标签:style blog http color io os 使用 ar java
【泛型可迭代的基础集合数据类型的API】
背包:就是一种不支持从中删除元素的集合数据类型——它的目的就是帮助用例收集元素并迭代遍历所有收集到的元素。(用例也可以检查背包是否为空, 或者获取背包中元素的数量)
public class Bag<Item> implements Iterable<Item>
Bag() 创建一个空背包
void add(Item item) 添加一个元素
boolean isEmpty() 背包是否为空
int size() 背包中的元素数量
使用Bag的API, 用例可以将元素添加到背包,并通过foreach循环来访问所有元素。用例也可以使用栈或者队列, 但使用Bag可以说明元素的处理顺序不重要 。
先进先出(FIFO)队列:
public class Queue<Item> implements Iterable<Item>
Queue() 创建一个空队列
void enqueue(Item item) 添加一个元素
Item dequeue() 删除最近添加的元素
boolean isEmpty() 队列是否为空
int size() 队列中的元素数量
下压(后进先出,LIFO)栈
public class Stack<Item> implements Iterable<Item>
Stack() 创建一个空栈
void push(Item item) 添加一个元素
Item pop() 删除最近添加的元素
boolean isEmpty() 栈是否为空
int size() 栈中元素数量
Stats类是Bag的一个典型用例。
它的任务是简单地计算标准输入中的所有double值的平均值和样本标准差。数的计算顺序和结果无关,因此我们将它们保存在一个Bag对象中, 并使用foreach循环来计算每个和。
用Bag对象保存所有数字是更复杂的统计计算所必须的 。
背包的典型用例:Stats.java
public class Stats { public static void main(String[] args) { Bag<Double> numbers = new Bag<Double>(); while(!StdIn.isEmpty()) numbers.add(StdIn.readDouble()); int N = numbers.size(); double sum = 0.0; for (Double x : numbers) sum += x; double mean = sum / N; sum = 0.0; for (Double x : numbers) sum += (x-mean)*(x-mean); double std = Math.sqrt(sum/(N-1)); StdOut.printf("mean : %.2f\n", mean); StdOut.printf("Std dev : %.2f\n", std); } }
【打印结果】
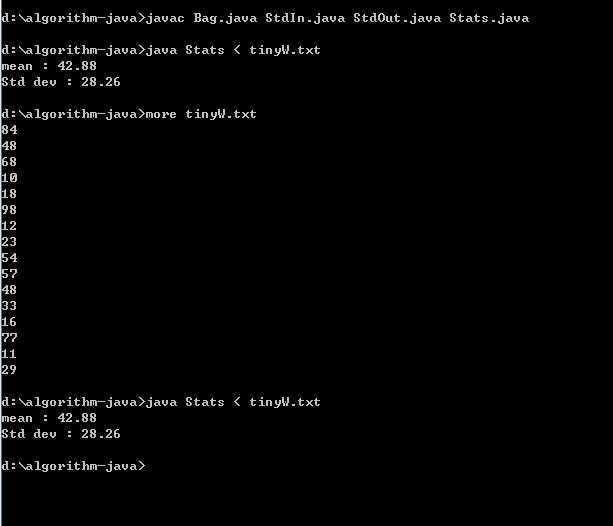
【Bag.java】
import java.util.Iterator; import java.util.NoSuchElementException; public class Bag<Item> implements Iterable<Item> { private int N; // number of elements in bag private Node<Item> first; // beginning of bag // helper linked list class private static class Node<Item> {//嵌套类 private Item item; private Node<Item> next; } /** * Initializes an empty bag. */ public Bag() { first = null; N = 0; } /** * Is this bag empty? * @return true if this bag is empty; false otherwise */ public boolean isEmpty() { return first == null; } /** * Returns the number of items in this bag. * @return the number of items in this bag */ public int size() { return N; } /** * Adds the item to this bag. * @param item the item to add to this bag */ public void add(Item item) {//由add()方法可以看出,是头插法。 Node<Item> oldfirst = first; first = new Node<Item>(); first.item = item; first.next = oldfirst; N++; } /** * Returns an iterator that iterates over the items in the bag in arbitrary order. * @return an iterator that iterates over the items in the bag in arbitrary order */ public Iterator<Item> iterator() { return new ListIterator<Item>(first); } // an iterator, doesn‘t implement remove() since it‘s optional private class ListIterator<Item> implements Iterator<Item> { private Node<Item> current; public ListIterator(Node<Item> first) { current = first; } public boolean hasNext() { return current != null; } public void remove() { throw new UnsupportedOperationException(); } public Item next() { if (!hasNext()) throw new NoSuchElementException(); Item item = current.item; current = current.next; return item; } } /** * Unit tests the <tt>Bag</tt> data type. */ public static void main(String[] args) { Bag<String> bag = new Bag<String>(); while (!StdIn.isEmpty()) { String item = StdIn.readString(); bag.add(item); } StdOut.println("size of bag = " + bag.size()); for (String s : bag) { StdOut.println(s); } } }
【Queue.java】
import java.util.Iterator; import java.util.NoSuchElementException; public class Queue<Item> implements Iterable<Item> { private int N; // number of elements on queue private Node<Item> first; // beginning of queue private Node<Item> last; // end of queue // helper linked list class private static class Node<Item> { private Item item; private Node<Item> next; } /** * Initializes an empty queue. */ public Queue() { first = null; last = null; N = 0; } /** * Is this queue empty? * @return true if this queue is empty; false otherwise */ public boolean isEmpty() { return first == null; } /** * Returns the number of items in this queue. * @return the number of items in this queue */ public int size() { return N; } /** * Returns the item least recently added to this queue. * @return the item least recently added to this queue * @throws java.util.NoSuchElementException if this queue is empty */ public Item peek() { if (isEmpty()) throw new NoSuchElementException("Queue underflow"); return first.item; } /** * Adds the item to this queue. * @param item the item to add */ public void enqueue(Item item) { Node<Item> oldlast = last; last = new Node<Item>(); last.item = item; last.next = null; if (isEmpty()) first = last; else oldlast.next = last; N++; } /** * Removes and returns the item on this queue that was least recently added. * @return the item on this queue that was least recently added * @throws java.util.NoSuchElementException if this queue is empty */ public Item dequeue() { if (isEmpty()) throw new NoSuchElementException("Queue underflow"); Item item = first.item; first = first.next; N--; if (isEmpty()) last = null; // to avoid loitering return item; } /** * Returns a string representation of this queue. * @return the sequence of items in FIFO order, separated by spaces */ public String toString() { StringBuilder s = new StringBuilder(); for (Item item : this) s.append(item + " "); return s.toString(); } /** * Returns an iterator that iterates over the items in this queue in FIFO order. * @return an iterator that iterates over the items in this queue in FIFO order */ public Iterator<Item> iterator() { return new ListIterator<Item>(first); } // an iterator, doesn‘t implement remove() since it‘s optional private class ListIterator<Item> implements Iterator<Item> { private Node<Item> current; public ListIterator(Node<Item> first) { current = first; } public boolean hasNext() { return current != null; } public void remove() { throw new UnsupportedOperationException(); } public Item next() { if (!hasNext()) throw new NoSuchElementException(); Item item = current.item; current = current.next; return item; } } /** * Unit tests the <tt>Queue</tt> data type. */ public static void main(String[] args) { Queue<String> q = new Queue<String>(); while (!StdIn.isEmpty()) { String item = StdIn.readString(); if (!item.equals("-")) q.enqueue(item); else if (!q.isEmpty()) StdOut.print(q.dequeue() + " "); } StdOut.println("(" + q.size() + " left on queue)"); } }
【Stack.java】
import java.util.Iterator; import java.util.NoSuchElementException; public class Stack<Item> implements Iterable<Item> { private int N; // size of the stack private Node<Item> first; // top of stack // helper linked list class private static class Node<Item> { private Item item; private Node<Item> next; } /** * Initializes an empty stack. */ public Stack() { first = null; N = 0; } /** * Is this stack empty? * @return true if this stack is empty; false otherwise */ public boolean isEmpty() { return first == null; } /** * Returns the number of items in the stack. * @return the number of items in the stack */ public int size() { return N; } /** * Adds the item to this stack. * @param item the item to add */ public void push(Item item) { Node<Item> oldfirst = first; first = new Node<Item>(); first.item = item; first.next = oldfirst; N++; } /** * Removes and returns the item most recently added to this stack. * @return the item most recently added * @throws java.util.NoSuchElementException if this stack is empty */ public Item pop() { if (isEmpty()) throw new NoSuchElementException("Stack underflow"); Item item = first.item; // save item to return first = first.next; // delete first node N--; return item; // return the saved item } /** * Returns (but does not remove) the item most recently added to this stack. * @return the item most recently added to this stack * @throws java.util.NoSuchElementException if this stack is empty */ public Item peek() { if (isEmpty()) throw new NoSuchElementException("Stack underflow"); return first.item; } /** * Returns a string representation of this stack. * @return the sequence of items in the stack in LIFO order, separated by spaces */ public String toString() { StringBuilder s = new StringBuilder(); for (Item item : this) s.append(item + " "); return s.toString(); } /** * Returns an iterator to this stack that iterates through the items in LIFO order. * @return an iterator to this stack that iterates through the items in LIFO order. */ public Iterator<Item> iterator() { return new ListIterator<Item>(first); } // an iterator, doesn‘t implement remove() since it‘s optional private class ListIterator<Item> implements Iterator<Item> { private Node<Item> current; public ListIterator(Node<Item> first) { current = first; } public boolean hasNext() { return current != null; } public void remove() { throw new UnsupportedOperationException(); } public Item next() { if (!hasNext()) throw new NoSuchElementException(); Item item = current.item; current = current.next; return item; } } /** * Unit tests the <tt>Stack</tt> data type. */ public static void main(String[] args) { Stack<String> s = new Stack<String>(); while (!StdIn.isEmpty()) { String item = StdIn.readString(); if (!item.equals("-")) s.push(item); else if (!s.isEmpty()) StdOut.print(s.pop() + " "); } StdOut.println("(" + s.size() + " left on stack)"); } }
【Queue测试用例 QueueCase.java】
public class QueueCase { public static void main(String[] args) { int[] temp = readInts(name); for (int i = 0; i < temp.length; i++) System.out.println(temp[i] + " "); } public static int[] readInts(String name){ In in = new In(name); Queue<Integer> q = new Queue<Integer>(); while(!in.isEmpty()) q.enqueue(in.readInt()); int N = q.size(); int[] a = new int[N]; for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) a[i] = q.dequeue(); return a; } }
【Stack 测试用例 StackCase.java】
public class StackCase { public static void main(String[] args) { In in = new In(args[0]); Stack<Integer> s = new Stack<Integer>(); while(!StdIn.isEmpty()) s.push(StdIn.readInt()); for (int i : s) { System.out.println(i + " "); } } }
page74-泛型可迭代的基础集合数据类型的API-Bag+Queue+Stack
标签:style blog http color io os 使用 ar java
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/pacoson/p/4004326.html