标签:注意 增加 新建 for ring remove 创建对象 a+b 内容
一、ArrayList 容器
1、记事本
package booknote;
import java.util.ArrayList;
public class NoteBook {
private ArrayList<String> notes=new ArrayList<String>();//引入ArrayList类,容器;包括容器类型,内容类型
public void add(String s)//增加字符串
{
notes.add(s);//ArrayList 自带的add
}
public void add(String s, int location)// add 函数重载
{
notes.add(location, s);
}
public int getSize()//得到字符串的个数
{
return notes.size();
}
public String getNote(int index)//获取第n个字符
{
return notes.get(index);
}
public void removeNote(int index)//删除 注意void 不返回值就可以了
{
notes.remove(index);
}
public String[] list()
{
String[] a=new String[notes.size()];
// for(int i=0;i<notes.size();i++)
// {
// a[i]=notes.get(i);
// }
notes.toArray(a); //黄色和绿色都可以实现将notes中的字符串赋给 字符串数组a中,一个是使用遍历的方法,一个是使用自带函数
return a;
}
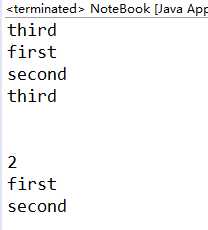
public static void main(String[] args) {
NoteBook nb=new NoteBook();
nb.add("first");
nb.add("second ");
nb.add("third",0);//插入到0位置
String[] a=nb.list();
for(String s:a)
{
System.out.println(s);
}
System.out.println(nb.getNote(0));//得到0位置的字符串
System.out.println("\n");
nb.removeNote(0);//删除0位置元素
System.out.println(nb.getSize());
a=nb.list();//刷新a
for(String s:a)
{
System.out.println(s);
}
}
}
2、对象数组
package Hello;
public class hello {
public int SUM(int a,int b)//必须创建对象调用
{
return a+b;
}
public static int Sum(int a,int b)//static 方便在没有创建对象的情况下调用
{
return a+b;
}
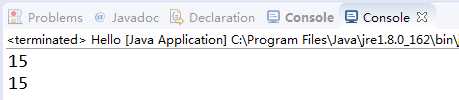
public static void main(String[] args) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
int x=10;
int y=5;
hello num=new hello();
System.out.println(Sum(x,y));//直接调用就可以
System.out.println(num.SUM(x,y));//必须创建对象,利用 对象.函数 才可以
}
}
3、对象数组和普通数组赋值差异
package Hello;
class Value{ //新建类这样建
private int i;
public void set(int i)
{
this.i=i;
}
public int get()
{
return i;
}
}
public class hello {
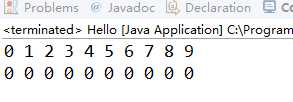
public static void main(String[] args) {
Value[] a=new Value[10];
for(int i=0;i<a.length;i++)
{
a[i]=new Value();
a[i].set(i);
}
for(Value v:a)
{
System.out.print(v.get()+" ");
v.set(0);
}
System.out.println();
for(Value v:a)
{
System.out.print(v.get()+" ");
}
}
}
package Hello;
public class test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] a=new int[10];
for(int i=0;i<a.length;i++)
{
a[i]=i;
}
for(int v:a)
{
System.out.print(v+" ");
v=0;//无效
}
System.out.println();
for(int v:a)
{
System.out.print(v+" ");
}
System.out.println();
for(int i=0;i<a.length;i++)
{
a[i]=0;
}
for(int v:a)
{
System.out.print(v+" ");
}
}
}
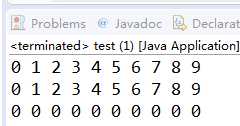
可以看到在对象数组中for each可以改变赋值
但是在普通数组中 for each 不可以改变赋值。
这是因为,对象数组中指向的是对象的位置,可以改变对象的位置上的值。而int[]这类数组,指向的是数组上的值,不能通过值改变值。
4、
package Hello;
class Value{ //新建类这样建
private int i;
public void set(int i)
{
this.i=i;
}
public int get()
{
return i;
}
// public String toString() //转化为字符串输出
// {
// return ""+i;
// }
}
public class hello {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Value[] a=new Value[5];
for(int i=0;i<a.length;i++)
{
a[i]=new Value();
a[i].set(i);
}
for(Value v:a)
{
System.out.println(v);
}
}
}
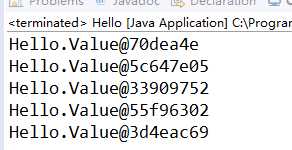
得到的其实是位置。
加入public String toString()后程序如下图
package Hello;
class Value{ //新建类这样建
private int i;
public void set(int i)
{
this.i=i;
}
public int get()
{
return i;
}
public String toString() //转化为字符串输出
{
return ""+i;
}
}
public class hello {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Value[] a=new Value[5];
for(int i=0;i<a.length;i++)
{
a[i]=new Value();
a[i].set(i);
}
for(Value v:a)
{
System.out.println(v);
}
}
}
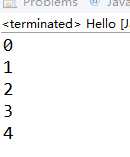
二、set容器
package Hello;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.HashSet;
public class test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ArrayList<String> s=new ArrayList<String>();
s.add("first");
s.add("second");
s.add("first");
for(String a:s)
{
System.out.println(a);
}
System.out.println(s);
System.out.println("************************");
HashSet<String> s1=new HashSet<String>();
s1.add("first");
s1.add("second");
s1.add("first");
s1.add("airst");
for(String a:s1)
{
System.out.println(a);
}
System.out.println(s1);
}
}
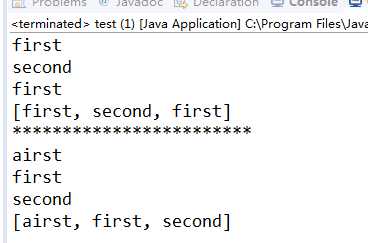
HashSet容器可以去重并且排序。
标签:注意 增加 新建 for ring remove 创建对象 a+b 内容
原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/ruo-li-suo-yi/p/9168320.html