标签:用户 scheme text one http pac authorize 输入 为什么
本文将介绍在Springboot中如何通过代码实现Http到Https的重定向,本文仅讲解Tomcat作为容器的情况,其它容器将在以后一一道来。
建议阅读之前的相关文章:
(2)HTTPS之密钥知识与密钥工具Keytool和Keystore-Explorer
所谓重定向,就是本来你想浏览地址A的,但是到达服务端后,服务端认为地址A的界面不在了或者你没权限访问等原因,不想你访问地址A;就告诉你另一个地址B,然后你再去访问地址B。
对于重定向一般有两个返回码:
通过Chrome查看网络详情,记录了几个网站的重定向情况:
| 网站 | 域名 | 重定向代码 | 重定向后的网址 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 南瓜慢说 | www.pkslow.com | 301 | https://www.pkslow.com |
| www.google.com | 307 | https://www.google.com | |
| Apple | www.apple.com | 307 | https://www.apple.com |
| 支付宝 | www.alipay.com | 301 | https://www.alipay.com |
| www.qq.com | 302 | https://www.qq.com | |
| 百度 | www.baidu.com | 307 | https://www.baidu.com |
注:307也是重定向的一种,是新的状态码。
结合我上面特意列的表格,是不是大概想到了为何要做这种重定向?不难发现上面的重定向都在做一件事,就是把http重定向为https。原因如下:
(1)http是不安全的,应该使用安全的https网址;
(2)但不能要求用户每次输入网站都输入https:// 吧,这也太麻烦了,所以大家都是习惯于只输入域名,甚至连www. 都不愿意输入。因此,用户的输入其实都是访问http的网页,就需要重定向到https以达到安全访问的要求。
首先,服务器必须要同时支持http和https,不然也就没有重定向一说了。因为https是必须提供支持的,那为何还要提供http的服务呢?直接访问https不就行了,不是多此一举吗?原因之前已经讲过了,大家是习惯于只输入简单域名访问的,这时到达的就是http,如果不提供http的支持,用户还以为你的网站已经挂了呢。
两种协议都提供支持,所以是需要打开两个Socket端口的,一般http为80,而https为443。然后就需要把所有访问http的请求,重定向到https即可。不同的服务器有不同的实现,现在介绍Springboot+Tomcat的实现。
Springboot以Tomcat作为Servlet容器时,有两种方式可以实现重定向,一种是没有使用Spring Security的,另一种是使用了Spring Security的。代码结构如下:
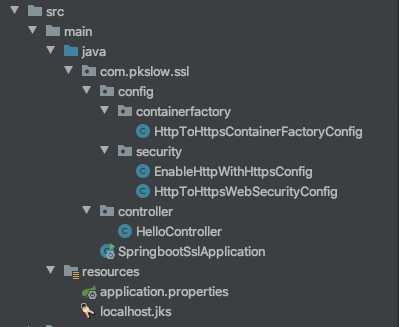
主类的代码如下:
package com.pkslow.ssl;
import com.pkslow.ssl.config.containerfactory.HttpToHttpsContainerFactoryConfig;
import com.pkslow.ssl.config.security.EnableHttpWithHttpsConfig;
import com.pkslow.ssl.config.security.HttpToHttpsWebSecurityConfig;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.ComponentScan;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Import;
@SpringBootApplication
@Import({EnableHttpWithHttpsConfig.class, HttpToHttpsWebSecurityConfig.class})
//@Import(HttpToHttpsContainerFactoryConfig.class)
@ComponentScan(basePackages = "com.pkslow.ssl.controller")
public class SpringbootSslApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(SpringbootSslApplication.class, args);
}
}
@ComponentScan(basePackages = "com.pkslow.ssl.controller"):没有把config包扫描进来,是因为想通过@Import来控制使用哪种方式来进行重定向。当然还可以使用其它方式来控制,如@ConditionalOnProperty,这里就不展开讲了。
当没有使用Spring Security时,使用@Import(HttpToHttpsContainerFactoryConfig.class);
当使用Spring Security时,使用@Import({EnableHttpWithHttpsConfig.class, HttpToHttpsWebSecurityConfig.class})。
配置文件application.properties内容如下:
server.port=443
http.port=80
server.ssl.enabled=true
server.ssl.key-store-type=jks
server.ssl.key-store=classpath:localhost.jks
server.ssl.key-store-password=changeit
server.ssl.key-alias=localhost
需要指定两个端口,server.port为https端口;http.port为http端口。注意在没有https的情况下,server.port指的是http端口。
配置的类为HttpToHttpsContainerFactoryConfig,代码如下:
package com.pkslow.ssl.config.containerfactory;
import org.apache.catalina.Context;
import org.apache.tomcat.util.descriptor.web.SecurityCollection;
import org.apache.tomcat.util.descriptor.web.SecurityConstraint;
import org.springframework.boot.web.embedded.tomcat.TomcatServletWebServerFactory;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.apache.catalina.connector.Connector;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
@Configuration
public class HttpToHttpsContainerFactoryConfig {
@Value("${server.port}")
private int httpsPort;
@Value("${http.port}")
private int httpPort;
@Bean
public TomcatServletWebServerFactory servletContainer() {
TomcatServletWebServerFactory tomcat =
new TomcatServletWebServerFactory() {
@Override
protected void postProcessContext(Context context) {
SecurityConstraint securityConstraint = new SecurityConstraint();
securityConstraint.setUserConstraint("CONFIDENTIAL");
SecurityCollection collection = new SecurityCollection();
collection.addPattern("/*");
securityConstraint.addCollection(collection);
context.addConstraint(securityConstraint);
}
};
tomcat.addAdditionalTomcatConnectors(createHttpConnector());
return tomcat;
}
private Connector createHttpConnector() {
Connector connector =
new Connector(TomcatServletWebServerFactory.DEFAULT_PROTOCOL);
connector.setScheme("http");
connector.setSecure(false);
connector.setPort(httpPort);
connector.setRedirectPort(httpsPort);
return connector;
}
}
createHttpConnector():这个方法主要是实现了在有https前提下,打开http的功能,并配置重定向的https的端口。
有两个配置类,一个为打开http服务,一个为实现重定向。
EnableHttpWithHttpsConfig主要作用是在已经有https的前提下,还要打开http服务。
package com.pkslow.ssl.config.security;
import org.apache.catalina.connector.Connector;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
import org.springframework.boot.web.embedded.tomcat.TomcatServletWebServerFactory;
import org.springframework.boot.web.server.WebServerFactoryCustomizer;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Configuration
public class EnableHttpWithHttpsConfig {
@Value("${http.port}")
private int httpPort;
@Component
public class CustomContainer implements WebServerFactoryCustomizer<TomcatServletWebServerFactory> {
@Override
public void customize(TomcatServletWebServerFactory factory) {
Connector connector = new Connector(TomcatServletWebServerFactory.DEFAULT_PROTOCOL);
connector.setPort(httpPort);
connector.setScheme("http");
connector.setSecure(false);
factory.addAdditionalTomcatConnectors(connector);
}
}
}
HttpToHttpsWebSecurityConfig主要是针对Spring Security的配置,众所周知,Spring Security是功能十分强大,但又很复杂的。代码中已经写了关键的注释:
package com.pkslow.ssl.config.security;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.security.config.annotation.web.builders.HttpSecurity;
import org.springframework.security.config.annotation.web.builders.WebSecurity;
import org.springframework.security.config.annotation.web.configuration.WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter;
@Configuration
public class HttpToHttpsWebSecurityConfig extends WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter {
@Value("${server.port}")
private int httpsPort;
@Value("${http.port}")
private int httpPort;
@Override
protected void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
//redirect to https - 用spring security实现
http.portMapper().http(httpPort).mapsTo(httpsPort);
http.requiresChannel(
channel -> channel.anyRequest().requiresSecure()
);
//访问路径/hello不用登陆获得权限
http.authorizeRequests()
.antMatchers("/hello").permitAll()
.anyRequest().authenticated().and();
}
@Override
public void configure(WebSecurity web) throws Exception {
//过滤了actuator后,不会重定向,也不用权限校验,这个功能非常有用
web.ignoring()
.antMatchers("/actuator")
.antMatchers("/actuator/**");
}
}
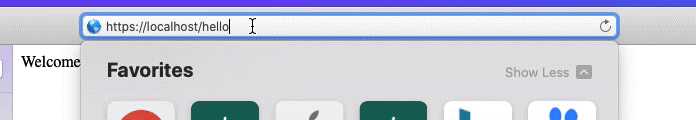
最后实现了重定向,结果展示:
本文详细代码可在南瓜慢说公众号回复<SpringbootSSLRedirectTomcat>获取。
参考链接:
Spring Security: https://docs.spring.io/spring-security/site/docs/5.3.2.BUILD-SNAPSHOT/reference/html5/#servlet-http-redirect
Springboot 1.4重定向:https://jonaspfeifer.de/redirect-http-https-spring-boot/
欢迎访问南瓜慢说 www.pkslow.com获取更多精彩文章!
欢迎关注微信公众号<南瓜慢说>,将持续为你更新...

Springboot以Tomcat为容器实现http重定向到https的两种方式
标签:用户 scheme text one http pac authorize 输入 为什么
原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/larrydpk/p/12806699.html