标签:
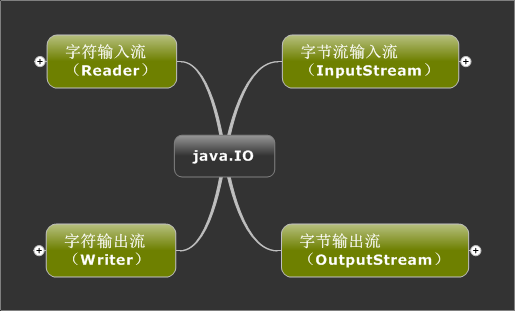
字节流:以字节(8位二进制)为单位进行处理。主要用于读写诸如图像或声音的二进制数据。
字符流:以字符(16位二进制)为单位进行处理。
都是通过字节流的方式实现的。字符流是对字节流进行了封装,方便操作。在最底层,所有的输入输出都是字节形式的。
后缀是Stream是字节流,而后缀是Reader,Writer是字符流。
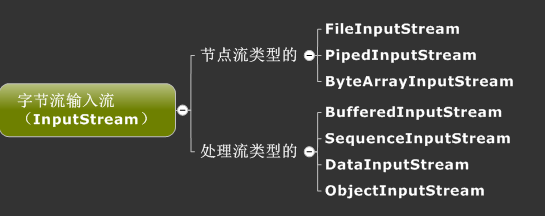
节点流:从特定的地方读写的流类,如磁盘或者一块内存区域。
过滤流:使用节点流作为输入或输出。过滤流是使用一个已经存在的输入流或者输出流连接创建的。
JDK提供的流继承了四大类:InputStream(字节输入流),OutputStream(字节输出流),Reader(字符输入流),Writer(字符输出流)。
java.io.InputStream abstract int read()
int read(byte[] b)
int read(byte[] b, int off, int len)
这里使用InputStream的子类FileInputStream读入文件:
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//创建文件输入流
InputStream is = new FileInputStream("D:/itzhai/arthinking.txt");
//创建字节缓冲
byte[] buffer = new byte[100];
int length = 0;
//以字节形式循环读取文件
while((length = is.read(buffer, 0, buffer.length)) != -1){
//把字节转换成字符并输出
String str =new String(buffer, 0, length);
System.out.println(str);
}
}
把字节数组作为源的输入流。
字节数组输入流:
public static void main(String[] args) {
//创建读取数据源
String input = "arthinking";
//获取字节数组
byte[] b = input.getBytes();
//创建字节数组输出流
ByteArrayInputStream bis = new ByteArrayInputStream(b);
//循环逐个读取
for(int i = 0; i < input.length(); i++){
int c;
//读取下一个字节
while((c = bis.read()) != -1){
System.out.print((char)c);
}
}
//将缓冲区的位置重置为标记位置
bis.reset();
}
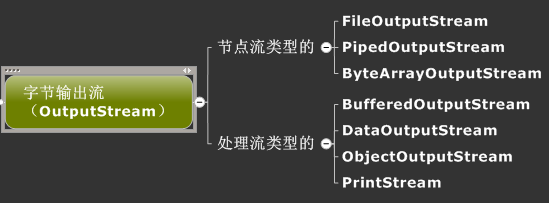
字节数组输出流:
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//创建字节输出流
ByteArrayOutputStream bos = new ByteArrayOutputStream();
String output = "arthinking";
//创建需要输出的字节数组
byte[] buffer = output.getBytes();
//把字节数组写到输出流
bos.write(buffer);
//创建文件输出流
OutputStream os = new FileOutputStream("D:/itzhai/arthinking.txt");
//把字节输出流写到文件输出流
bos.writeTo(os);
}
类 OutputStream java.lang.Object java.io.OutputStream void write(byte[] b)
void write(byte[] b, int off, int len)
将指定 byte 数组中从偏移量 off 开始的 len 个字节写入此输出流。
abstract void write(int b)
由此可以看出,只有最后一个方法才是抽象的,原因是前面两个都调用了第三个抽象方法,这样继承这个抽象类的子类都必须提供抽象的write(int b)的实现,从而使得每个子类的实现都不一样。
这里使用了OutputStream的子类FileOutputStream输出到文件:
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//创建一个输出流
OutputStream os = new FileOutputStream("D:/itzhai/arthinking.txt", true);
String output = "http://www.itzhai.com";
//从字符串中获取字节数组
byte[] buffer = output.getBytes();
//写出到输出流
os.write(buffer);
//关闭输出流
os.close();
}
过滤流不能直接跟文件打交道,只能通过节点流进行相关的操作。可以从其构造方法中看出:
FilterOutputStream(OutputStream out)
需要传入一个OutputStream。
在InputStream和OutputStream的子类中,
FilterInputStream和FilterOutputStream是过滤流,其又派生出子类DataInputStream和DataOutputStream数据输入流和数据输出流。
过滤流的主要特点是在输入输出数据同时对所传输的数据做指定类型或格式的转换。
该类实现缓冲的输出流。通过设置这种输出流,应用程序就可以将各个字节写入底层输出流中,而不必针对每次字节写入调用底层系统。
当缓冲区写满或者关闭输出流时,一次性输出到流,或者调用flush()方法主动将缓冲区输出到流。
使用过滤流类BufferedOutputStream和DataOutputStream装饰FilterOutputStream的例子:
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//创建数据输出流
DataOutputStream dos = new DataOutputStream(
new BufferedOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("D:/itzhai/arthinking.txt")));
byte a = 1;
char b = ‘a‘;
int c = 2;
//使用数据输出流对象的方法写出数据到输出流
dos.write(a);
dos.write(b);
dos.write(c);
//关闭数据输出流
dos.close();
//创建数据输入流
DataInputStream dis = new DataInputStream(
new BufferedInputStream(new FileInputStream("D:/itzhai/arthinking.txt")));
//使用数据输入流的方法从输入流中读取数据
System.out.println(dis.readByte() + dis.readChar() + dis.readInt());
//关闭数据输入流
dis.close();
}
使用DataInputStream和DataOutputStream数据文件流的一般步骤:

标签:
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/binyue/p/4562515.html