标签:runnable elf let 上下 启动过程 ORC exec success except
每个channel内部都会持有一个ChannelPipeline对象pipeline. pipeline默认实现DefaultChannelPipeline内部维护了一个DefaultChannelHandlerContext链表。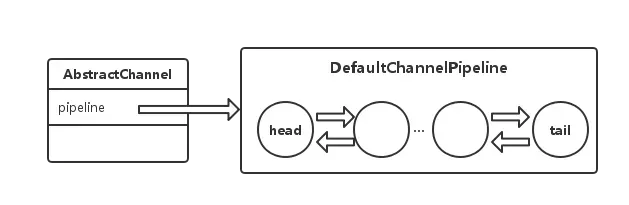
当channel完成register、active、read等操作时,会触发pipeline的相应方法。
1、当channel注册到selector时,触发pipeline的fireChannelRegistered方法。
2、当channel的socket绑定完成时,触发pipeline的fireChannelActive方法。
3、当有客户端请求时,触发pipeline的fireChannelRead方法。
4、当本次客户端请求,pipeline执行完fireChannelRead,触发pipeline的fireChannelReadComplete方法。
接下去看看pipeline是如何组织并运行handler对应的方法。
DefaultChannelPipeline
其中DefaultChannelHandlerContext保存了当前handler的上下文,如channel、pipeline等信息,默认实现了head和tail。
class DefaultChannelPipeline implements ChannelPipeline {
final Channel channel; // pipeline所属的channel
//head和tail都是handler上下文
final DefaultChannelHandlerContext head;
final DefaultChannelHandlerContext tail;
...
public DefaultChannelPipeline(AbstractChannel channel) {
if (channel == null) {
throw new NullPointerException("channel");
}
this.channel = channel;
tail = new TailContext(this);
head = new HeadContext(this);
head.next = tail;
tail.prev = head;
}
}1、TailContext实现了ChannelOutboundHandler接口。
2、HeadContext实现了ChannelInboundHandler接口。
3、head和tail形成了一个链表。
对于Inbound的操作,当channel注册到selector时,触发pipeline的fireChannelRegistered,从head开始遍历,找到实现了ChannelInboundHandler接口的handler,并执行其fireChannelRegistered方法。
@Override
public ChannelPipeline fireChannelRegistered() {
head.fireChannelRegistered();
return this;
}
@Override
public ChannelHandlerContext fireChannelRegistered() {
final DefaultChannelHandlerContext next = findContextInbound();
EventExecutor executor = next.executor();
if (executor.inEventLoop()) {
next.invokeChannelRegistered();
} else {
executor.execute(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
next.invokeChannelRegistered();
}
});
}
return this;
}
private DefaultChannelHandlerContext findContextInbound() {
DefaultChannelHandlerContext ctx = this;
do {
ctx = ctx.next;
} while (!(ctx.handler() instanceof ChannelInboundHandler));
return ctx;
}
private void invokeChannelRegistered() {
try {
((ChannelInboundHandler) handler()).channelRegistered(this);
} catch (Throwable t) {
notifyHandlerException(t);
}
}假如我们通过pipeline的addLast方法添加一个inboundHandler实现。
public class ClientHandler extends ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter {
@Override
public void channelRegistered(ChannelHandlerContext ctx)
throws Exception {
super.channelRegistered(ctx);
System.out.println(" ClientHandler registered channel ");
}
} 当channel注册完成时会触发pipeline的channelRegistered方法,从head开始遍历,找到ClientHandler,并执行channelRegistered方法。
对于Outbound的操作,则从tail向前遍历,找到实现ChannelOutboundHandler接口的handler,具体实现和Inbound一样。
服务启动过程中,ServerBootstrap在init方法中,会给ServerSocketChannel的pipeline添加ChannelInitializer对象,其中ChannelInitializer继承ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter,并实现了ChannelInboundHandler接口,所以当ServerSocketChannel注册到selector之后,会触发其channelRegistered方法。
public final void channelRegistered(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception {
initChannel((C) ctx.channel());
ctx.pipeline().remove(this);
ctx.fireChannelRegistered();
}
public void initChannel(Channel ch) throws Exception {
ChannelPipeline pipeline = ch.pipeline();
ChannelHandler handler = handler();
if (handler != null) {
pipeline.addLast(handler);
}
pipeline.addLast(new ServerBootstrapAcceptor(
currentChildGroup, currentChildHandler, currentChildOptions, currentChildAttrs));
}在initChannel实现中,添加ServerBootstrapAcceptor实例到pipeline中。
ServerBootstrapAcceptor继承自ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter,负责把接收到的客户端socketChannel注册到childGroup中,由childGroup中的eventLoop负责数据处理。
public void channelRead(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg) {
final Channel child = (Channel) msg;
child.pipeline().addLast(childHandler);
for (Entry<ChannelOption<?>, Object> e: childOptions) {
try {
if (!child.config().setOption((ChannelOption<Object>) e.getKey(), e.getValue())) {
logger.warn("Unknown channel option: " + e);
}
} catch (Throwable t) {
logger.warn("Failed to set a channel option: " + child, t);
}
}
for (Entry<AttributeKey<?>, Object> e: childAttrs) {
child.attr((AttributeKey<Object>) e.getKey()).set(e.getValue());
}
try {
childGroup.register(child).addListener(new ChannelFutureListener() {
@Override
public void operationComplete(ChannelFuture future) throws Exception {
if (!future.isSuccess()) {
forceClose(child, future.cause());
}
}
});
} catch (Throwable t) {
forceClose(child, t);
}
}标签:runnable elf let 上下 启动过程 ORC exec success except
原文地址:http://blog.51cto.com/14028890/2324938