标签:containe which 访问 ota algorithm 函数对象 integer wing create
匿名函数是许多编程语言都支持的概念,有函数体,没有函数名。1958年,lisp首先采用匿名函数,匿名函数最常用的是作为回调函数的值。正因为有这样的需求,c++引入了lambda 函数,你可以在你的源码中内联一个lambda函数,这就使得创建快速的,一次性的函数变得简单了。例如,你可以把lambda函数可在参数中传递给std::sort函数。
#include "stdafx.h"
#include <algorithm> //标准模板库算法库
#include <cmath> //数学库
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
//绝对值排序
void abssort(float* x, unsigned n)
{
//模板库排序函数
std::sort(x, x + n,
// Lambda 开始位置
[](float a, float b)
{
return (std::abs(a) < std::abs(b));
} // lambda表达式结束
);
}
int _tmain(int argc, _TCHAR* argv[])
{
float a[5] = { 2.1f, 3.5f, 4.0f, 5.2f, 3.3f };
abssort(a, 5);
for (auto& x : a)
{
cout << x << endl;
}
system("pause");
return 0;
}

基本形式如下:
[capture](parameters)->return-type {body}
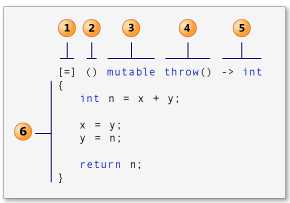
外部变量的捕获规则
默认情况下,即捕获字段为 [] 时,lambda表达式是不能访问任何外部变量的,即表达式的函数体内无法访问当前作用域下的变量。
如果要设定表达式能够访问外部变量,可以在 [] 内写入 & 或者 = 加上变量名,其中 & 表示按引用访问,= 表示按值访问,变量之间用逗号分隔,比如 [=factor, &total] 表示按值访问变量 factor,而按引用访问 total。
不加变量名时表示设置默认捕获字段,外部变量将按照默认字段获取,后面在书写变量名时不加符号表示按默认字段设置,比如下面三条字段都是同一含义:
[&total, factor]
[&, factor]
[=, &total]
#include <functional>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;int _tmain(int argc, _TCHAR* argv[])
{
//lambd函数对象
auto fl = [](int x, int y){return x + y; };
cout << fl(2, 3) << endl;
function<int(int, int)>f2 = [](int x, int y){return x + y; };
cout << f2(3, 4) << endl;
system("pause");
return 0;
}
不能访问任何局部变量
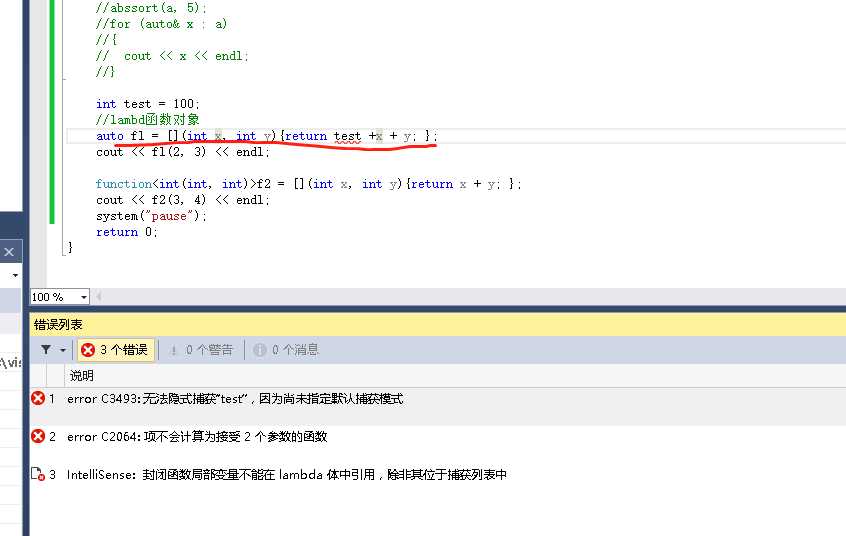
如何传进去局部变量
int test = 100;
//lambd函数对象捕获局部变量
auto fl = [test](int x, int y){return test +x + y; };
cout << fl(2, 3) << endl;
默认访问所有局部变量
int test = 100;
//lambd函数对象捕获所有局部变量
auto fl = [=](int x, int y){return test +x + y; };
cout << fl(2, 3) << endl;
在C++11中这一部分被成为捕获外部变量
[captures] (params) mutable-> type{...} //lambda 表达式的完整形式
在 lambda 表达式引出操作符[ ]里的“captures”称为“捕获列表”,可以捕获表达式外部作用域的变量,在函数体内部直接使用,这是与普通函数或函数对象最大的不同(C++里的包闭必须显示指定捕获,而lua语言里的则是默认直接捕获所有外部变量。)
捕获列表里可以有多个捕获选项,以逗号分隔,使用了略微“新奇”的语法,规则如下
下面代码示范了这些捕获列表的用法:、
int x = 0,y=0;
值得注意的是变化的捕获发生在了lambda表达式的声明之时,如果使用值方式捕获,即使之后变量的值发生变化,lambda表达式也不会感知,仍然使用最初的值。如果想要使用外部变量的最新值就必须使用引用的捕获方式,但也需要当心变量的生命周期,防止引用失效。
刚才的lambda表达式运行结果是:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
|
#include <functional>#include <iostream>int main(){ using namespace std; int i = 3; int j = 5; // The following lambda expression captures i by value and // j by reference. function<int (void)> f = [i, &j] { return i + j; }; // Change the values of i and j. i = 22; j = 44; // Call f and print its result. cout << f() << endl;} |
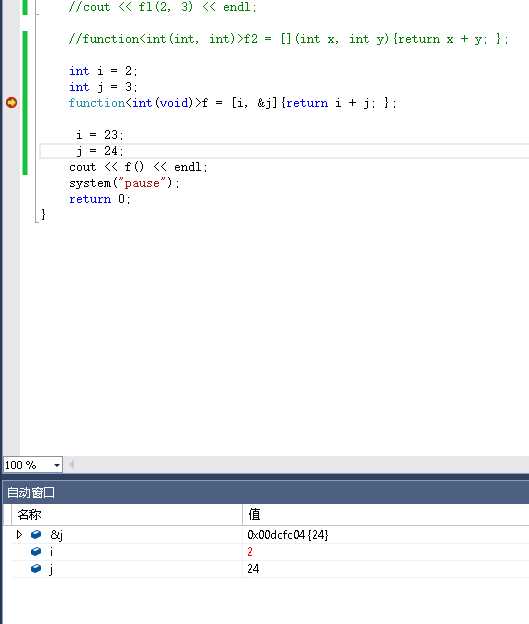
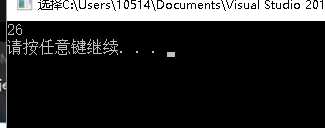
可以看到i是拷贝值,j是引用值,所以是24,结果26
#include <list>
#include <algorithm>
#include <iostream>
int main()
{
using namespace std;
// Create a list of integers with a few initial elements.
list<int> numbers;
numbers.push_back(13);
numbers.push_back(17);
numbers.push_back(42);
numbers.push_back(46);
numbers.push_back(99);
// Use the find_if function and a lambda expression to find the
// first even number in the list.
const list<int>::const_iterator result =
find_if(numbers.begin(), numbers.end(),[](int n) { return (n % 2) == 0; });//查找第一个偶数
// Print the result.
if (result != numbers.end())
{
cout << "The first even number in the list is " << *result << "." << endl;
} else
{
cout << "The list contains no even numbers." << endl;
}
}
#include <iostream>
int main()
{
using namespace std;
// The following lambda expression contains a nested lambda
// expression.
int timestwoplusthree = [](int x) { return [](int y) { return y * 2; }(x) + 3; }(5);
// Print the result.
cout << timestwoplusthree << endl;
}
#include <iostream>
#include <functional>
int main()
{
using namespace std;
auto addtwointegers = [](int x) -> function<int(int)> {
return [=](int y) { return x + y; };
};
auto higherorder = [](const function<int(int)>& f, int z) {
return f(z) * 2;
};
// Call the lambda expression that is bound to higherorder.
auto answer = higherorder(addtwointegers(7), 8);
// Print the result, which is (7+8)*2.
cout << answer << endl;
}
标签:containe which 访问 ota algorithm 函数对象 integer wing create
原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/lidabo/p/13181459.html