标签:
前言:
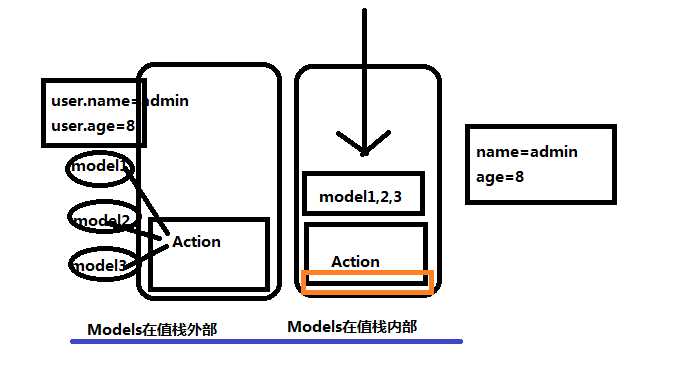
前面已经有一篇随笔介绍了Struts2的大概原理。本文就Struts2中Action与jsp页面进行数据对接时介绍几种常见方法!
Action1
package com.gdufe.action;
import com.opensymphony.xwork2.ActionSupport;
/*
* Action接收参数之后通过set方法赋给普通变量age,name;
*/
public class UserAction1 extends ActionSupport{
private int age;
private String name;
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String execute(){
return SUCCESS;
}
public String test(){
System.out.println(age +"|"+ name);
return SUCCESS;
}
}
Action2

package com.gdufe.action;
import com.gdufe.pojo.User;
import com.opensymphony.xwork2.ActionSupport;
/*
* Action接收参数之后赋给引用对象“user”,内部是set方法赋值
*/
public class UserAction2 extends ActionSupport {
private User user;
public User getUser() {
return user;
}
public void setUser(User user) {
this.user = user;
}
public String test(){
System.out.println(user.getName() + "|" + user.getAge());
return "success";
}
}
Action3

package com.gdufe.action;
import com.gdufe.pojo.User;
import com.opensymphony.xwork2.ActionSupport;
import com.opensymphony.xwork2.ModelDriven;
public class UserAction3 extends ActionSupport implements ModelDriven<User> {
private User user = new User();
public String test(){
System.out.println(user.getName() + "|" + user.getAge());
return "success";
}
public User getModel() {
return user;
}
}
index.jsp
<%@ page language="java" import="java.util.*" pageEncoding="UTF-8"%>
<%@ taglib prefix="s" uri="/struts-tags" %>
<%
String path = request.getContextPath();
String basePath = request.getScheme()+"://"+request.getServerName()+":"+request.getServerPort()+path+"/";
%>
<!DOCTYPE HTML PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN">
<html>
<head>
<base href="<%=basePath%>">
<title>My JSP ‘index.jsp‘ starting page</title>
<meta http-equiv="pragma" content="no-cache">
<meta http-equiv="cache-control" content="no-cache">
<meta http-equiv="expires" content="0">
<meta http-equiv="keywords" content="keyword1,keyword2,keyword3">
<meta http-equiv="description" content="This is my page">
</head>
<body>
<h2>Action传值测试</h2>
<a href="userAction1!test?age=8&name=admin">test1:Attribution</a> <br>
<a href="userAction2!test?user.age=8&user.name=admin">test2:JavaBean</a> <br>
<a href="userAction3!test?age=8&name=admin">test3:ModelDriven</a> <br>
</body> </html>
success.jsp
<%@ page language="java" import="java.util.*" pageEncoding="UTF-8"%>
<%@ taglib prefix="s" uri="/struts-tags" %>
<%
String path = request.getContextPath();
String basePath = request.getScheme()+"://"+request.getServerName()+":"+request.getServerPort()+path+"/";
%>
<!DOCTYPE HTML PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN">
<html>
<head>
<base href="<%=basePath%>">
<title>My JSP ‘index.jsp‘ starting page</title>
<meta http-equiv="pragma" content="no-cache">
<meta http-equiv="cache-control" content="no-cache">
<meta http-equiv="expires" content="0">
<meta http-equiv="keywords" content="keyword1,keyword2,keyword3">
<meta http-equiv="description" content="This is my page">
</head>
<body>
<h2>Action传值双击debug</h2>
<s:debug></s:debug>
<!-- debug重要的strut2标签调试工具 -->
</body>
</html>
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<!DOCTYPE struts PUBLIC
"-//Apache Software Foundation//DTD Struts Configuration 2.0//EN"
"http://struts.apache.org/dtds/struts-2.0.dtd">
<struts>
<!-- devMode设置为开发模式 -->
<constant name="struts.devMode" value="true" />
<package name="default" extends="struts-default">
<!-- 注:因为Action采用DMI方式,故不需要指明method 以及 ‘result’ -->
<action name="userAction1" class="com.gdufe.action.UserAction1" >
<result>/success.jsp</result>
</action>
<action name="userAction2" class="com.gdufe.action.UserAction2" >
<result>/success.jsp</result>
</action>
<action name="userAction3" class="com.gdufe.action.UserAction3" >
<result>/success.jsp</result>
</action>
</package>
</struts>
运行结果:
对应Action1——------------------*-------------------------

对应Action2——------------------*-------------------------
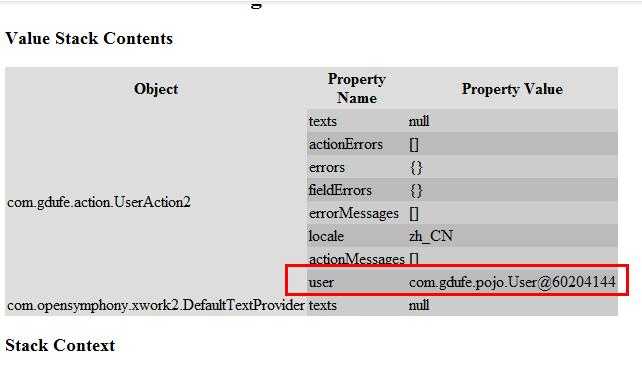
对应Action3——------------------*-------------------------

标签:
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/dengyuqing/p/5978166.html