标签:大型 需要 创建文件 文件大小 write 个数 false exception i++
由于项目需要,需要对二进制文件进行读写、转换。
文件说明:由其他程序得到的二进制文件,文件内容为:包含23543个三角形、13270个顶点的三角网所对应的721组流速矢量(u、v)文件,通俗些说,一条数据包含两个双精度型的数值,每组数组包含23543条数据,如果以一个双精度数值为单位,则总共有23543 * 721 * 2 =33,949,006条数据。由Fortran程序以每 8 Byte存储一个数值的二进制文件存储,最终文件大小为下图所示:
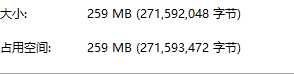
测试:从该文件读出数据之后,转换为十进制,存储到另一个文件中。
/** * 针对大文件存储,请依次调用beginSave、AddSave、endSave。 * * @author CK * */ public class DataUtil { DataOutputStream BinaryOut=null; BufferedWriter TextOut=null; String FilePath=null; enum SaveFileType{Text,Binary}; SaveFileType SaveFileType; /** * double转byte[] * * @param d * @return */ public static byte[] double2Bytes(double d) { long value = Double.doubleToRawLongBits(d); byte[] byteRet = new byte[8]; for (int i = 0; i < 8; i++) { byteRet[i] = (byte) ((value >> 8 * i) & 0xff); } return byteRet; } /** * byte[]转double * * @param arr * @return */ public static double bytes2Double(byte[] arr) { long value = 0; for (int i = 0; i < 8; i++) { value |= ((long) (arr[i] & 0xff)) << (8 * i); } return Double.longBitsToDouble(value); } /** * 大型数据存储之开始存储 * @param FilePath 文件路径 * @param saveFileType 保存的文件类型,文本文件、双精度所存的二进制文件 * @return * @throws IOException */ public boolean BeginSave(String FilePath,SaveFileType saveFileType) throws IOException { if (FilePath == "" || FilePath == null) { System.out.println("the SavePath is null."); return false; } this.FilePath=FilePath; this.SaveFileType=saveFileType; File dataFile = new File(FilePath); if (!dataFile.getParentFile().exists()) { dataFile.getParentFile().mkdirs(); } if (dataFile.exists()) { dataFile.delete(); } dataFile.createNewFile(); switch(this.SaveFileType){ case Text: TextOut= new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter(dataFile,true)); break; case Binary: BinaryOut = new DataOutputStream(new FileOutputStream(dataFile,true)); break; default: break; } return true; } /** * 大型文件存储之追加存储 * @param DataStr 若是文本存储则无要求,若是双精度的二进制文件,以若干空格隔开 * @return * @throws IOException */ public boolean AddSave(String DataStr) throws IOException{ switch(this.SaveFileType){ case Text: this.TextOut.append(DataStr); break; case Binary: DataStr=DataStr.trim(); String[] dataArray=DataStr.split("\\s+"); for(int i=0;i<dataArray.length;i++){ this.BinaryOut.write(double2Bytes(Double.parseDouble(dataArray[i]))); } break; default: break; } return true; } /** * 大型文件存储之结束保存,清空缓存、关闭文件。 * @return * @throws IOException */ public boolean EndSave() throws IOException{ switch(this.SaveFileType){ case Text: this.TextOut.flush(); this.TextOut.close(); break; case Binary: this.BinaryOut.flush(); this.BinaryOut.close(); break; default: break; } return true; } /** * 将字符串保存为文本文件(一次完成) * * @param DataStr * 文件内容 * @param SavePath * 文件路径,包含文件名、后缀 * @return * @throws IOException */ public boolean saveTextFile(String DataStr, String SavePath) throws IOException { if (DataStr == "" || DataStr == null) { System.out.println("the dataStr is null."); return false; } if (SavePath == "" || SavePath == null) { System.out.println("the SavePath is null."); return false; } File dataFile = new File(SavePath); if (!dataFile.getParentFile().exists()) { dataFile.getParentFile().mkdirs(); } if (dataFile.exists()) { dataFile.delete(); } dataFile.createNewFile(); BufferedWriter out; out = new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter(dataFile)); out.append(DataStr); out.flush(); out.close(); return true; } /** * 双精度存为二进制数据(一次存储) * * @param DataStr 双精度数据组成的字符串,以若干空格隔开 * @param OutputPath * @return * @throws IOException */ public boolean saveBinaryFile(String DataStr, String OutputPath) throws IOException { if (DataStr == "" || DataStr == null) { System.out.println("the dataStr is null."); return false; } if (OutputPath == "" || OutputPath == null) { System.out.println("the OutputPath is null."); return false; } File dataFile = new File(OutputPath); if (!dataFile.getParentFile().exists()) { dataFile.getParentFile().mkdirs(); } if (dataFile.exists()) { dataFile.delete(); } dataFile.createNewFile(); DataOutputStream out; out = new DataOutputStream(new FileOutputStream(dataFile)); // 数据处理 DataStr=DataStr.trim(); String[] dataArray=DataStr.split("\\s+"); for(int i=0;i<dataArray.length;i++){ out.write(double2Bytes(Double.parseDouble(dataArray[i]))); } out.flush(); out.close(); return true; } }
代码说明:其中byte[]与double互转为在互联网上查到的方法,具体是哪位大神的我忘记了,在这里为了记录就贴出来啦,上述代码包含了处理小型文件时,将所有内容存在缓存中,之后再一次性写入文本文件、二进制文件中的方法,还包含了对较大型文件的读写方法,下面是自己的一个读写测试。
/** * 测试二进制大文件读写(200M左右) * @author ck * */ public class FileTest { static String inputFilePath=""; //输入文件路径,包含文件名后缀 static String outputFilePath=""; //输出文件名,包含文件名后缀 public static void file2file() throws IOException{ DataUtil dataUtil=new DataUtil(); DataInputStream br=new DataInputStream( new BufferedInputStream( new FileInputStream(inputFilePath))); dataUtil.BeginSave(outputFilePath, SaveFileType.Text); //初始化,创建文件,采用文件追加存储的思路 byte[] oneData=new byte[8]; int i=0,count =0 ; while(br.read(oneData, 0, 8)!=-1){ i=i+1; dataUtil.AddSave(String.valueOf(DataUtil.bytes2Double(oneData))); if(i/23543==0){ count++; System.out.println(count+"\n"); } } dataUtil.EndSave(); //将还在缓存中的数据写入到文件中,关闭文件。 } }
此次测试代码很快就run完了,但是输出文件的生成大概用了近半分钟(刻意秒表计时了一次),尝试用一次性读写的办法,卡很久,也没有出结果。所得的十进制文本文件,大小为这么多:

我想,原来Fortran程序作者的初衷应该是觉得二进制存储比十进制节省空间吧,事实上也确实节省了一半多的空间。
恩,此次记录完毕。
标签:大型 需要 创建文件 文件大小 write 个数 false exception i++
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/ForRickHuan/p/6421796.html