标签:-- slist target integer contain ide strong ati stat
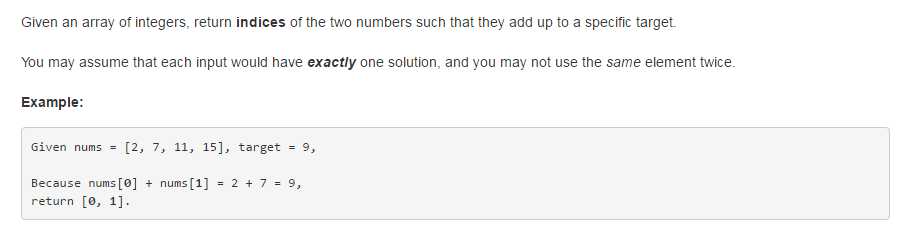
1、2Sum
题目:
方法一:两次迭代

public class TwoSum { public static int[] twoSum(int[] nums, int target) { int[] indices = {-1,-1}; for(int i=0; i<nums.length-1; i++ ){ if(target>=nums[i]){ for(int k=i+1; k<=nums.length-1; k++){ if(nums[k] == (target-nums[i])){ indices[0]=i; indices[1]=k; return indices; } } } } return indices; } }
方法二:利用HashMap,减少一次迭代

import java.util.HashMap; public class Two_Sum1 { public static int[] twosum(int[] nums, int target){ int[] result = new int[2]; if(nums.length < 2) return result; HashMap<Integer,Integer> map = new HashMap<Integer,Integer>(); for(int i=0; i<nums.length; i++){ if(!map.containsKey(target-nums[i])){ map.put(nums[i],i); }else{ result[0]=map.get(target-nums[i]); result[1]=i; break; } } return result; } }
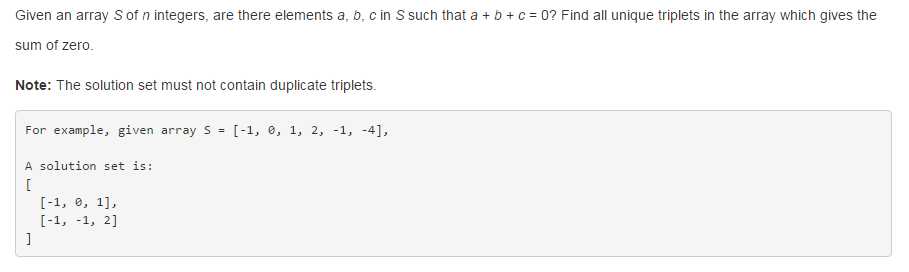
2、3Sum
思路分析:数组排序 + twoPointers

public class _3Sum { public static List<List<Integer>> threeSum(int[] num){ Arrays.sort(num); List<List<Integer>> res = new LinkedList<>(); for(int i=0; i<num.length-2; i++){ if(i==0 || (i>0 && num[i]!= num[i-1])){ int lo=i+1, hi=num.length-1, sum=0-num[i]; while(lo<hi){ if(num[lo]+num[hi]==sum){ res.add(Arrays.asList(num[i],num[lo],num[hi])); while(lo<hi && num[lo] == num[lo+1]) lo++; while(lo<hi && num[hi] == num[hi-1]) hi--; lo++; hi--; }else if(num[lo]+num[hi]<sum) lo++; else hi--; } } } return res; } }
3、3Sum Cloest

思路分析:数组排序 + twoPointers

public class _3SumClosest { public static int threeSumClosest(int[] nums, int target){ Arrays.sort(nums); int diff = Integer.MAX_VALUE, closest=0; for(int i=0;i<nums.length-2;i++){ int lo=i+1, hi=nums.length-1; while(lo<hi){ int sum = nums[i]+nums[lo]+nums[hi]; if(sum == target) return target; else if(sum > target){ if(sum-target<diff){ diff = sum - target; closest = sum; } hi--; }else{ if(target-sum<diff){ diff = target - sum; closest = sum; } lo++; } } } return closest; } }
4、4Sum

思路分析:数组排序+转化问题为3Sum + 2Sum

public class FourSum { public static List<List<Integer>> fourSum(int[] nums, int target){ LinkedList<List<Integer>> res = new LinkedList<List<Integer>>(); if(nums==null || nums.length<4) return res; Arrays.sort(nums); int len = nums.length; int max = nums[len-1]; if(4*nums[0]>target || 4*max<target) return res; for(int i=0; i<len-3; i++){ int z=nums[i]; if(i>0 && z==nums[i-1]) continue; if(z+3*max<target) continue; if(4*z>target) break; if(4*z==target) { if(i+3<len && nums[i+3]==z) res.add(Arrays.asList(z,z,z,z)); break; } threeSum(nums,target-z,i+1,len-1,res,z); } return res; } public static void threeSum(int[] nums, int target, int lo, int hi, LinkedList<List<Integer>> fourSumList, int z1){ if(lo+1>=hi) return; int max = nums[hi]; if(3*nums[lo]>target || 3*max<target) return; for(int i=lo; i<hi-1; i++){ int z=nums[i]; if(i>lo && z==nums[i-1]) continue; if(z+2*max<target) continue; if(3*z>target) break; if(3*z == target){ if(i+1<hi && nums[i+2]==z) fourSumList.add(Arrays.asList(z1,z,z,z)); break; } twoSum(nums,target-z,i+1,hi,fourSumList,z1,z); } } public static void twoSum(int[] nums, int target, int lo, int hi, LinkedList<List<Integer>> fourSumList, int z1, int z2){ if(lo>=hi) return; if(2*nums[lo]>target || 2*nums[hi]<target) return; while(lo<hi){ int sum = nums[lo]+nums[hi]; if(sum == target){ fourSumList.add(Arrays.asList(z1,z2,nums[lo],nums[hi])); while(lo<hi && nums[lo]==nums[lo+1]) lo++; while(lo<hi && nums[hi]==nums[hi-1]) hi--; lo++;hi--; } if(sum<target) lo++; if(sum>target) hi--; } return; } }
5、kSum

public class KSum { public ArrayList<List<Integer>> kSum(int[] nums, int target, int k, int index){ ArrayList<List<Integer>> res = new ArrayList<List<Integer>>(); if(nums==null || nums.length<k) return res; Arrays.sort(nums); int len = nums.length; int max = nums[len-1]; if(k*nums[0]>target || k*max<target) { return res; } if(index >= len) { return res; } if(k==2){ int i=index, j=len-1; while(i<j){ if(nums[i]+nums[j] == target){ res.add(Arrays.asList(nums[i],nums[j])); while(i<j && nums[i]==nums[i+1]) i++; while(i<j && nums[j]==nums[j-1]) j--; i++;j--; } else if(nums[i]+nums[j]<target) i++; else j--; } //while循环结束 }else{ for (int i = index; i < len - k + 1; i++) { ArrayList<List<Integer>> temp = kSum(nums,target-nums[i],k-1,i+1); if(temp!=null && temp.size()!=0){ for(List<Integer> t : temp){ t.add(0,nums[i]); } res.addAll(temp); } while(i<len-1 && nums[i] == nums[i+1]){ i++; } }//for循环结束 } return res; } }
标签:-- slist target integer contain ide strong ati stat
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/zhiyangjava/p/6725379.html