VFS只存在于内存中,它在系统启动时被创建,系统关闭时注销。
VFS的作用就是屏蔽各类文件系统的差异,给用户、应用程序、甚至Linux其他管理模块提供统一的接口集合。
管理VFS数据结构的组成部分主要包括超级块和inode。
VFS是物理文件系统与服务之间的一个接口层,它对Linux的每个文件系统的所有细节进行抽象,使得不同的文件系统在Linux核心以及系统中运行的进程看来都是相同的。
严格的说,VFS并不是一种实际的文件系统。它只存在于内存中,不存在于任何外存空间。VFS在系统启动时建立,在系统关闭时消亡。
VFS使Linux同时安装、支持许多不同类型的文件系统成为可能。VFS拥有关于各种特殊文件系统的公共界面,当某个进程发布了一个面向文件的系统调用时,内核将调用VFS中对应的函数,这个函数处理一些与物理结构无关的操作,并且把它重定向为真实文件系统中相应的函数调用,后者用来处理那些与物理结构相关的操作。
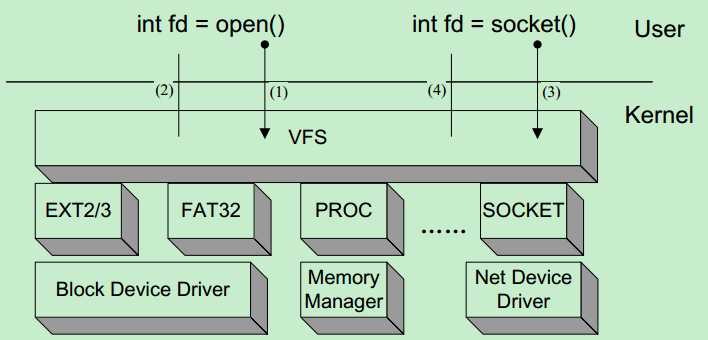
下图就是逻辑上对VFS及其下层实际文件系统的组织图,可以看到用户层只能于VFS打交道,而不能直接访问实际的文件系统,比如EXT2、EXT3、PROC,换句话说,
就是用户层不用也不能区别对待这些真正的文件系统,不过,SOCKET虽然也属于VFS的管辖范围,但是有其特殊性,
就是不能像打开大部分文件系统下的“文件”一样打开socket,它只能被创建,而且内核中对其有特殊性处理。
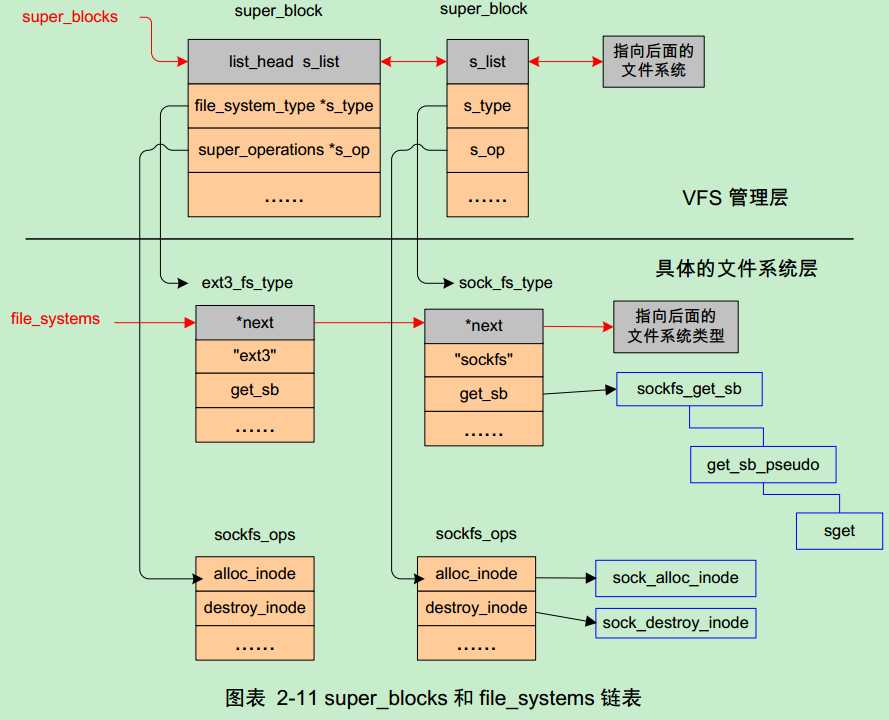
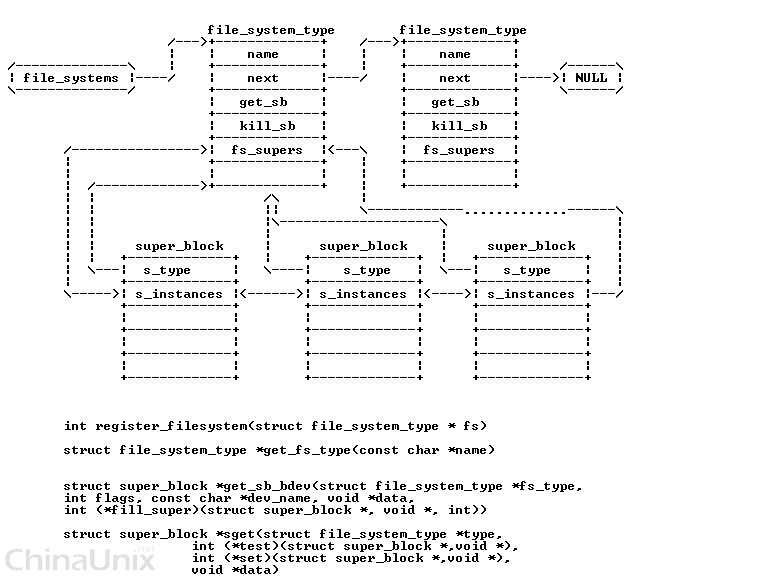
VFS描述文件系统使用超级块和inode 的方式,所谓超级块就是对所有文件系统的管理机构,每种文件系统都要把自己的信息挂到super_blocks这么一个全局链表上。
内核中是分成2个步骤完成:首先每个文件系统必须通过register_filesystem函数将自己的file_system_type挂接到file_systems这个全局变量上,
然后调用kern_mount函数把自己的文件相关操作函数集合表挂到super_blocks上。每种文件系统类型的读超级块的例程(get_sb)必须由自己实现。
文件系统由子目录和文件构成。每个子目录和文件只能由唯一的inode 描述。inode 是Linux管理文件系统的最基本单位,也是文件系统连接任何子目录、文件的桥梁。
VFS inode的内容取自物理设备上的文件系统,由文件系统指定的操作函数(i_op 属性指定)填写。VFS inode只存在于内存中,可通过inode缓存访问。
1、super_block
- 相关的数据结构为:
struct super_block{struct list_head s_list;/* Keep this first */// 连接super_block的链表dev_t s_dev;/* search index; _not_ kdev_t */unsignedlong s_blocksize;unsignedlong s_old_blocksize;unsignedchar s_blocksize_bits;unsignedchar s_dirt;unsignedlonglong s_maxbytes;/* Max file size */struct file_system_type *s_type;// 所表示的文件系统的类型struct super_operations *s_op;// 文件相关操作函数集合表struct dquot_operations *dq_op;//struct quotactl_ops *s_qcop;//struct export_operations *s_export_op;//unsignedlong s_flags;//unsignedlong s_magic;//struct dentry *s_root;// Linux文件系统中某个索引节点(inode)的链接struct rw_semaphore s_umount;//struct semaphore s_lock;//int s_count;//int s_syncing;//int s_need_sync_fs;//atomic_t s_active;//void*s_security;//struct xattr_handler **s_xattr;//struct list_head s_inodes;/* all inodes */// 链接文件系统的inodestruct list_head s_dirty;/* dirty inodes */struct list_head s_io;/* parked for writeback */struct hlist_head s_anon;/* anonymous dentries for (nfs) exporting */struct list_head s_files;// 对于每一个打开的文件,由file对象来表示。链接文件系统中filestruct block_device *s_bdev;//struct list_head s_instances;//struct quota_info s_dquot;/* Diskquota specific options */int s_frozen;//wait_queue_head_t s_wait_unfrozen;//char s_id[32];/* Informational name */void*s_fs_info;/* Filesystem private info *//*** The next field is for VFS *only*. No filesystems have any business* even looking at it. You had been warned.*/struct semaphore s_vfs_rename_sem;/* Kludge *//* Granuality of c/m/atime in ns.Cannot be worse than a second */u32 s_time_gran;};
- super_block存在于两个链表中,一个是系统所有super_block的链表, 一个是对于特定的文件系统的super_block链表.
所有的super_block都存在于 super_blocks(VFS管理层) 链表中:
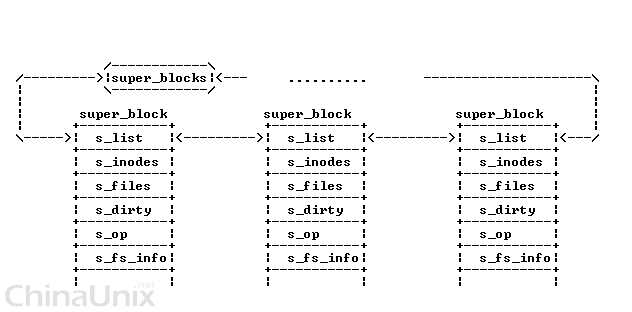
- 对于特定的文件系统(文件系统层的具体文件系统), 该文件系统的所有的super_block 都存在于file_sytem_type中的fs_supers链表中.
int register_filesystem(struct file_system_type * fs)
2、inode
inode(发音:eye-node)译成中文就是索引节点,它用来存放档案及目录的基本信息,包含时间、档名、使用者及群组等。
inode 是 UNIX 操作系统中的一种数据结构,其本质是结构体,它包含了与文件系统中各个文件相关的一些重要信息。在 UNIX 中创建文件系统时,同时将会创建大量的 inode 。
通常,文件系统磁盘空间中大约百分之一空间分配给了 inode 表。
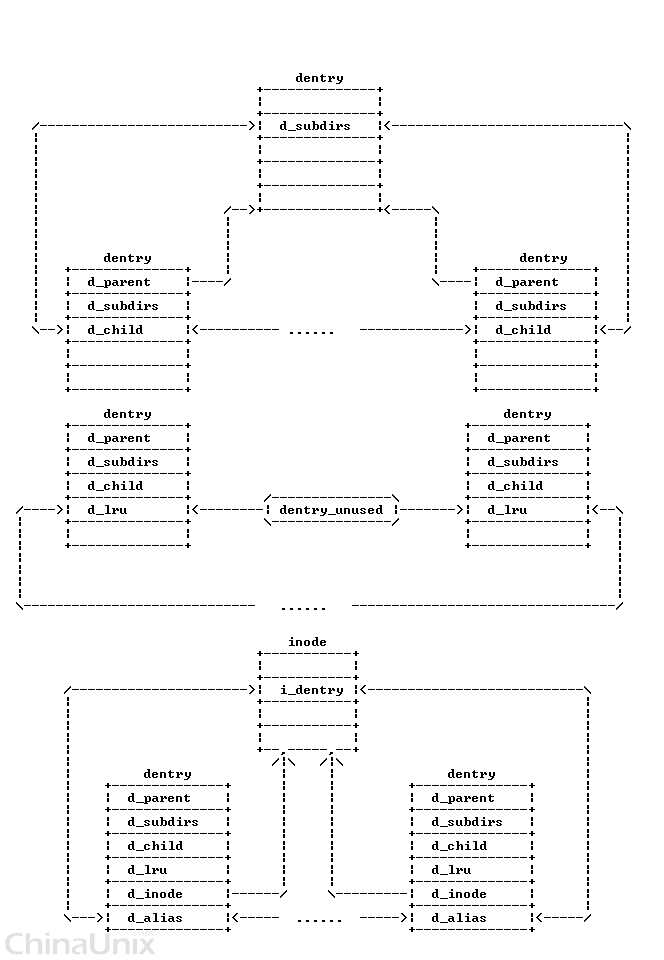
inode对应于物理磁盘上的具体对象,dentry是一个内存实体,其中的d_inode成员指向对应的inode。
相关的数据结构为:
/** Keep mostly read-only and often accessed (especially for* the RCU path lookup and ‘stat‘ data) fields at the beginning* of the ‘struct inode‘*/struct inode{umode_t i_mode;unsignedshort i_opflags;kuid_t i_uid;kgid_t i_gid;unsignedint i_flags;#ifdef CONFIG_FS_POSIX_ACLstruct posix_acl *i_acl;struct posix_acl *i_default_acl;#endifconststruct inode_operations *i_op;struct super_block *i_sb;struct address_space *i_mapping;#ifdef CONFIG_SECURITYvoid*i_security;#endif/* Stat data, not accessed from path walking */unsignedlong i_ino;/** Filesystems may only read i_nlink directly. They shall use the* following functions for modification:** (set|clear|inc|drop)_nlink* inode_(inc|dec)_link_count*/union{constunsignedint i_nlink;unsignedint __i_nlink;};dev_t i_rdev;loff_t i_size;struct timespec i_atime;struct timespec i_mtime;struct timespec i_ctime;spinlock_t i_lock;/* i_blocks, i_bytes, maybe i_size */unsignedshort i_bytes;unsignedint i_blkbits;blkcnt_t i_blocks;#ifdef __NEED_I_SIZE_ORDEREDseqcount_t i_size_seqcount;#endif/* Misc */unsignedlong i_state;struct mutex i_mutex;unsignedlong dirtied_when;/* jiffies of first dirtying */unsignedlong dirtied_time_when;struct hlist_node i_hash;struct list_head i_wb_list;/* backing dev IO list */struct list_head i_lru;/* inode LRU list */struct list_head i_sb_list;union{struct hlist_head i_dentry;struct rcu_head i_rcu;};u64 i_version;atomic_t i_count;atomic_t i_dio_count;atomic_t i_writecount;#ifdef CONFIG_IMAatomic_t i_readcount;/* struct files open RO */#endifconststruct file_operations *i_fop;/* former ->i_op->default_file_ops */struct file_lock_context *i_flctx;struct address_space i_data;struct list_head i_devices;union{struct pipe_inode_info *i_pipe;struct block_device *i_bdev;struct cdev *i_cdev;};__u32 i_generation;#ifdef CONFIG_FSNOTIFY__u32 i_fsnotify_mask;/* all events this inode cares about */struct hlist_head i_fsnotify_marks;#endifvoid*i_private;/* fs or device private pointer */};
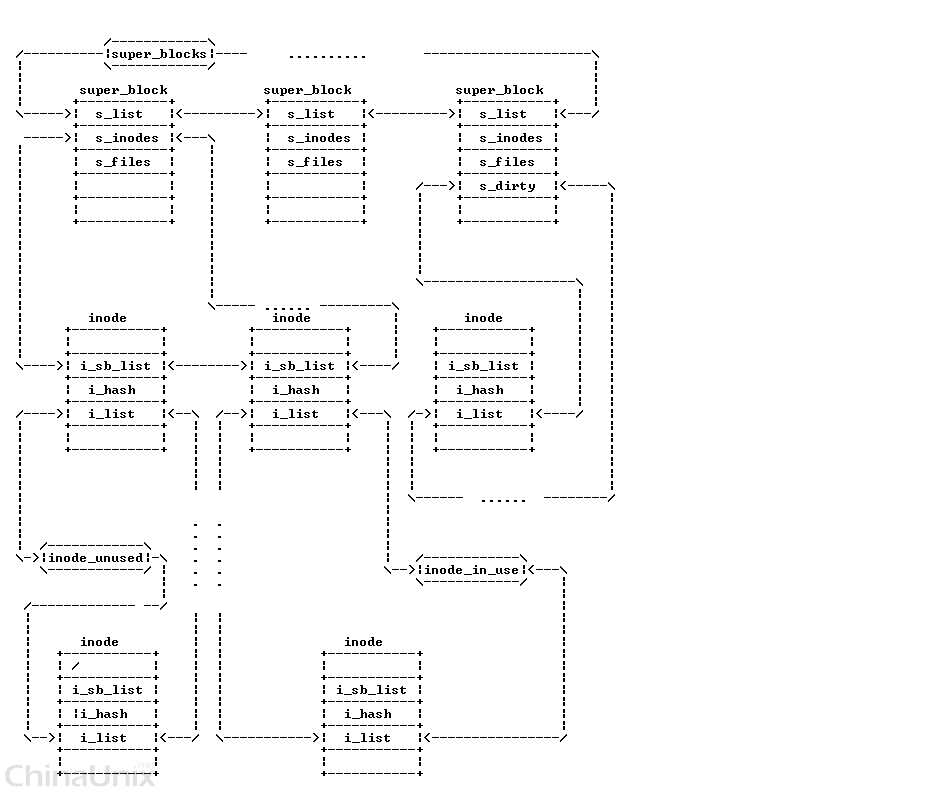
inode存在于两个双向链表中:
一个是inode所在文件系统的super_block的 s_inodes 链表中
一个是根据inode的使用状态存在于以下三个链表中的某个链表中:
一个是inode所在文件系统的super_block的 s_inodes 链表中
一个是根据inode的使用状态存在于以下三个链表中的某个链表中:
- 未用的: inode_unused 链表
- 正在使用的: inode_in_use 链表
- 脏的: super block中的s_dirty 链表
3、dentry
struct dentry{/* RCU lookup touched fields */unsignedint d_flags;/* protected by d_lock */seqcount_t d_seq;/* per dentry seqlock */struct hlist_bl_node d_hash;/* lookup hash list */struct dentry *d_parent;/* parent directory */struct qstr d_name;struct inode *d_inode;/* Where the name belongs to - NULL is* negative */unsignedchar d_iname[DNAME_INLINE_LEN];/* small names *//* Ref lookup also touches following */struct lockref d_lockref;/* per-dentry lock and refcount */conststruct dentry_operations *d_op;struct super_block *d_sb;/* The root of the dentry tree */unsignedlong d_time;/* used by d_revalidate */void*d_fsdata;/* fs-specific data */struct list_head d_lru;/* LRU list */struct list_head d_child;/* child of parent list */struct list_head d_subdirs;/* our children *//** d_alias and d_rcu can share memory*/union{struct hlist_node d_alias;/* inode alias list */struct rcu_head d_rcu;} d_u;};
dentry对象存在于三个双向链表中:
- 所有未用的目录项: dentry_unused 链表
- 正在使用的目录项: 对应inode的 i_dentry 链表
- 表示父子目录结构的链表