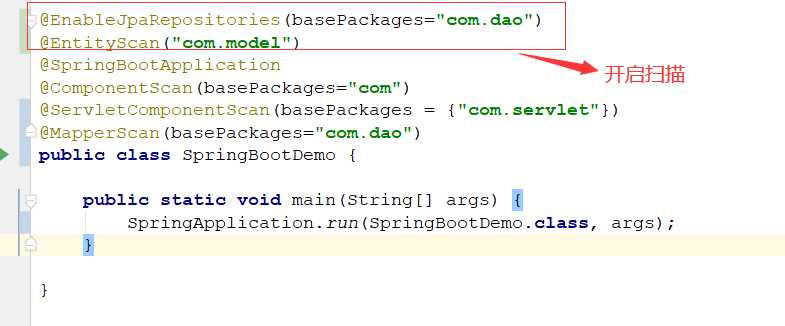
标签:etc path prope 扫描 服务 分布式 ber null mes
一:与JPA规范整合
jpa是一套orm的规范,提供api接口,hirebnate就是对jpa的一套实现,下面我们看看springboot如何
与jpa整合
1:添加依赖和配置
<!--5: 整合jpa--> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-jpa</artifactId> </dependency>
#自动创建表 spring.jpa.hibernate.ddl-auto:update #打印 sql 语句 spring.jpa.show-sql:true
2:定义service 、dao以及实体类
@Service
public class StudentServiceImpl implements StudentService {
@Autowired
private StudentDao studentDao;
@Override
public Student findById(Integer id) {
Optional<Student> optional = studentDao.findById(id);
if(optional.isPresent()){
return optional.get();
}
return null;
}
@Override
public Student insertStudent(Student student) {
return studentDao.save(student);
}
}
@Repository
public interface StudentDao extends JpaRepository<Student,Integer> {
}
@Data
@Entity
@Table(name="student")
public class Student {
@Id
@GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.IDENTITY)
private Integer id;
@Column(name="name")
private String name;
@Column(name="cardId")
private String cardId;
}
服务启动从日志看,会创建表:

测试类:
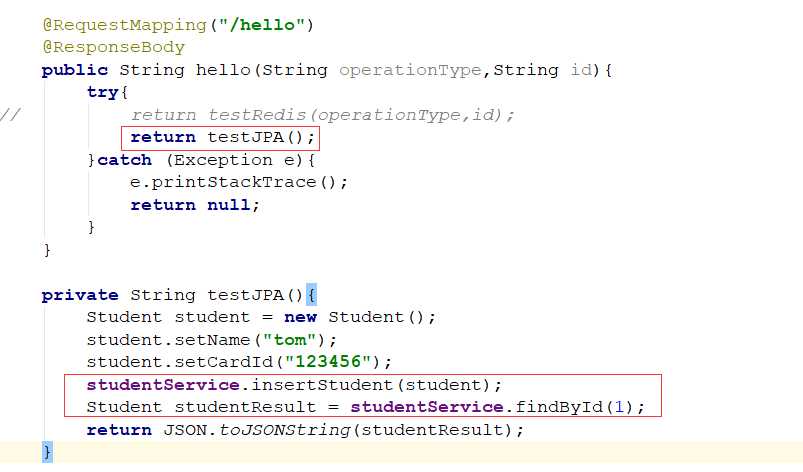
生成insert语句,插入数据:
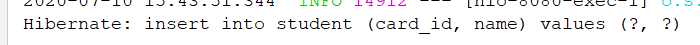
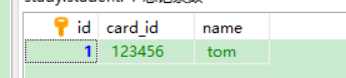
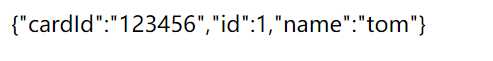
与JPA整合完成,很简单
二:与atomikos整合,实现分布式事务
如果同时在一个方法内使用两个数据源,想实现事务,该怎么办?
1:添加依赖和配置
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-jta-atomikos</artifactId>
</dependency>
# Mysql 1 mysql.datasource.test1.url = jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/enjoy?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf-8 mysql.datasource.test1.username = root mysql.datasource.test1.password = root mysql.datasource.test1.minPoolSize = 3 mysql.datasource.test1.maxPoolSize = 25 mysql.datasource.test1.maxLifetime = 20000 mysql.datasource.test1.borrowConnectionTimeout = 30 mysql.datasource.test1.loginTimeout = 30 mysql.datasource.test1.maintenanceInterval = 60 mysql.datasource.test1.maxIdleTime = 60 # Mysql 2 mysql.datasource.test2.url =jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/study?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf-8 mysql.datasource.test2.username =root mysql.datasource.test2.password =root mysql.datasource.test2.minPoolSize = 3 mysql.datasource.test2.maxPoolSize = 25 mysql.datasource.test2.maxLifetime = 20000 mysql.datasource.test2.borrowConnectionTimeout = 30 mysql.datasource.test2.loginTimeout = 30 mysql.datasource.test2.maintenanceInterval = 60 mysql.datasource.test2.maxIdleTime = 60 #日志级别 logging.level.root=info #所有包下面都以debug级别输出 #logging.level.org.springframework.*=debug #sql日志 logging.level.com.xiangxue.atomikos.db1.dao=debug logging.level.com.xiangxue.atomikos.db2.dao=debug #热部署 #热部署生效 spring.devtools.restart.enabled=true #设置重启的目录 spring.devtools.restart.additional-paths=src/main/java #classpath目录下的WEB-INF文件夹内容修改不重启 spring.devtools.restart.exclude=WEB-INF/**
将配置封装到对象上,使用@ConfigurationProperties注解,会把mysql.datasource.test1为前缀的配置封装到对应的属性上,维护到spring
容器缓存中
@Data
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "mysql.datasource.test1")
public class DBConfig1 {
private String url;
private String username;
private String password;
private int minPoolSize;
private int maxPoolSize;
private int maxLifetime;
private int borrowConnectionTimeout;
private int loginTimeout;
private int maintenanceInterval;
private int maxIdleTime;
private String testQuery;
}
创建数据源DataSource、sqlSessionFactory以及sqlSessionTemplate对象,并且添加@MapperScan扫描,将MapperFactoryBean维护到spring容器中,
key为Mapper文件的全限定名类名,value为MapperFactoryBean对象
@Configuration
@MapperScan(basePackages = "com.xiangxue.jack.atomikos.db1.dao", sqlSessionFactoryRef = "test1SqlSessionFactory",sqlSessionTemplateRef="test1SqlSessionTemplate")
public class Db1Config {
@Autowired
DBConfig1 testConfig;
@Bean(name = "test1DataSource")
public DataSource testDataSource() {
MysqlXADataSource mysqlXaDataSource = new MysqlXADataSource();
mysqlXaDataSource.setUrl(testConfig.getUrl());
mysqlXaDataSource.setPinGlobalTxToPhysicalConnection(true);
mysqlXaDataSource.setPassword(testConfig.getPassword());
mysqlXaDataSource.setUser(testConfig.getUsername());
mysqlXaDataSource.setPinGlobalTxToPhysicalConnection(true);
AtomikosDataSourceBean xaDataSource = new AtomikosDataSourceBean();
xaDataSource.setXaDataSource(mysqlXaDataSource);
xaDataSource.setUniqueResourceName("test1DataSource");
xaDataSource.setMinPoolSize(testConfig.getMinPoolSize());
xaDataSource.setMaxPoolSize(testConfig.getMaxPoolSize());
xaDataSource.setMaxLifetime(testConfig.getMaxLifetime());
xaDataSource.setBorrowConnectionTimeout(testConfig.getBorrowConnectionTimeout());
try {
xaDataSource.setLoginTimeout(testConfig.getLoginTimeout());
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
xaDataSource.setMaintenanceInterval(testConfig.getMaintenanceInterval());
xaDataSource.setMaxIdleTime(testConfig.getMaxIdleTime());
xaDataSource.setTestQuery(testConfig.getTestQuery());
return xaDataSource;
}
@Bean(name = "test1SqlSessionFactory")
public SqlSessionFactory testSqlSessionFactory(@Qualifier("test1DataSource") DataSource dataSource)
throws Exception {
SqlSessionFactoryBean bean = new SqlSessionFactoryBean();
bean.setDataSource(dataSource);
return bean.getObject();
}
@Bean(name = "test1SqlSessionTemplate")
public SqlSessionTemplate testSqlSessionTemplate(
@Qualifier("test1SqlSessionFactory") SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory) throws Exception {
return new SqlSessionTemplate(sqlSessionFactory);
}
}
创建Mapper类:
public interface CommonMapper1 {
@Select("select * from people")
List<People> listPeoples();
@Insert("insert into people(name) values(#{name})")
int addPeople(People people);
}
另一个数据源也需要创建DataSource、SqlSessionFactory、sqlSessionTemplate对象,扫描对应的Mapper接口文件路径,和上一个数据源创建方式一样
创建一个service的测试类:在方法上添加@Transactional注解,方法内部,两个不同的mapper新增数据,两个mapper对应不同的数据源
@Service
public class AreaServiceImpl implements AreaService {
@Autowired
private CommonMapper1 commonMapper1;
@Autowired
private CommonMapper2 commonMapper2;
@Autowired
TransactionManager transactionManager;
@Transactional
public int saveArea(ConsultConfigArea area) {
System.out.println(transactionManager);
JtaTransactionManager jtaTransactionManager = (JtaTransactionManager)transactionManager;
System.out.println(jtaTransactionManager.getUserTransaction());
UserTransaction userTransaction = jtaTransactionManager.getUserTransaction();
People people = new People();
people.setName("Lucy");
int count = commonMapper1.addPeople(people);
System.out.println("插入一条People,count:"+count);
Student student = new Student();
student.setCardId("122334");
student.setName("hello");
int count1 = commonMapper2.addStudent(student);
System.out.println("插入一条Student,count1:"+count1);
int i = 10/0;
return count;
}
}
先把会导致异常的这行代码注释掉:


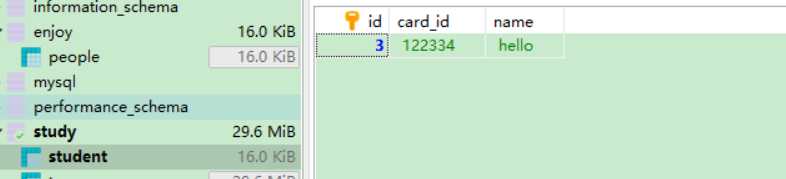
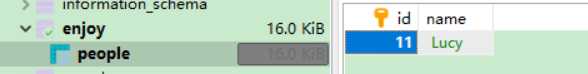
数据插入成功!
现在把会导致运行时异常的代码放开,看看效果
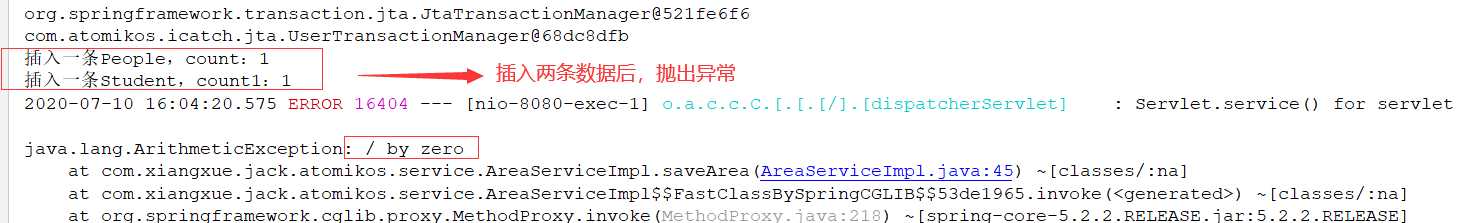
数据没有插入,说明回滚成功!
三:与redis整合
1:添加依赖和配置
<!--6:整合redis--> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-redis</artifactId> </dependency>
#Redis数据库索引(默认为0) spring.redis.database=0 #redis服务器地址 spring.redis.host=127.0.0.1 #redis暴露端口 spring.redis.port=6379 #redis服务器连接密码 spring.redis.password= #连接池最大连接 spring.redis.pool.max-active=8 #连接池最大阻塞等待时间 spring.redis.pool.max-wait=-1 #连接池中的最大空闲连接 spring.redis.pool.max-idle=8 #连接池中的最小空闲连接 spring.redis.pool.min-idle=0 #连接超时时间 spring.redis.timeout=5000
2:创建缓存管理类
@Configuration
@EnableCaching
public class RedisConfig {
//缓存管理器
@Bean
public CacheManager cacheManager(RedisConnectionFactory redisConnectionFactory) {
RedisCacheConfiguration redisCacheConfiguration = RedisCacheConfiguration.defaultCacheConfig()
.entryTtl(Duration.ofHours(1)); // 设置缓存有效期一小时
return RedisCacheManager
.builder(RedisCacheWriter.nonLockingRedisCacheWriter(redisConnectionFactory))
.cacheDefaults(redisCacheConfiguration).build();
}
@Bean
public RedisTemplate<String, Object> redisTemplate(RedisConnectionFactory factory) {
RedisTemplate<String, Object> template = new RedisTemplate<>();
// 配置连接工厂
template.setConnectionFactory(factory);
//使用Jackson2JsonRedisSerializer来序列化和反序列化redis的value值(默认使用JDK的序列化方式)
Jackson2JsonRedisSerializer jacksonSeial = new Jackson2JsonRedisSerializer(Object.class);
ObjectMapper om = new ObjectMapper();
// 指定要序列化的域,field,get和set,以及修饰符范围,ANY是都有包括private和public
om.setVisibility(PropertyAccessor.ALL, JsonAutoDetect.Visibility.ANY);
// 指定序列化输入的类型,类必须是非final修饰的,final修饰的类,比如String,Integer等会跑出异常
om.enableDefaultTyping(ObjectMapper.DefaultTyping.NON_FINAL);
jacksonSeial.setObjectMapper(om);
// 值采用json序列化
template.setValueSerializer(jacksonSeial);
//使用StringRedisSerializer来序列化和反序列化redis的key值
template.setKeySerializer(new StringRedisSerializer());
// 设置hash key 和value序列化模式
template.setHashKeySerializer(new StringRedisSerializer());
template.setHashValueSerializer(jacksonSeial);
template.afterPropertiesSet();
return template;
}
}
创建使用类:
@Component
public class RedisServiceImpl implements RedisService{
@Autowired
private UserMapper userMapper;
@Cacheable(cacheNames = "redisCache",key = "‘jack‘+ #id")
@Override
public String queryData(String id) {
System.out.println("RedisServiceImpl -- queryData");
List<User> list = userMapper.queryUserById(id);
return JSON.toJSONString(list);
}
@CachePut(cacheNames = "redisCache",key = "‘jack‘+ #id")
@Override
public String putCache(String id) {
System.out.println("RedisServiceImpl -- putCache");
User user = new User();
user.setName("Tom");
user.setAge("30");
user.setId(id);
userMapper.updateUser(user);
return JSON.toJSONString(user);
}
}
下面我们把redis服务器和应用启动,测试一下:

首先查询redis缓存,缓存中没有数据,然后查询数据库,数据缓存到redis,返回数据,我们来看看redis服务器

数据已经被放入redis缓存中,我们再次从页面查询一次:
没有查询数据库,queryData还是上次查询数据库的日志,但是页面显示正常,说明查询的是redis服务器
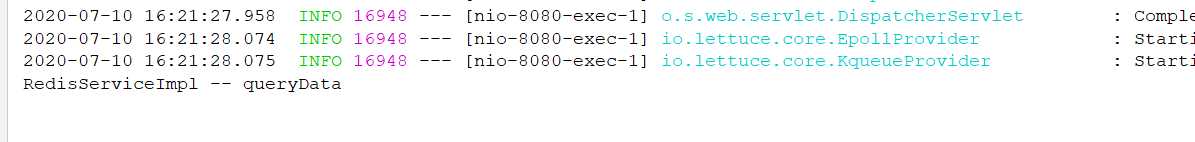
那如果我们想修改数据库的数据,会怎么样?
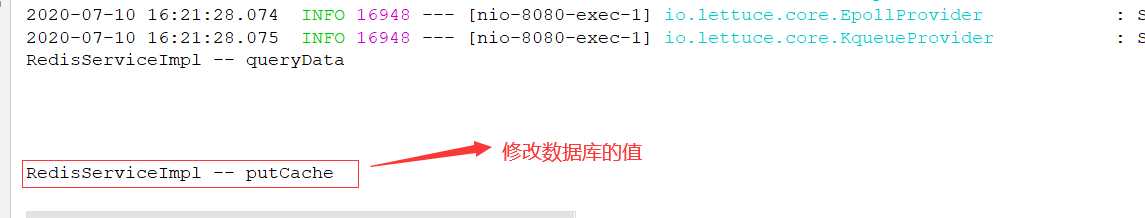
我们来看看redis内存库的数据会不会变化:
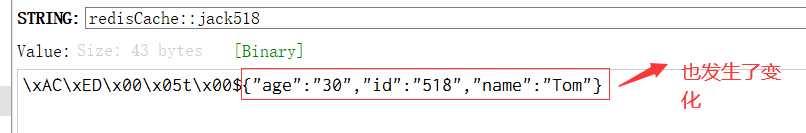
说明修改数据库的数据,redis会同步更新
这样springboot和redis的整合就完成了!!!
springboot分析——与其他组件的整合(JPA规范/atomikos/redis)
标签:etc path prope 扫描 服务 分布式 ber null mes
原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/warrior4236/p/13279914.html