AVL树得名于它的发明者 G.M. Adelson-Velsky 和 E.M. Landis,是一种高度平衡的自平衡二叉查找树
它的查找、插入和删除在平均和最坏情况下都是O(log n),这得益于它的性质:
在满足二叉查找树的性质情况下,还满足每个结点的左右子树的高度之差的绝对值(平衡因子)最多为1
具体实现
节点存储
struct AVL{ int key,height,num,size;//size只有在求排名和第k大时才需要,num在有重复加入时才需要,其它AVL中可以不用 AVL *son[2]; AVL(){ memset(this,0,sizeof(AVL)); } AVL(int x){ key=x,size=height=num=1,son[0]=son[1]=0; } }*root;
在插入和删除和操作后,AVL树可能不满足节点平衡因子最多为1的性质,这时就需要对AVL树进行平衡维护
平衡维护的基本操作就是旋转
旋转操作和其他平衡树都一样
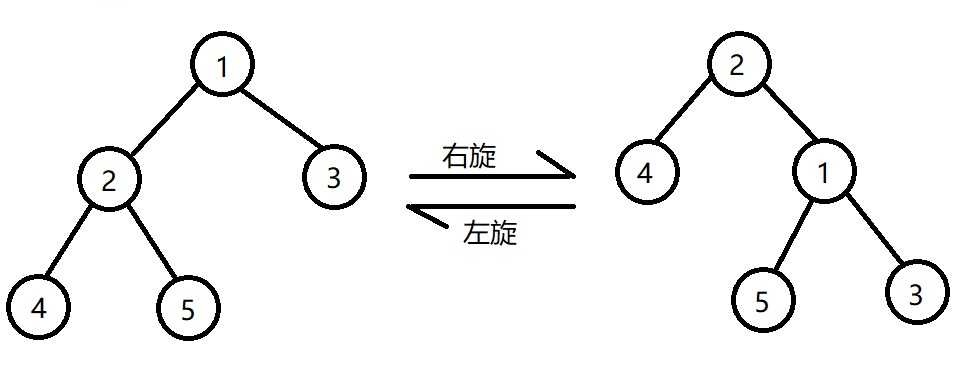
#define getheight(x) (x?x->height:0) #define size(x) (x?x->size:0) void rotate(AVL *&x,int d){ AVL *p=x->son[d^1]; x->son[d^1]=p->son[d],p->son[d]=x;//更新指向关系 x->height=max(getheight(x->son[0]),getheight(x->son[1]))+1,//更新高度和size p->height=max(getheight(p->son[0]),getheight(p->son[1]))+1; p->size=x->size,x->size=x->num+size(x->son[0])+size(x->son[1]); }
平衡维护
AVL在插入或删除操作后,造成的不平衡大致分为两种情况(左右对称算一种,这里以左子树高度大为例):
- 左子树高度-右子树高度>1,并且左子节点的左子树高度>左子节点的右子树高度,如下图:
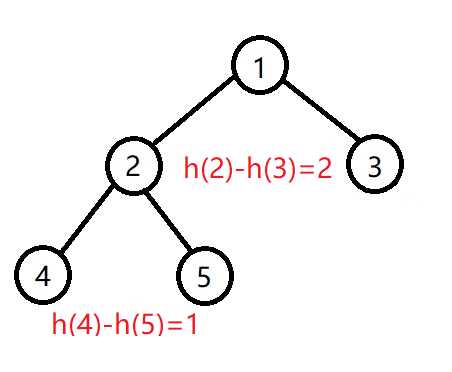
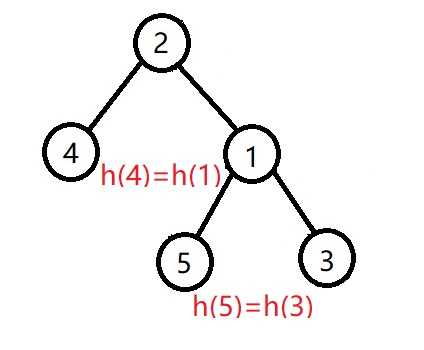
其中3,4,5都是AVL子树,只是子节点被省略这时只用右旋子树1即可
- 左子树高度-右子树高度>1,并且左子节点的右子树高度>左子节点的左子树高度,如下图:
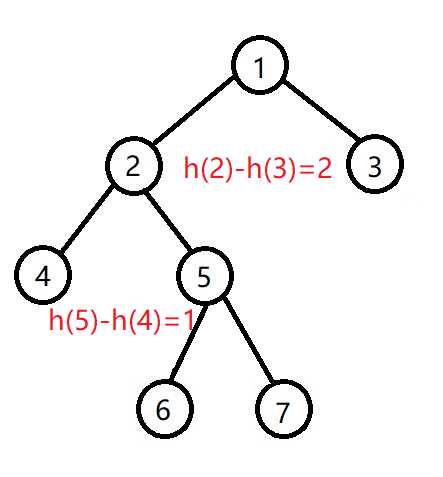
这时要先左旋子树2
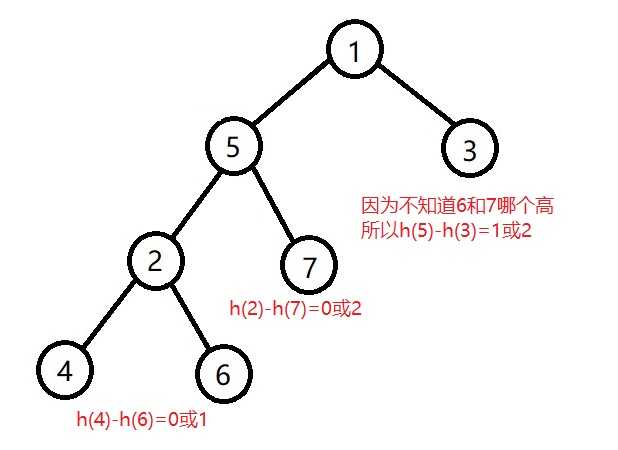
然后再右旋子树1
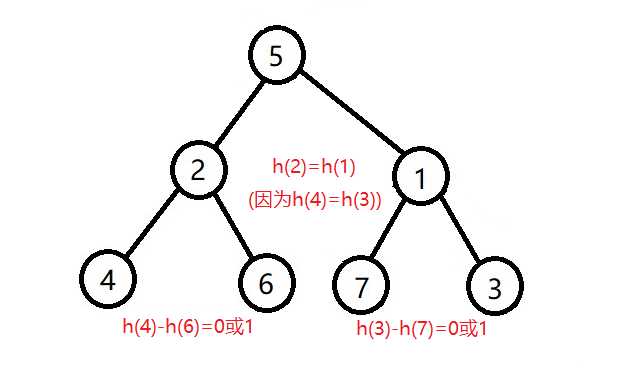
插入和删除(和二叉查找树一样,结束后平衡一下即可)
void insert(AVL *&x,int key){//插入key if(!x){ x=new AVL(key);return; } x->size++; if(key==x->key){x->num++;return;} insert(x->son[key>x->key],key); maintain(x); } void del(AVL *&x,int key){//删除key if(!x)return; if(x->key!=key){ del(x->son[x->key<key],key); x->size=size(x->son[0])+size(x->son[1])+x->num,maintain(x); return; } x->size--; if(x->num>1){x->num--;return;} AVL *p=x; if(x->son[0]==NULL)x=x->son[1],delete p; else if(x->son[1]==NULL)x=x->son[0],delete p; else{//用后继替换当前节点,删除后继 p=x->son[1]; while(p->son[0]){ p=p->son[0]; } x->num=p->num,x->key=p->key,p->num=1,del(x->son[1],p->key); } }
其他操作
int query_id(AVL *x,int key){//求数列中比key小的有几个 if(!x)return 0; if(x->key>key)return query_id(x->son[0],key); if(x->key==key)return size(x->son[0]); return query_id(x->son[1],key)+size(x->son[0])+x->num; } int query_k(AVL *x,int k){//求排第k的数 if(!x)return 0; if(size(x->son[0])>=k)return query_k(x->son[0],k); if(size(x->son[0])+x->num>=k)return x->key; return query_k(x->son[1],k-size(x->son[0])-x->num); } int ans; void pre(AVL *x,int num){//求num的前驱(即小于num的最大的数),并存在ans里 if(!x)return; if(x->key<num)ans=x->key,pre(x->son[1],num); else pre(x->son[0],num); } void suc(AVL *x,int num){//求后继 if(!x)return; if(x->key>num)ans=x->key,suc(x->son[0],num); else suc(x->son[1],num); } void mid_traversal(AVL *x){//中序遍历 if(x->son[0])mid_traversal(x->son[0]); printf("%d ",x->key); if(x->son[1])mid_traversal(x->son[1]); }
例题luoguP3369 【模板】普通平衡树(Treap/SBT)
#include<cstdio> #include<cstring> #include<algorithm> #include<cmath> using namespace std; #define getheight(x) (x?x->height:0) #define size(x) (x?x->size:0) struct AVL{ int key,height,num,size;//size只有在求排名和第k大时才需要,num在有重复加入时才需要,其它AVL中可以不用 AVL *son[2]; AVL(){ memset(this,0,sizeof(AVL)); } AVL(int x){ key=x,size=height=num=1,son[0]=son[1]=0; } }*root; void rotate(AVL *&x,int d){ AVL *p=x->son[d^1]; x->son[d^1]=p->son[d],p->son[d]=x;//更新指向关系 x->height=max(getheight(x->son[0]),getheight(x->son[1]))+1,//更新高度和size p->height=max(getheight(p->son[0]),getheight(p->son[1]))+1; p->size=x->size,x->size=x->num+size(x->son[0])+size(x->son[1]); } void maintain(AVL *&x){//平衡操作 if(abs(getheight(x->son[0])-getheight(x->son[1]))<2)return; int d=getheight(x->son[0])<getheight(x->son[1]); if(getheight(x->son[d]->son[d])>getheight(x->son[d]->son[d^1]))rotate(x,d^1); else rotate(x->son[d],d),rotate(x,d^1); } void insert(AVL *&x,int key){//插入key if(!x){ x=new AVL(key);return; } x->size++; if(key==x->key){x->num++;return;} insert(x->son[key>x->key],key); maintain(x); } void del(AVL *&x,int key){//删除key if(!x)return; if(x->key!=key){ del(x->son[x->key<key],key); x->size=size(x->son[0])+size(x->son[1])+x->num,maintain(x); return; } x->size--; if(x->num>1){x->num--;return;} AVL *p=x; if(x->son[0]==NULL)x=x->son[1],delete p; else if(x->son[1]==NULL)x=x->son[0],delete p; else{//用后继替换当前节点,删除后继 p=x->son[1]; while(p->son[0]){ p=p->son[0]; } x->num=p->num,x->key=p->key,p->num=1,del(x->son[1],p->key); } } int query_id(AVL *x,int key){//求数列中比key小的有几个 if(!x)return 0; if(x->key>key)return query_id(x->son[0],key); if(x->key==key)return size(x->son[0]); return query_id(x->son[1],key)+size(x->son[0])+x->num; } int query_k(AVL *x,int k){//求排第k的数 if(!x)return 0; if(size(x->son[0])>=k)return query_k(x->son[0],k); if(size(x->son[0])+x->num>=k)return x->key; return query_k(x->son[1],k-size(x->son[0])-x->num); } int ans; void pre(AVL *x,int num){//求num的前驱(即小于num的最大的数),并存在ans里 if(!x)return; if(x->key<num)ans=x->key,pre(x->son[1],num); else pre(x->son[0],num); } void suc(AVL *x,int num){//求后继 if(!x)return; if(x->key>num)ans=x->key,suc(x->son[0],num); else suc(x->son[1],num); } void mid_traversal(AVL *x){//中序遍历 if(x->son[0])mid_traversal(x->son[0]); printf("%d ",x->key); if(x->son[1])mid_traversal(x->son[1]); } int main(){ int n,x,y;scanf("%d",&n); while(n--){ scanf("%d%d",&x,&y); switch(x){ case 1: insert(root,y); break; case 2: del(root,y); break; case 3: printf("%d\n",query_id(root,y)+1); break; case 4: printf("%d\n",query_k(root,y)); break; case 5: pre(root,y);printf("%d\n",ans); break; default: suc(root,y);printf("%d\n",ans); } } return 0; }
