标签:img span names put ptr pointer png ret point
①指针访问:最快
②迭代器iterator:较慢,非常安全,指针访问可能出现越界问题
③动态地址计算:更慢,通过at()实现。适用于访问具体某个第i行,j列的像素,而不适用遍历像素
灰度图的存储形式
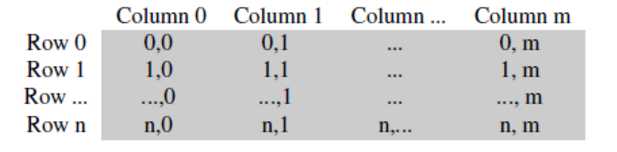
RGB的存储形式
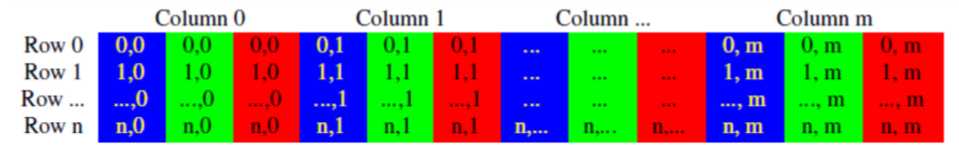
一般情况下,Mat是连续存储的,按行连接。可以通过isContinuous()函数,判断矩阵是否连续存储,若连续返回true。
1.指针访问
1 void VisitImgByPointer(Mat &inputImg, Mat &dstImg) 2 { 3 dstImg = inputImg.clone(); 4 int rows = dstImg.rows; 5 int cols = dstImg.cols * dstImg.channels(); 6 7 for(int i = 0; i < rows; i++) 8 { 9 uchar* data = dstImg.ptr<uchar>(i); 10 for(int j = 0; j < cols; j++) 11 { 12 data[j] = 0; //处理每一个像素 13 //add code 14 } 15 } 16 }
当Mat按行连续存储时,可以用指针直接访问所有数据。
1 void VisitContinueImgByPointer(Mat &inputImg, Mat &dstImg) 2 { 3 dstImg = inputImg.clone(); 4 int rows = dstImg.rows; 5 int cols = dstImg.cols; 6 int channels = dstImg.channels(); 7 8 if(dstImg.isContinuous()) 9 { 10 cols *= rows; 11 rows = 1; 12 //cout << "is continuous " << endl; 13 } 14 15 for(int i = 0; i < rows; i++) 16 { 17 uchar* data = dstImg.ptr<uchar>(i); 18 for(int j = 0; j < cols * channels; j++) 19 { 20 data[j] = 155; //处理每一个像素 21 //add code 22 } 23 } 24 //若存储连续,等效于以下代码 25 //uchar* data = dstImg.data; 26 //for(int i = 0; i < cols * rows * channels; i++) 27 // data[i] = 155; //处理每一个像素 28 29 }
2.迭代器访问
1 void VisitImgByIterator(Mat &inputImg, Mat &dstImg) 2 { 3 dstImg = inputImg.clone(); 4 const int channels = dstImg.channels(); 5 6 switch(channels) 7 { 8 case 1: 9 { 10 Mat_<uchar>::iterator it= dstImg.begin<uchar>(); 11 Mat_<uchar>::iterator itend= dstImg.end<uchar>(); 12 for ( ; it!= itend; it++) //处理每一个像素 13 { 14 *it = 150; 15 } 16 break; 17 } 18 case 3: 19 { 20 Mat_<Vec3b>::iterator it3= dstImg.begin<Vec3b>(); 21 Mat_<Vec3b>::iterator itend3= dstImg.end<Vec3b>(); 22 for ( ; it3!= itend3; it3++) //处理每一个像素 23 { 24 (*it3)[0]= 255; 25 (*it3)[1]= 0; 26 (*it3)[2]= 0; 27 } 28 break; 29 } 30 } 31 }
3.动态地址访问
1 void VisitImgByAt(Mat &inputImg, Mat &dstImg) 2 { 3 dstImg = inputImg.clone(); 4 int rows = dstImg.rows; 5 int cols = dstImg.cols; 6 int channels = dstImg.channels(); 7 8 switch(channels) 9 { 10 case 1: 11 { 12 for(int i = 0; i < rows; i++) 13 for(int j = 0; j < cols; j++) 14 dstImg.at<uchar>(i,j) = 150; 15 break; 16 } 17 case 3: 18 { 19 for(int i = 0; i < rows; i++) 20 for(int j = 0; j < cols; j++) 21 { 22 dstImg.at<Vec3b>(i,j)[0] = 0; 23 dstImg.at<Vec3b>(i,j)[1] = 0; 24 dstImg.at<Vec3b>(i,j)[2] = 255; 25 } 26 break; 27 } 28 } 29 }
测试代码-总
1 #include <iostream> 2 #include <opencv2/opencv.hpp> 3 using namespace cv; 4 using namespace std; 5 6 void VisitImgByPointer(Mat &inputImg, Mat &dstImg); 7 void VisitContinueImgByPointer(Mat &inputImg, Mat &dstImg); 8 void VisitImgByIterator(Mat &inputImg, Mat &dstImg); 9 void VisitImgByAt(Mat &inputImg, Mat &dstImg); 10 11 int main() 12 { 13 Mat srcImg = imread("pig.png"), dstImg; 14 Mat grayImg; 15 cvtColor(srcImg, grayImg, CV_BGR2GRAY); 16 //VisitImgByPointer(srcImg,dstImg); 17 //VisitContinueImgByPointer(grayImg,dstImg); 18 19 //VisitImgByIterator(srcImg,dstImg); 20 //VisitImgByIterator(grayImg,dstImg); 21 22 //VisitImgByAt(srcImg,dstImg); 23 VisitImgByAt(grayImg,dstImg); 24 25 //imshow("原始图", srcImg); 26 //imshow("灰度图", grayImg); 27 imshow("生成图", dstImg); 28 29 waitKey(0); 30 return 0; 31 } 32 33 void VisitImgByPointer(Mat &inputImg, Mat &dstImg) 34 { 35 dstImg = inputImg.clone(); 36 int rows = dstImg.rows; 37 int cols = dstImg.cols * dstImg.channels(); 38 39 for(int i = 0; i < rows; i++) 40 { 41 uchar* data = dstImg.ptr<uchar>(i); 42 for(int j = 0; j < cols; j++) 43 { 44 data[j] = 0; //处理每一个像素 45 //add code 46 } 47 } 48 } 49 50 void VisitContinueImgByPointer(Mat &inputImg, Mat &dstImg) 51 { 52 dstImg = inputImg.clone(); 53 int rows = dstImg.rows; 54 int cols = dstImg.cols; 55 int channels = dstImg.channels(); 56 57 if(dstImg.isContinuous()) 58 { 59 cols *= rows; 60 rows = 1; 61 //cout << "is continuous " << endl; 62 } 63 64 for(int i = 0; i < rows; i++) 65 { 66 uchar* data = dstImg.ptr<uchar>(i); 67 for(int j = 0; j < cols * channels; j++) 68 { 69 data[j] = 155; //处理每一个像素 70 //add code 71 } 72 } 73 //若存储连续,等效于一下代码 74 //uchar* data = dstImg.data; 75 //for(int i = 0; i < cols * rows * channels; i++) 76 // data[i] = 155; //处理每一个像素 77 78 } 79 80 81 void VisitImgByIterator(Mat &inputImg, Mat &dstImg) 82 { 83 dstImg = inputImg.clone(); 84 const int channels = dstImg.channels(); 85 86 switch(channels) 87 { 88 case 1: 89 { 90 Mat_<uchar>::iterator it= dstImg.begin<uchar>(); 91 Mat_<uchar>::iterator itend= dstImg.end<uchar>(); 92 for ( ; it!= itend; it++) //处理每一个像素 93 { 94 *it = 150; 95 } 96 break; 97 } 98 case 3: 99 { 100 Mat_<Vec3b>::iterator it3= dstImg.begin<Vec3b>(); 101 Mat_<Vec3b>::iterator itend3= dstImg.end<Vec3b>(); 102 for ( ; it3!= itend3; it3++) //处理每一个像素 103 { 104 (*it3)[0]= 255; 105 (*it3)[1]= 0; 106 (*it3)[2]= 0; 107 } 108 break; 109 } 110 } 111 } 112 113 void VisitImgByAt(Mat &inputImg, Mat &dstImg) 114 { 115 dstImg = inputImg.clone(); 116 int rows = dstImg.rows; 117 int cols = dstImg.cols; 118 int channels = dstImg.channels(); 119 120 switch(channels) 121 { 122 case 1: 123 { 124 for(int i = 0; i < rows; i++) 125 for(int j = 0; j < cols; j++) 126 dstImg.at<uchar>(i,j) = 150; 127 break; 128 } 129 case 3: 130 { 131 for(int i = 0; i < rows; i++) 132 for(int j = 0; j < cols; j++) 133 { 134 dstImg.at<Vec3b>(i,j)[0] = 0; 135 dstImg.at<Vec3b>(i,j)[1] = 0; 136 dstImg.at<Vec3b>(i,j)[2] = 255; 137 } 138 break; 139 } 140 } 141 }
标签:img span names put ptr pointer png ret point
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/kuotian/p/6389260.html