标签:blog http 使用 os io strong for ar
今天改了一个项目,大概是这样的:
有一个服务进程,和一群客户进程,客户进程在服务进程中订阅消息,每当服务进程有新消息时,就会将新消息放到共享内存,然后根据消息的类型通知相应的客户进程。业务逻辑很简单。在当中用到了两种进程通信方式,共享内存和信号量。
实现细节是,当服务进程去通知客户进程时,需要用一个for循环一个个去通知,我想换成使用信号来一次性全唤醒(把订阅相同消息的放进同一个进程组中),因为忽略了屏蔽信号这件事,所以就开始了我蛋疼的一天。
我们先来看一个利用信号通信的简单示例:
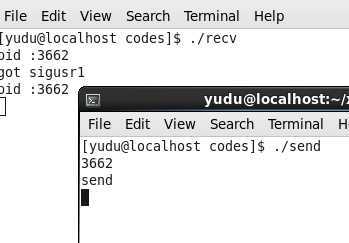
send发送一个信号给recv,recv收到后输出。
贴上代码:
/*************************************************************************
> File Name: sigSend.cpp
> Author: duyu
> Mail: duyu_ics@163.com
> Created Time: Wed 20 Aug 2014 09:30:43 PM CST
************************************************************************/
#include<iostream>
#include <signal.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
using namespace std;
int main(int argc,char *argv[])
{
pid_t pid;
while(1)
{
cin>>pid;
if(-1 == kill(pid,SIGUSR1))
perror("kill");
cout<<"send"<<endl;
}
return 0;
}
/*************************************************************************
> File Name: sigRevc.cpp
> Author: duyu
> Mail: duyu_ics@163.com
> Created Time: Wed 20 Aug 2014 09:33:30 PM CST
************************************************************************/
#include<iostream>
#include <signal.h>
#include <unistd.h>
using namespace std;
void handle(int signo)
{
if(signo == SIGUSR1)
cout<<"got sigusr1"<<endl;
}
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
if(SIG_ERR == signal(SIGUSR1,handle))//注册信号
cout<<"fail to install"<<endl;
while(1)
{
cout<<"pid :"<<getpid()<<endl;
pause();
}
return 0;
}
先运行recv,再运行send,就可以出来上述效果了。
在有了直观认识之后,就可以看看linux当中的API了:
1、常见信号
#define SIGHUP 1 #define SIGINT 2 #define SIGQUIT 3 #define SIGILL 4 #define SIGTRAP 5 #define SIGABRT 6 #define SIGIOT 6 #define SIGBUS 7 #define SIGFPE 8 #define SIGKILL 9 #define SIGUSR1 10 #define SIGSEGV 11 #define SIGUSR2 12 #define SIGPIPE 13 #define SIGALRM 14 #define SIGTERM 15 #define SIGSTKFLT 16 #define SIGCHLD 17 #define SIGCONT 18 #define SIGSTOP 19 #define SIGTSTP 20 #define SIGTTIN 21 #define SIGTTOU 22 #define SIGURG 23 #define SIGXCPU 24 #define SIGXFSZ 25 #define SIGVTALRM 26 #define SIGPROF 27 #define SIGWINCH 28 #define SIGIO 29 #define SIGPOLL SIGIO /* #define SIGLOST 29 */ #define SIGPWR 30 #define SIGSYS 31 #define SIGUNUSED 31 /* These should not be considered constants from userland. */ #define SIGRTMIN 32 #define SIGRTMAX _NSIG
上面是/usr/include/asm/signal.h中的内容,是系统定义的信号,其中_NSIG是65。
有几种常见的信号介绍一下,SIGCHLD退出时会给父进程发送该信号,父进程收到后可以根据该信号来完成对子进程PCB的回收;SIGSTOP和SIGKILL不能被屏蔽与安装,一个进程在收到SIGSTOP后会暂停执行,进入暂停状态,当收到SIGCONT后会继续执行;SIGSEGV信号也经常见到,段错误了,也就是内存访问的问题。
上面提到的安装就是指,设置收到该信号后做什么,用户可以指定一个函数,如前面例子中的handle来处理。每一种信号都有默认的处理方式,如下图。
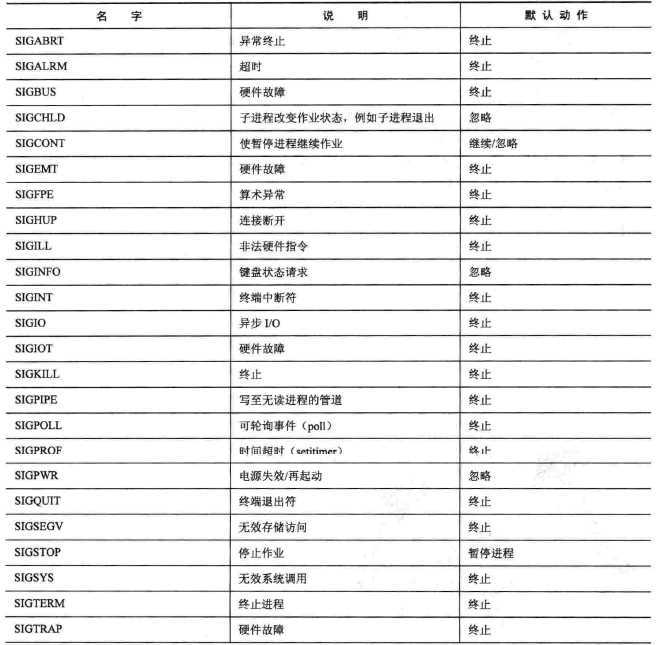
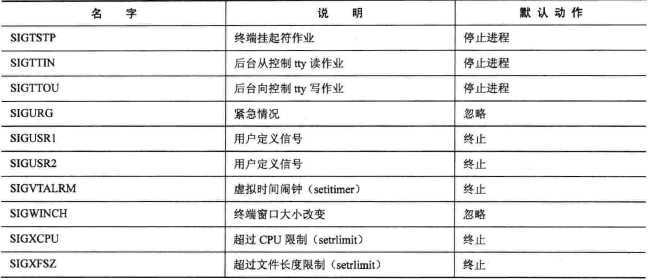
我们也可以自己定义信号,范围是32~64,不能超过了,否则在安装(signal函数)的时候会返回SIG_ERR。
标签:blog http 使用 os io strong for ar
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/dy-techblog/p/3925611.html