标签:
popen 函数相当于做了以下几件事:
1、创建一个无名管道文件
2、 fork()
3、在子进程里, exec command
4、 在子进程里,
若 type == “r” , 相当于进行:
int fd_new = fopen("Pipe_Name",O_RDONLY); dup2(0,fd_new);
若 type == “w” , 相当于进行:
int fd_new = fopen("Pipe_Name",O_WRONLY); dup2(0,fd_new);
5、返回值 为 对管道文件 type类型操作的 文件指针
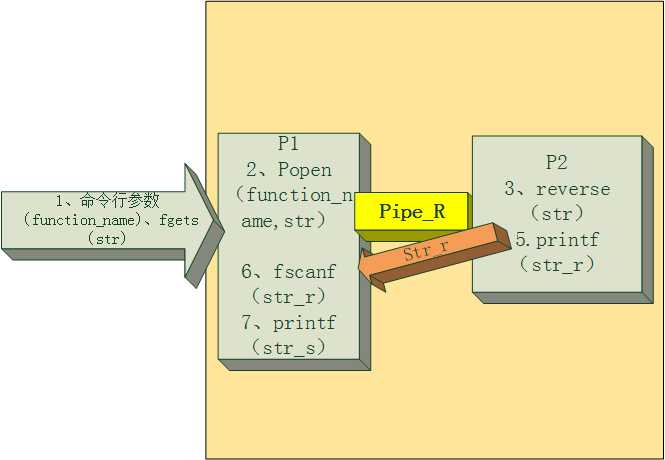
P1中:
1 fp_in = popen(cmd, "r") ;
popen的返回值 fp_in 文件指针 是管道文件的读文件指针
P2中:
popen(,“r”)把P2中的标准输出重定向到 管道文件 ,printf 相当于向管道文件 fputs
1 printf("%s\n", src );
具体代码:
p1:
1 #include<stdio.h> 2 #include<string.h> 3 #include<stdlib.h> 4 int main(int argc, char* argv[])// ./my_reverse 5 { 6 printf("pid: %d\n", getpid()); 7 FILE* fp_in ; 8 char cmd[1024] ; 9 char str[1024] ; 10 while(memset(str, 0, 1024), fgets(str, 1024, stdin) != NULL) 11 { 12 memset(cmd, 0, 1024); 13 sprintf(cmd, "%s %s", argv[1], str); 14 fp_in = popen(cmd, "r") ; 15 if(fp_in == NULL) 16 { 17 perror("popen"); 18 exit(1); 19 } 20 memset(str, 0, 1024) ; 21 fscanf( fp_in, "%s", str ); 22 printf("res: %s\n", str); 23 24 } 25 return 0 ; 26 }
p2:
1 #include<stdio.h> 2 #include<string.h> 3 #include<stdlib.h> 4 void handle(char* str) 5 { 6 int bg, end ; 7 int tmp ; 8 bg = 0; 9 end = strlen(str) - 1; 10 while(bg < end) 11 { 12 tmp = str[bg] ; 13 str[bg] = str[end] ; 14 str[end] = tmp ; 15 bg ++ ; 16 end -- ; 17 } 18 } 19 int main(int argc, char* argv[])//argv[1] 20 { 21 char src[1024] ; 22 strcpy(src, argv[1]); 23 handle(src); 24 printf("%s\n", src ); 25 return 0 ; 26 }
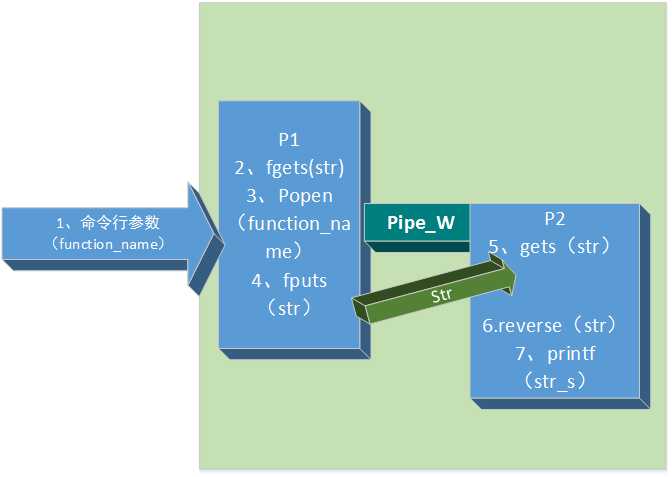
P1中:
1 fp_out = popen(argv[1], "w") ;
popen 的返回值 为 管道文件的 写文件指针
P2中:
popen(,“w”)把P2中的标准输入重定向到 管道文件 ,gets 相当于从管道文件 fgets
1 gets(src)
具体代码:
p1:
1 #include<stdio.h> 2 #include<string.h> 3 #include<stdlib.h> 4 int main(int argc, char* argv[])// ./my_reverse 5 { 6 printf("pid: %d\n", getpid()); 7 FILE* fp_out ; 8 char cmd[1024] ; 9 char str[1024] ; 10 fp_out = popen(argv[1], "w") ; 11 if(fp_out == NULL) 12 { 13 perror("popen"); 14 exit(1); 15 } 16 while(memset(str, 0, 1024), fgets(str, 1024, stdin) != NULL) 17 { 18 fputs(str, fp_out); 19 fflush(fp_out); 20 21 } 22 pclose(fp_out); 23 return 0 ; 24 }
P2:
1 #include<stdio.h> 2 #include<string.h> 3 #include<stdlib.h> 4 void handle(char* str) 5 { 6 int bg, end ; 7 int tmp ; 8 bg = 0; 9 end = strlen(str) - 1; 10 while(bg < end) 11 { 12 tmp = str[bg] ; 13 str[bg] = str[end] ; 14 str[end] = tmp ; 15 bg ++ ; 16 end -- ; 17 } 18 } 19 int main(int argc, char* argv[]) 20 { 21 char src[1024] ; 22 while(memset(src, 0, 1024), gets(src) != NULL ) 23 { 24 handle(src); 25 printf("pid: %d %s\n", getpid() ,src ); 26 } 27 return 0 ; 28 }
标签:
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/xiaoyesoso/p/4297174.html