Python for 循环语句
Python for循环可以遍历任何序列的项目,如一个列表或者一个字符串。
语法:
for循环的语法格式如下:
for iterating_var in sequence:
statements(s)
流程图:
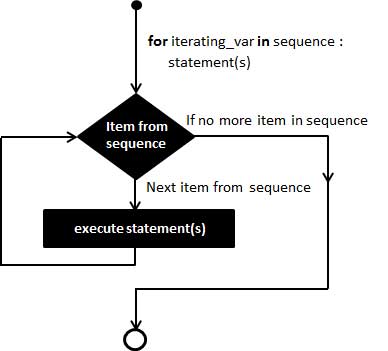
实例:
实例
#!/usr/bin/python # -*- coding: UTF-8 -*- for letter in ‘Python‘: # 第一个实例 print ‘当前字母 :‘, letter fruits = [‘banana‘, ‘apple‘, ‘mango‘] for fruit in fruits: # 第二个实例 print ‘当前水果 :‘, fruit print "Good bye!"
尝试一下 ?
以上实例输出结果:
当前字母 : P
当前字母 : y
当前字母 : t
当前字母 : h
当前字母 : o
当前字母 : n
当前水果 : banana
当前水果 : apple
当前水果 : mango
Good bye!
通过序列索引迭代
另外一种执行循环的遍历方式是通过索引,如下实例:
实例
#!/usr/bin/python
# -*- coding: UTF-8 -*-
fruits = [‘banana‘, ‘apple‘, ‘mango‘]
for index in range(len(fruits)):
print ‘当前水果 :‘, fruits[index]
print "Good bye!"
以上实例输出结果:
当前水果 : banana
当前水果 : apple
当前水果 : mango
Good bye!
以上实例我们使用了内置函数 len() 和 range(),函数 len() 返回列表的长度,即元素的个数。 range返回一个序列的数。
循环使用 else 语句
在 python 中,for … else 表示这样的意思,for 中的语句和普通的没有区别,else 中的语句会在循环正常执行完(即 for 不是通过 break 跳出而中断的)的情况下执行,while … else 也是一样。
实例
#!/usr/bin/python
# -*- coding: UTF-8 -*-
for num in range(10,20): # 迭代 10 到 20 之间的数字
for i in range(2,num): # 根据因子迭代
if num%i == 0: # 确定第一个因子
j=num/i # 计算第二个因子
print ‘%d 等于 %d * %d‘ % (num,i,j)
break # 跳出当前循环
else: # 循环的 else 部分
print num, ‘是一个质数‘
尝试一下 ?
以上实例输出结果:
10 等于 2 * 5
11 是一个质数
12 等于 2 * 6
13 是一个质数
14 等于 2 * 7
15 等于 3 * 5
16 等于 2 * 8
17 是一个质数
18 等于 2 * 9
19 是一个质数
更多实例:python 打印菱形、三角形、矩形

缘分天注定
738***641@qq.com
参考地址
使用内置 enumerate 函数进行遍历:
for index, item in enumerate(sequence): process(index, item)实例
>>> sequence = [12, 34, 34, 23, 45, 76, 89] >>> for i, j in enumerate(sequence): ... print i,j ... 0 12 1 34 2 34 3 23 4 45 5 76 6 89缘分天注定
738***641@qq.com
参考地址
shenwenwin
she***nwin@163.com
for 使用案例
使用list.append()模块对质数进行输出。
#!/usr/bin/python # -*- coding: UTF-8 -*- # 输出 2 到 100 简的质数 prime = [] for num in range(2,100): # 迭代 2 到 100 之间的数字 for i in range(2,num): # 根据因子迭代 if num%i == 0: # 确定第一个因子 break # 跳出当前循环 else: # 循环的 else 部分 prime.append(num) print prime输出结果:
[2, 3, 5, 7, 11, 13, 17, 19, 23, 29, 31, 37, 41, 43, 47, 53, 59, 61, 67, 71, 73, 79, 83, 89, 97]shenwenwin
she***nwin@163.com
kimiYang
943***010@qq.com
打印空心等边三角形:
#!/usr/bin/python # -*- coding: UTF-8 -*- # 打印空心等边三角形 rows = int(raw_input(‘输入行数:‘)) for i in range(0, rows): for k in range(0, 2 * rows - 1): if (i != rows - 1) and (k == rows - i - 1 or k == rows + i - 1): print " * ", elif i == rows - 1: if k % 2 == 0: print " * ", else: print " ", else: print " ", print "\n"kimiYang
943***010@qq.com
feng
124***7699@qq.com
打印1-9三角形阵列:
#!/usr/bin/python # -*- coding: UTF-8 -*- for i in range(1,11): for k in range(1,i): print k, k +=1 i +=1 print "\n"输出结果:
1 1 2 1 2 3 1 2 3 4 1 2 3 4 5 1 2 3 4 5 6 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9feng
124***7699@qq.com
ljm
131***1561@qq.com
#!/usr/bin/python # -*- coding: UTF-8 -*- ‘‘‘在python中,for循环后的in跟随一个序列的话,循环每次使用的序列元素,而不是序列 的下标‘‘‘ s = ‘qazxswedcvfr‘ for i in range(0,len(s),2): print s[i] ‘‘‘enumerate() : 在每次循环中,可以同时得到下标和元素 际上,enumerate(),在每次循环中返回的是包含每个元素的定值表,两个元素分别赋值 index,char‘‘‘ for (index,char) in enumerate(s): print "index=%s ,char=%s" % (index,char)ljm
131***1561@qq.com
为梦而来
183***85363@163.com
冒泡排序,来至于高学军:
#!/usr/bin/python # -*- coding: UTF-8 -*- # 冒泡排序# 定义列表 list arays = [1,8,2,6,3,9,4] for i in range(len(arays)): for j in range(i+1): if arays[i] < arays[j]: # 实现连个变量的互换 arays[i],arays[j] = arays[j],arays[i] print arays为梦而来
183***85363@163.com
forMyPeople
lwy***68957@126.com
更多实例:python 打印菱形、三角形、矩形的代码感觉,写的有点复杂了,如果让你画圆或者其他图形呢?
其实运用数学公式,就可以了。比如菱形 |x - w/2| + |y - w/2| = w/2 轻松搞定。
#!/usr/bin/python # -*- coding: UTF-8 -*- width = int(raw_input(‘输入对角线长度: ‘)) for row in range(width + 1): for col in range(width + 1): if ((abs(row - width/2) + abs(col - width/2)) == width/2): print "*", else: print " ", print " "