标签:
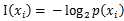
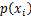 是选择该分类的概率。
是选择该分类的概率。1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 | #基于最后一列的分类标签,计算给定数据集的香农熵def calcShannonEnt(dataset): num_of_entries = len(dataset) label_counts = {} for feat_vec in dataset: current_lebel = feat_vec[-1] if current_lebel not in label_counts.keys(): label_counts[current_lebel] = 0 label_counts[current_lebel] += 1 shannonEnt = 0.0 for value in label_counts.values(): prob = float(value)/num_of_entries shannonEnt -= prob*log(prob, 2) return shannonEnt |
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 | # =================================# 按照给定特征划分数据集# 输入:dataset数据集;# axis指定特征,用下标表示;# value需要返回的特征的值# 返回:数据集中特征值等于value的子集# =================================def splitDataset(dataset, axis, value): retDataset = [] for featVec in dataset: if featVec[axis] == value: reducedFeatVec = featVec[0:axis] reducedFeatVec.extend(featVec[axis+1:]) retDataset.append(reducedFeatVec) return retDataset |
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 | # ===============================================# 输入:# dataSet: 数据集# 输出:# bestFeature: 和原数据集熵差最大划分对应的特征的列号# ===============================================def chooseBestFeatureToSplit(dataSet): # 最后一列用于标签,剩下的才是特征 numFeatures = len(dataSet[0]) - 1 # 根据标签计算的熵 baseEntropy = calcShannonEnt(dataSet) bestInfoGain = 0.0; bestFeature = -1 # iterate over all the features for i in range(numFeatures): # 取出某个特征列的所有值 featList = [example[i] for example in dataSet] # 去重 uniqueVals = set(featList) newEntropy = 0.0 for value in uniqueVals: subDataSet = splitDataset(dataSet, i, value) prob = len(subDataSet)/float(len(dataSet)) newEntropy += prob * calcShannonEnt(subDataSet) # calculate the info gain,计算信息增益 infoGain = baseEntropy - newEntropy # 和目前最佳信息增益比较,如果更大则替换掉 if (infoGain > bestInfoGain): bestInfoGain = infoGain bestFeature = i # 返回代表某个特征的下标 return bestFeature |
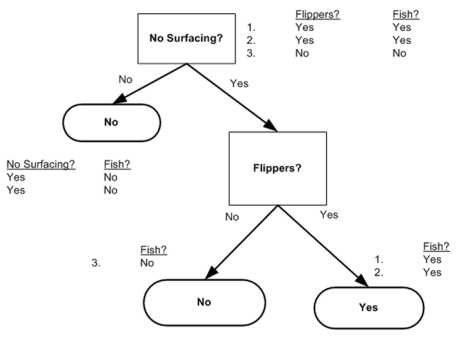
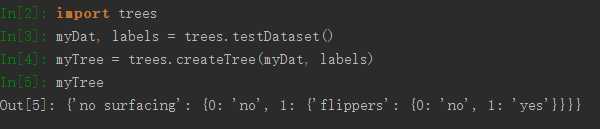
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 | #用于生成数据集,测试计算熵的函数def testDataset(): dataset1 = [[1, 1, ‘yes‘], [1, 1, ‘yes‘], [1, 0, ‘no‘], [0, 1, ‘no‘], [0, 1, ‘no‘]] labels = [‘no surfacing‘, ‘flippers‘] return dataset1, labels# 用于测试的函数def test(): mydata, labels = testDataset() print chooseBestFeatureToSplit(mydata) |
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 | # 传入分类名称组成的列表,返回出现次数最多的分类名称import operatordef majorityCnt(class_list): classCount = {} for vote in class_list: if vote not in classCount: classCount[vote] = 0 classCount[vote] += 1 sorted_class_list = sorted(classCount.iteritems(), key = operator.itemgetter(1), reverse=True) return sorted_class_list[0][0] |
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 | # ===============================================# 本函数用于创建决策树# 输入:# dataSet: 数据集# labels: 划分特征标签集# 输出:# myTree: 生成的决策树# ===============================================def createTree(dataSet, labels): # 获得类别标签列表 classList = [example[-1] for example in dataSet] # 递归终止条件一:如果数据集内所有分类一致 if classList.count(classList[0]) == len(classList): return classList[0] # 递归终止条件二:如果所有特征都划分完毕,任然不能将数据集划分成仅仅包含唯一类别的分组 if len(dataSet[0]) == 1: # 只剩下一列为类别列 return majorityCnt(classList) # 返回出现次数最多的类别 # 选择最佳划分特征,返回的时候特征的下标 best_feature = chooseBestFeatureToSplit(dataSet) best_feat_label = labels[best_feature] # 创建空树 myTree = {best_feat_label:{}} # 删除划分后的特征标签 del(labels[best_feature]) # 获取最佳划分特征中全部的特征值 featValues = [example[best_feature] for example in dataSet] # 去重 uniqueVals = set(featValues) for value in uniqueVals: subLabels = labels[:] # 保存用于下一次递归 myTree[best_feat_label][value] = createTree(splitDataset(dataSet, best_feature, value), subLabels) return myTree |
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 | # 把传入的树序列化之后存入文件def storeTree(inputTree, filename): import pickle # 用于序列化的模块 fw = open(filename, ‘w‘) pickle.dump(inputTree, fw) fw.close()# 从文件中把存好的树反序列化出来def grabTree(filename): import pickle fr = open(filename) return pickle.load(filename) |
标签:
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/mooba/p/5413980.html