({
moduleId: module.id,
selector: ‘my-app‘,
template: "this is in angular2",
})
export class AppComponent {
}
可以发现被@Component装饰属性装饰了AppComponent,selector指代你Component的占位符,比如本例中你可以再Home/index.cshtml中发现一段这样的标记
<my-app>Loading...</my-app>
template既为该Component的View,不要忘记moduleId,不添加它会出现很多奇怪的问题。
app.module.ts
import { NgModule } from "@angular/core";
import { BrowserModule } from "@angular/platform-browser";
import { AppComponent } from "./app.component";
@NgModule({
bootstrap: [AppComponent],
imports: [
BrowserModule
],
declarations: [
AppComponent
]
})
export class AppModule { }
main.ts
import { platformBrowserDynamic } from ‘@angular/platform-browser-dynamic‘;
import { AppModule } from ‘./app.module‘;
const platform = platformBrowserDynamic();
platform.bootstrapModule(AppModule);
基础整合完毕。
按F5 Debug一下,现在你能再浏览器中看到一句话:this is in angular 2
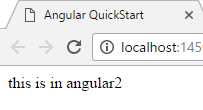
---分割线-------------------------------------------------------------------------
废了半天劲,看着很傻,没有任何成就感。怎么办,让我们再深入一点,接下来我们来为Angular2完成一个Token base的身份验证,我会把Angular2的routing,data bind,service,http,等等你工作中最常用到的挨个演示一遍。
4.1.1.1.在项目根目录下创建一个文件夹Auth,并添加RSAKeyHelper.cs以及TokenAuthOption.cs两个文件
在RSAKeyHelper.cs中
using System.Security.Cryptography;
namespace CSTokenBaseAuth.Auth
{
public class RSAKeyHelper
{
public static RSAParameters GenerateKey()
{
using (var key = new RSACryptoServiceProvider(2048))
{
return key.ExportParameters(true);
}
}
}
}
在TokenAuthOption.cs中
using System;
using Microsoft.IdentityModel.Tokens;
namespace CSTokenBaseAuth.Auth
{
public class TokenAuthOption
{
public static string Audience { get; } = "ExampleAudience";
public static string Issuer { get; } = "ExampleIssuer";
public static RsaSecurityKey Key { get; } = new RsaSecurityKey(RSAKeyHelper.GenerateKey());
public static SigningCredentials SigningCredentials { get; } = new SigningCredentials(Key, SecurityAlgorithms.RsaSha256Signature);
public static TimeSpan ExpiresSpan { get; } = TimeSpan.FromMinutes(20);
}
}
4.1.1.2.在项目根目录下创建目录Model,并在其中添加RequestResult.cs,代码应该是这样。
public class RequestResult
{
public RequestState State { get; set; }
public string Msg { get; set; }
public Object Data { get; set; }
}
public enum RequestState
{
Failed = -1,
NotAuth = 0,
Success = 1
}
在ConfigureServices中添加如下代码:
services.AddAuthorization(auth =>
{
auth.AddPolicy("Bearer", new AuthorizationPolicyBuilder()
.AddAuthenticationSchemes(JwtBearerDefaults.AuthenticationScheme??)
.RequireAuthenticatedUser().Build());
});
这里是添加身份认证服务
在Configure方法中添加如下代码:
app.UseExceptionHandler(appBuilder =>
{
appBuilder.Use(async (context, next) =>
{
var error = context.Features[typeof(IExceptionHandlerFeature)] as IExceptionHandlerFeature;
//when authorization has failed, should retrun a json message to client
if (error != null && error.Error is SecurityTokenExpiredException)
{
context.Response.StatusCode = 401;
context.Response.ContentType = "application/json";
await context.Response.WriteAsync(JsonConvert.SerializeObject(new RequestResult
{
State = RequestState.NotAuth,
Msg = "token expired"
}));
}
//when orther error, retrun a error message json to client
else if (error != null && error.Error != null)
{
context.Response.StatusCode = 500;
context.Response.ContentType = "application/json";
await context.Response.WriteAsync(JsonConvert.SerializeObject(new RequestResult
{
State = RequestState.Failed,
Msg = error.Error.Message
}));
}
//when no error, do next.
else await next();
});
});
本段是Handle当身份认证失败时抛出的异常,并返回合适的json
在相同的方法中添加另外一段代码:
app.UseJwtBearerAuthentication(new JwtBearerOptions()
{
TokenValidationParameters = new TokenValidationParameters()
{
IssuerSigningKey = TokenAuthOption.Key,
ValidAudience = TokenAuthOption.Audience,
ValidIssuer = TokenAuthOption.Issuer,
// When receiving a token, check that we‘ve signed it.
ValidateIssuerSigningKey = true,
// When receiving a token, check that it is still valid.
ValidateLifetime = true,
// This defines the maximum allowable clock skew - i.e. provides a tolerance on the token expiry time
// when validating the lifetime. As we‘re creating the tokens locally and validating them on the same
// machines which should have synchronised time, this can be set to zero. Where external tokens are
// used, some leeway here could be useful.
ClockSkew = TimeSpan.FromMinutes(0)
}
});
本段代码是应用JWTBearerAuthentication身份认证。
在Controllers中新建一个Web API Controller Class,命名为TokenAuthController.cs。我们将在这里完成登录授权,
在同文件下添加两个类,分别用来模拟用户模型,以及用户存储,代码应该是这样:
public class User
{
public Guid ID { get; set; }
public string Username { get; set; }
public string Password { get; set; }
}
public static class UserStorage
{
public static List<User> Users { get; set; } = new List<User> {
new User {ID=Guid.NewGuid(),Username="user1",Password = "user1psd" },
new User {ID=Guid.NewGuid(),Username="user2",Password = "user2psd" },
new User {ID=Guid.NewGuid(),Username="user3",Password = "user3psd" }
};
}
接下来在TokenAuthController.cs中添加如下方法
private string GenerateToken(User user, DateTime expires)
{
var handler = new JwtSecurityTokenHandler();
ClaimsIdentity identity = new ClaimsIdentity(
new GenericIdentity(user.Username, "TokenAuth"),
new[] {
new Claim("ID", user.ID.ToString())
}
);
var securityToken = handler.CreateToken(new SecurityTokenDescriptor
{
Issuer = TokenAuthOption.Issuer,
Audience = TokenAuthOption.Audience,
SigningCredentials = TokenAuthOption.SigningCredentials,
Subject = identity,
Expires = expires
});
return handler.WriteToken(securityToken);
}
该方法仅仅只是生成一个Auth Token,接下来我们来添加另外一个方法来调用它
在相同文件中添加如下代码
[HttpPost]
public string GetAuthToken(User user)
{
var existUser = UserStorage.Users.FirstOrDefault(u => u.Username == user.Username && u.Password == user.Password);
if (existUser != null)
{
var requestAt = DateTime.Now;
var expiresIn = requestAt + TokenAuthOption.ExpiresSpan;
var token = GenerateToken(existUser, expiresIn);
return JsonConvert.SerializeObject(new {
stateCode = 1,
requertAt = requestAt,
expiresIn = TokenAuthOption.ExpiresSpan.TotalSeconds,
accessToken = token
});
}
else
{
return JsonConvert.SerializeObject(new { stateCode = -1, errors = "Username or password is invalid" });
}
}
接下来我们来完成授权部分,在相同的文件中添加如下代码:
public string GetUserInfo()
{
var claimsIdentity = User.Identity as ClaimsIdentity;
return JsonConvert.SerializeObject(new RequestResult
{
State = RequestState.Success,
Data = new
{
UserName = claimsIdentity.Name
}
});
}
为方法添加装饰属性
[HttpGet]
[Authorize("Bearer")]
第二行代码说明这个action需要身份验证。
该文件完整的代码应该是这个样子:
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Mvc;
using CSAuthorAngular2InASPNetCore.Auth;
using System.IdentityModel.Tokens.Jwt;
using Newtonsoft.Json;
using System.Security.Claims;
using System.Security.Principal;
using Microsoft.IdentityModel.Tokens;
using CSAuthorAngular2InASPNetCore.Model;
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Authorization;
namespace CSAuthorAngular2InASPNetCore.Controllers
{
[Route("api/[controller]")]
public class TokenAuthController : Controller
{
[HttpPost]
public string GetAuthToken([FromBody]User user)
{
var existUser = UserStorage.Users.FirstOrDefault(u => u.Username == user.Username && u.Password == user.Password);
if (existUser != null)
{
var requestAt = DateTime.Now;
var expiresIn = requestAt + TokenAuthOption.ExpiresSpan;
var token = GenerateToken(existUser, expiresIn);
return JsonConvert.SerializeObject(new RequestResult
{
State = RequestState.Success,
Data = new
{
requertAt = requestAt,
expiresIn = TokenAuthOption.ExpiresSpan.TotalSeconds,
tokeyType = TokenAuthOption.TokenType,
accessToken = token
}
});
}
else
{
return JsonConvert.SerializeObject(new RequestResult
{
State = RequestState.Failed,
Msg = "Username or password is invalid"
});
}
}
private string GenerateToken(User user, DateTime expires)
{
var handler = new JwtSecurityTokenHandler();
ClaimsIdentity identity = new ClaimsIdentity(
new GenericIdentity(user.Username, "TokenAuth"),
new[] {
new Claim("ID", user.ID.ToString())
}
);
var securityToken = handler.CreateToken(new SecurityTokenDescriptor
{
Issuer = TokenAuthOption.Issuer,
Audience = TokenAuthOption.Audience,
SigningCredentials = TokenAuthOption.SigningCredentials,
Subject = identity,
Expires = expires
});
return handler.WriteToken(securityToken);
}
[HttpGet]
[Authorize("Bearer")]
public string GetUserInfo()
{
var claimsIdentity = User.Identity as ClaimsIdentity;
return JsonConvert.SerializeObject(new RequestResult
{
State = RequestState.Success,
Data = new
{
UserName = claimsIdentity.Name
}
});
}
}
public class User
{
public Guid ID { get; set; }
public string Username { get; set; }
public string Password { get; set; }
}
public static class UserStorage
{
public static List<User> Users { get; set; } = new List<User> {
new User {ID=Guid.NewGuid(),Username="user1",Password = "user1psd" },
new User {ID=Guid.NewGuid(),Username="user2",Password = "user2psd" },
new User {ID=Guid.NewGuid(),Username="user3",Password = "user3psd" }
};
}
}
4.2.1创建View Model
在wwwroot/app下创建一个目录:_model, 并添加一个Typescript文件RequestResult.ts,内容应该是这样。
export class RequestResult {
State: number;
Msg: string;
Data: Object;
}
4.2.2创建Service
在wwwroot/app下创建一个目录:_services,并添加一个Typescript文件auth.service.ts,内容应该是这样。
import { Injectable } from "@angular/core";
import { Headers, Http } from "@angular/http";
import "rxjs/add/operator/toPromise";
import { RequestResult } from "../_model/RequestResult";
@Injectable()
export class AuthService {
private tokeyKey = "token";
private token: string;
constructor(
private http: Http
) { }
login(userName: string, password: string): Promise<RequestResult> {
return this.http.post("/api/TokenAuth", { Username: userName, Password: password }).toPromise()
.then(response => {
let result = response.json() as RequestResult;
if (result.State == 1) {
let json = result.Data as any;
sessionStorage.setItem("token", json.accessToken);
}
return result;
})
.catch(this.handleError);
}
checkLogin(): boolean {
var token = sessionStorage.getItem(this.tokeyKey);
return token != null;
}
getUserInfo(): Promise<RequestResult> {
return this.authGet("/api/TokenAuth");
}
authPost(url: string, body: any): Promise<RequestResult> {
let headers = this.initAuthHeaders();
return this.http.post(url, body, { headers: headers }).toPromise()
.then(response => response.json() as RequestResult)
.catch(this.handleError);
}
authGet(url): Promise<RequestResult> {
let headers = this.initAuthHeaders();
return this.http.get(url, { headers: headers }).toPromise()
.then(response => response.json() as RequestResult)
.catch(this.handleError);
}
private getLocalToken(): string {
if (!this.token) {
this.token = sessionStorage.getItem(this.tokeyKey);
}
return this.token;
}
private initAuthHeaders(): Headers {
let token = this.getLocalToken();
if (token == null) throw "No token";
var headers = new Headers();
headers.append("Authorization", "Bearer " + token);
return headers;
}
private handleError(error: any): Promise<any> {
console.error(‘An error occurred‘, error);
return Promise.reject(error.message || error);
}
}
本文件主要用来完成登陆以及登陆验证工作,之后该service将可以被注入到Component中以便被Component调用。
注:主要的逻辑都应该写到service中
4.2.3.1.在wwwroot/app下创建一个目录home,该目录用来存放HomeComponent,home应拥有如下文件:
home.component.ts
import { Component, OnInit } from "@angular/core";
import { AuthService } from "../_services/auth.service";
@Component({
moduleId: module.id,
selector: "my-home",
templateUrl: "view.html",
styleUrls: ["style.css"]
})
export class HomeComponent implements OnInit {
isLogin = false;
userName: string;
constructor(
private authService: AuthService
) { }
ngOnInit(): void {
this.isLogin = this.authService.checkLogin();
if (this.isLogin) {
this.authService.getUserInfo().then(res => {
this.userName = (res.Data as any).UserName;
});
}
}
}
查阅代码,在@Component中指定了View以及style。
AuthService被在构造方法中被注入了本Component,ngOnInit是接口OnInit的一个方法,他在Component初始化时会被调用。
style.css
/*styles of this view*/
本例中没有添加任何样式,如有需要可以写在这里。
view.html
<div *ngIf="isLogin">
<h1>Hi <span>{{userName}}</span></h1>
</div>
<div *ngIf="!isLogin">
<h1>please login</h1>
<a routerLink="/login">Login</a>
</div>
*ngIf=""是Angular2 的其中一种标记语法,作用是当返回真时渲染该节点,完整教程请参阅官方文档。
4.2.3.2.在wwwroot/app下创建目录Login,该目录用来存放LoginComponent,文件结构类似于上一节。
login.component.ts
import { Component } from "@angular/core";
import { Router } from ‘@angular/router‘;
import { AuthService } from "../_services/auth.service";
@Component({
moduleId: module.id,
selector: "my-login",
templateUrl: "view.html",
styleUrls: ["style.css"]
})
export class LoginComponent {
private userName: string;
private password: string;
constructor(
private authService: AuthService,
private router: Router
) { }
login() {
this.authService.login(this.userName, this.password)
.then(result => {
if (result.State == 1) {
this.router.navigate(["./home"]);
}
else {
alert(result.Msg);
}
});
}
}
style.css
/*styles of this view*/
view.html
<table>
<tr>
<td>userName:</td>
<td><input [(ngModel)]="userName" placeholder="useName:try type user1" /></td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>userName:</td>
<td><input [(ngModel)]="password" placeholder="password:try type user1psd" /></td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td></td>
<td><input type="button" (click)="login()" value="Login" /></td>
</tr>
</table>
路由是切换多页面用的。
在wwwroot/app下新建一个Typescript文件,命名为app-routing.module.ts,内容应该是这个样子。
import { NgModule } from "@angular/core";
import { RouterModule, Routes } from "@angular/router";
import { HomeComponent } from "./home/home.component";
import { LoginComponent } from "./login/login.component"
const routes: Routes = [
{ path: "", redirectTo: "/home", pathMatch: "full" },
{ path: "home", component: HomeComponent },
{ path: "login", component: LoginComponent }
];
@NgModule({
imports: [RouterModule.forRoot(routes)],
exports: [RouterModule]
})
export class AppRoutingModule { }
接下来我们来应用这个路由,
打开app.module.ts,更新代码如下:
import { NgModule } from "@angular/core";
import { BrowserModule } from "@angular/platform-browser";
import { HttpModule } from "@angular/http";
import { FormsModule } from "@angular/forms";
import { AppRoutingModule } from "./app-routing.module";
import { AuthService } from "./_services/auth.service";
import { AppComponent } from "./app.component";
import { HomeComponent } from "./home/home.component";
import { LoginComponent } from "./login/login.component";
@NgModule({
bootstrap: [AppComponent],
imports: [
BrowserModule,
HttpModule,
AppRoutingModule,
FormsModule
],
declarations: [
AppComponent,
HomeComponent,
LoginComponent
],
providers: [AuthService]
})
export class AppModule { }
NgModule和BrowserModule你可以理解为基础模块,必加的。
HttpModule是做http请求用的。
FormsModule是做双向数据绑定用的,比如下面这样的,如果想把数据从view更新到component,就必须加这个。
<input [(ngModel)]="userName" placeholder="useName:try type user1" />
AppRoutingModule即为我们刚才添加的路由文件。
AuthService是我们最早添加的service文件。
AppComponent是我们最初添加的那个app.component.ts里的那个component.
HomeComponent,LoginComponent同上。
最后我们再app.component.ts中添加路由锚点,
把template的值为 "<router-outlet></router-outlet>"
完整的代码应该是这样:
import { Component } from ‘@angular/core‘;
@Component({
moduleId: module.id,
selector: ‘my-app‘,
template: "<router-outlet></router-outlet>",
})
export class AppComponent {
}
router-outlet是路由锚点的关键词。
至此,所有代码完成,F5调试吧。
完整的Angular2的入门教程,请参阅官方文档的《英雄指南》:中文传送门 | 英文传送门
关于本例完整的代码以及调试运行步骤,请访问:How to authorization Angular 2 app with asp.net core web api
NET Core中使用Angular2的Token base身份认证
标签:conf lin tty char 路由 作用 整合 action 构造
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/Leo_wl/p/6079360.html