标签:
今天复习了一下二叉树的前序遍历、中序遍历、后序遍历的递归与非递归算法,顺便记录一下:
//TreeTest.h #include <iostream> struct TreeNode { int value; TreeNode* leftChild; TreeNode* rightChild; void print() { printf("%d ",value); } }; class MyTree { private: TreeNode* m_root; TreeNode* create(TreeNode*& root); void destroy(TreeNode* root); void preOrderRecursive(TreeNode* root); void inOrderRecursive(TreeNode* root); void postOrderRecursive(TreeNode* root); void levelOrderRecursive(TreeNode* root); public: MyTree(); ~MyTree(); TreeNode* getTreeNode(int value); void createTreeForPreOrder(); void preOrderRecursive(); void inOrderRecursive(); void postOrderRecursive(); void levelOrderRecursive(); //非递归遍历 void preOrderUnRecursive(); void inOrderUnRecursive(); void postOrderUnRecursive(); }; //TreeTest.cpp #include "TreeTest.h" #include <iostream> #include <queue> #include <stack> using namespace std; MyTree::MyTree() : m_root(NULL) { } MyTree::~MyTree() { this->destroy(m_root); m_root = NULL; } void MyTree::destroy(TreeNode* root) { if (!root) return; TreeNode* left=NULL, *right=NULL; left = root->leftChild; right = root->rightChild; delete root; if (left) destroy(left); if (right) destroy(right); } TreeNode* MyTree::create(TreeNode*& root) { int value; cin>>value; if (value <= 0) return NULL; //小于或等于0代表NULL if (!root) root = this->getTreeNode(value); if (!root->leftChild) this->create(root->leftChild); if (!root->rightChild) this->create(root->rightChild); return root; } TreeNode* MyTree::getTreeNode(int value) { TreeNode* p = new TreeNode(); p->value = value; p->leftChild = p->rightChild = NULL; return p; } void MyTree::createTreeForPreOrder() { this->create(m_root); } void MyTree::preOrderRecursive(TreeNode* root) { if (!root) return; printf("%d ",root->value); if (root->leftChild) this->preOrderRecursive(root->leftChild); if (root->rightChild) this->preOrderRecursive(root->rightChild); } void MyTree::inOrderRecursive(TreeNode* root) { if (!root) return; if (root->leftChild) this->inOrderRecursive(root->leftChild); printf("%d ",root->value); if (root->rightChild) this->inOrderRecursive(root->rightChild); } void MyTree::postOrderRecursive(TreeNode* root) { if (!root) return; if (root->leftChild) this->postOrderRecursive(root->leftChild); if (root->rightChild) this->postOrderRecursive(root->rightChild); printf("%d ", root->value); } void MyTree::levelOrderRecursive(TreeNode* root) { queue<TreeNode*> Q; if (root) Q.push(root); while (!Q.empty()) { TreeNode* node = Q.front(); Q.pop(); node->print(); if (node->leftChild) Q.push(node->leftChild); if (node->rightChild) Q.push(node->rightChild); } } void MyTree::preOrderRecursive() { printf("递归前序遍历:"); this->preOrderRecursive(m_root); printf("\n"); } void MyTree::inOrderRecursive() { printf("递归中序遍历:"); this->inOrderRecursive(m_root); printf("\n"); } void MyTree::postOrderRecursive() { printf("递归后序遍历:"); this->postOrderRecursive(m_root); printf("\n"); } void MyTree::levelOrderRecursive() { printf("层序遍历:"); this->levelOrderRecursive(m_root); printf("\n"); } void MyTree::preOrderUnRecursive() { if (!m_root) return; printf("非递归先序遍历:"); stack<TreeNode*> S; S.push(m_root); while (!S.empty()) { TreeNode* node = S.top(); S.pop(); node->print(); if (node->rightChild) S.push(node->rightChild); if (node->leftChild) S.push(node->leftChild); } printf("\n"); } void MyTree::inOrderUnRecursive() { if (!m_root) return; printf("非递归中序遍历:"); stack<TreeNode*> S; TreeNode* p = m_root; while (p || !S.empty()) { while (p) { S.push(p); p = p->leftChild; } p = S.top(); S.pop(); p->print(); /*由于是中序遍历,那么访问了当前节点后, 下一步必定要访问该节点的右子树*/ p = p->rightChild; } printf("\n"); } void MyTree::postOrderUnRecursive() { if (!m_root) return; printf("非递归后序遍历:"); stack<TreeNode*> S; TreeNode* p = m_root; TreeNode* q = NULL; while (p || !S.empty()) { while (p) { S.push(p); p = p->leftChild; } p = S.top(); /* 判断表示当前节点的右节点没有或已经访问过 q表示上一次访问的节点,由于是后续遍历, 若当前节点有右节点,那么上一次访问的节点一定是当前节点的右节点 */ if (!p->rightChild || p->rightChild == q) { p->print(); q = p; p = NULL; S.pop(); } else { p = p->rightChild; } } printf("\n"); } //main.cpp #include "TreeTest.h" int main() { MyTree tree; tree.createTreeForPreOrder(); tree.preOrderRecursive(); tree.preOrderUnRecursive(); tree.inOrderRecursive(); tree.inOrderUnRecursive(); tree.postOrderRecursive(); tree.postOrderUnRecursive(); tree.levelOrderRecursive(); getchar(); getchar(); return 0; }
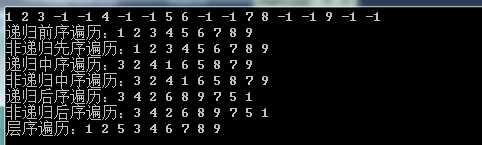
测试用例:
1 2 3 -1 -1 4 -1 -1 5 6 -1 -1 7 8 -1 -1 9 -1 -1
标签:
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/yu-chao/p/4316981.html