标签:vat war oid sort 实现 数据 包括 复杂 except
Java 迭代接口:Iterator、ListIterator 和 Spliterator原创 万想 锅外的大佬 2019-08-26
点击左上角蓝字,关注“锅外的大佬”
专注分享国外最新技术内容
当我们使用 for 或 while 循环来遍历一个集合的元素,Iterator 允许我们不用担心索引位置,甚至让我们不仅仅是遍历一个集合,同时还可以改变它。例如,你如果要删除循环中的元素,那么 for 循环不见得总是可行的。
结合自定义的迭代器,我们可以迭代更为复杂的对象,以及向前和向后移动,并且知晓如何利用其优势也将变得非常清楚。
本文将深入讨论如何使用 Iterator 和 Iterable 接口。
Iterator 接口用于迭代集合中的元素(List,Set 或 Map)。它用于逐个检索元素,并在需要时针对每个元素执行操作。
下面是用于遍历集合与执行操作的方法:
List<String> avengers = new ArrayList<>();
// Now lets add some Avengers to the list
avengers.add("Ant-Man");
avengers.add("Black Widow");
avengers.add("Captain America");
avengers.add("Doctor Strange");我们可以使用一个简单循环来遍历这个集合:
System.out.println("Simple loop example:\n");
for (int i = 0; i < avengers.size(); i++) {
System.out.println(avengers.get(i));
}不过,我们想探索迭代器:
System.out.println("\nIterator Example:\n");
// First we make an Iterator by calling
// the .iterator() method on the collection
Iterator<String> avengersIterator = avengers.iterator();
// And now we use .hasNext() and .next() to go through it
while (avengersIterator.hasNext()) {
System.out.println(avengersIterator.next());
}如果我们想从这个 ArrayList 中删除一个元素,会发生什么?让我们试着使用常规的 for 循环:
System.out.println("Simple loop example:\n");
for (int i = 0; i < avengers.size(); i++) {
if (avengers.get(i).equals("Doctor Strange")) {
avengers.remove(i);
}
System.out.println(avengers.get(i));
}我们会收到一个讨厌的 IndexOutOfBoundsException:
Simple loop example:
Ant-Man
Black Widow
Captain America
Exception in thread "main" java.lang.IndexOutOfBoundsException: Index: 3, Size: 3这在遍历集合时更改其大小是有意义的,增强 for 循环也一样:
System.out.println("Simple loop example:\n");
for (String avenger : avengers) {
if (avenger.equals("Doctor Strange")) {
avengers.remove(avenger);
}
System.out.println(avenger);
}我们再次收到了另一个异常:
Simple loop example:
Ant-Man
Black Widow
Captain America
Doctor Strange
Exception in thread "main" java.util.ConcurrentModificationException这时迭代器就派上用场了,由它充当中间人,从集合中删除元素,同时确保遍历按计划继续:
Iterator<String> avengersIterator = avengers.iterator();
while (avengersIterator.hasNext()) {
String avenger = avengersIterator.next();
// First we must find the element we wish to remove
if (avenger.equals("Ant-Man")) {
// This will remove "Ant-Man" from the original
// collection, in this case a List
avengersIterator.remove();
}
}这是保证在遍历集合时删除元素的安全方法。
并确认该元素是否已被删除:
/
/ We can also use the helper method .forEachRemaining()
System.out.println("For Each Remaining Example:\n");
Iterator<String> avengersIteratorForEach = avengers.iterator();
// This will apply System.out::println to all elements in the collection
avengersIteratorForEach.forEachRemaining(System.out::println);输出如下:
For Each Remaining Example:
Black Widow
Captain America
Doctor Strange正如你所看到的,蚁人已经从 复仇者联盟 的名单中删除了。
ListIterator 继承自 Iterator 接口。它只在 List 上进行使用,可以双向迭代,这意味着你可以从前到后或从后到前进行迭代。它也没有 current 元素,因为游标总是放在 List 的两个元素之间,所以我们用 .previous() 或 .next() 来访问元素。
Iterator 和 ListIterator 之间有什么区别呢?首先,Iterator 可以用于 任意集合 —— List、Map、Queue、Set 等。
ListIterator 只能应用于 List,通过添加这个限制,ListIterator 在方法方面可以更加具体,因此,我们引入了许多新方法,他们可以帮助我们在遍历时对其进行修改。
如果你正在处理 List 实现(ArrayList、LinkedList等),那么使用 ListIterator 更为可取一些。
下面是你可能会用到的方法:
ArrayList<String> defenders = new ArrayList<>();
defenders.add("Daredevil");
defenders.add("Luke Cage");
defenders.add("Jessica Jones");
defenders.add("Iron Fist");让我们用 ListIterator 来遍历 List 并打印其元素:
ListIterator listIterator = defenders.listIterator();
System.out.println("Original contents of our List:\n");
while (listIterator.hasNext())
System.out.print(listIterator.next() + System.lineSeparator());显然,它的工作方式与 Iterator 相同。输出如下:
Original contents of our List:
Daredevil
Luke Cage
Jessica Jones
Iron Fist现在,让我们来尝试修改一些元素:
System.out.println("Modified contents of our List:\n");
// Now let‘s make a ListIterator and modify the elements
ListIterator defendersListIterator = defenders.listIterator();
while (defendersListIterator.hasNext()) {
Object element = defendersListIterator.next();
defendersListIterator.set("The Mighty Defender: " + element);
}现在打印 List 的话会得到如下结果:
Modified contents of our List:
The Mighty Defender: Daredevil
The Mighty Defender: Luke Cage
The Mighty Defender: Jessica Jones
The Mighty Defender: Iron Fist现在,让我们倒着遍历列表,就像我们可以用 ListIterator 做的那样:
System.out.println("Modified List backwards:\n");
while (defendersListIterator.hasPrevious()) {
System.out.println(defendersListIterator.previous());
}输出如下:
Modified List backwards:
The Mighty Defender: Iron Fist
The Mighty Defender: Jessica Jones
The Mighty Defender: Luke Cage
The Mighty Defender: DaredevilSpliterator 接口在功能上与 Iterator 相同。你可能永远不需要直接使用 Spliterator,但让我们继续讨论一些用例。
但是,你应首先熟悉 Java Streams 和 Lambda Expressions in Java。
虽然我们将列出 Spliterator 拥有的所有方法,但是 Spliterator 接口的全部工作超出了本文的范畴。我们将通过一个例子讨论 Spliterator 如何使用并行化更有效地遍历我们可以分解的 Stream。
我们在处理 Spliterator 时使用的方法是:
* .characteristics()`:返回该 Spliterator 具有的作为
int值的特征。这些包括:
List<String> mutants = new ArrayList<>();
mutants.add("Professor X");
mutants.add("Magneto");
mutants.add("Storm");
mutants.add("Jean Grey");
mutants.add("Wolverine");
mutants.add("Mystique");现在,我们需要将 Spliterator 应用于 Stream。值得庆幸的是,由于 Collections 框架,很容易在 ArrayList 和 Stream 之间进行转换:
// Obtain a Stream to the mutants List.
Stream<String> mutantStream = mutants.stream();
// Getting Spliterator object on mutantStream.
Spliterator<String> mutantList = mutantStream.spliterator();为了展示其中的一些方法,让我们分别运行下它们:
// .estimateSize() method
System.out.println("Estimate size: " + mutantList.estimateSize());
// .getExactSizeIfKnown() method
System.out.println("\nExact size: " + mutantList.getExactSizeIfKnown());
System.out.println("\nContent of List:");
// .forEachRemaining() method
mutantList.forEachRemaining((n) -> System.out.println(n));
// Obtaining another Stream to the mutant List.
Spliterator<String> splitList1 = mutantStream.spliterator();
// .trySplit() method
Spliterator<String> splitList2 = splitList1.trySplit();
// If splitList1 could be split, use splitList2 first.
if (splitList2 != null) {
System.out.println("\nOutput from splitList2:");
splitList2.forEachRemaining((n) -> System.out.println(n));
}
// Now, use the splitList1
System.out.println("\nOutput from splitList1:");
splitList1.forEachRemaining((n) -> System.out.println(n));我们将得到输出:
Estimate size: 6
Exact size: 6
Content of List:
Professor X
Magneto
Storm
Jean Grey
Wolverine
Mystique
Output from splitList2:
Professor X
Magneto
Storm
Output from splitList1:
Jean Grey
Wolverine
Mystique如果出于某种原因,我们想要创建一个自定义的 Iterator 接口,应该怎么办?你首先要熟悉的是这张图: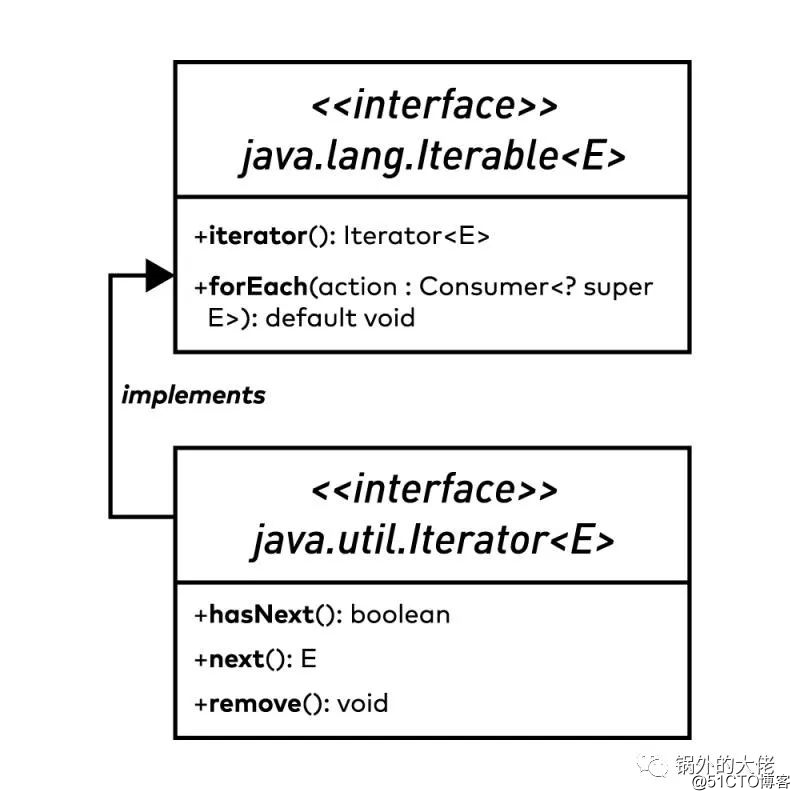
file
要创建自定义 Iterator,我们需要为 .hasNext()、.next() 和 .remove() 做自定义实现。
在 Iterator 接口中,有一个方法,它返回一个集合中元素的迭代器,即 .iterator() 方法,还有一个方法为迭代器中的每个元素执行一个操作的方法,即 .dorEach() 方法。
例如,假设我们是 Tony Stark,我们需要写个自定义迭代器来列出当前武器库中的每件钢铁侠套装。
首先,让我们创建一个类来获取和设置 suit 数据:
public class Suit {
private String codename;
private int mark;
public Suit(String codename, int mark) {
this.codename = codename;
this.mark = mark;
}
public String getCodename() { return codename; }
public int getMark() { return mark; }
public void setCodename (String codename) {this.codename=codename;}
public void setMark (int mark) {this.mark=mark;}
public String toString() {
return "mark: " + mark + ", codename: " + codename;
}
}接下来让我们编写自定义 Iterator:
// Our custom Iterator must implement the Iterable interface
public class Armoury implements Iterable<Suit> {
// Notice that we are using our own class as a data type
private List<Suit> list = null;
public Armoury() {
// Fill the List with data
list = new LinkedList<Suit>();
list.add(new Suit("HOTROD", 22));
list.add(new Suit("SILVER CENTURION", 33));
list.add(new Suit("SOUTHPAW", 34));
list.add(new Suit("HULKBUSTER 2.0", 48));
}
public Iterator<Suit> iterator() {
return new CustomIterator<Suit>(list);
}
// Here we are writing our custom Iterator
// Notice the generic class E since we do not need to specify an exact class
public class CustomIterator<E> implements Iterator<E> {
// We need an index to know if we have reached the end of the collection
int indexPosition = 0;
// We will iterate through the collection as a List
List<E> internalList;
public CustomIterator(List<E> internalList) {
this.internalList = internalList;
}
// Since java indexes elements from 0, we need to check against indexPosition +1
// to see if we have reached the end of the collection
public boolean hasNext() {
if (internalList.size() >= indexPosition +1) {
return true;
}
return false;
}
// This is our custom .next() method
public E next() {
E val = internalList.get(indexPosition);
// If for example, we were to put here "indexPosition +=2" we would skip every
// second element in a collection. This is a simple example but we could
// write very complex code here to filter precisely which elements are
// returned.
// Something which would be much more tedious to do with a for or while loop
indexPosition += 1;
return val;
}
// In this example we do not need a .remove() method, but it can also be
// written if required
}
}最后是 main 方法类:
public class IronMan {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Armoury armoury = new Armoury();
// Instead of manually writing .hasNext() and .next() methods to iterate through
// our collection we can simply use the advanced forloop
for (Suit s : armoury) {
System.out.println(s);
}
}
}输出如下:
mark: 22, codename: HOTROD
mark: 33, codename: SILVER CENTURION
mark: 34, codename: SOUTHPAW
mark: 48, codename: HULKBUSTER 2.0本文中,我们详细讨论了如何使用 Java 中的迭代器,甚至写了一个定制的迭代器来探索 Iterable 接口的所有新的可能性。
我们还讨论了 Java 是如何利用 Stream 的并行化,使用 Spliterator 接口对集合的遍历进行内部优化。
●Top11 构建和测试API的工具
●Spring Boot 默认的指标数据从哪来的?
●追踪JVM中的本地内存
右上角按钮分享给更多人哦~
Java 迭代接口:Iterator、ListIterator 和 Spliterator
标签:vat war oid sort 实现 数据 包括 复杂 except
原文地址:https://blog.51cto.com/14901350/2523565