标签:number span com tip stopwatch 精确 void bubuko 5*
F1: 迭代法
最慢,复杂度最高
F2: 直接法
F3: 矩阵法
参考《算法之道(The Way of Algorithm)》第38页-魔鬼序列:斐波那契序列

F4: 通项公式法
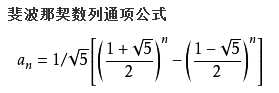
由于公式中包含根号5,无法取得精确的结果,数字越大误差越大
1 using System; 2 using System.Diagnostics; 3 4 5 namespace Fibonacci 6 { 7 class Program 8 { 9 static void Main(string[] args) 10 { 11 ulong result; 12 13 int number = 10; 14 Console.WriteLine("************* number={0} *************", number); 15 16 Stopwatch watch1 = new Stopwatch(); 17 watch1.Start(); 18 result = F1(number); 19 watch1.Stop(); 20 Console.WriteLine("F1({0})=" + result + " 耗时:" + watch1.Elapsed, number); 21 22 Stopwatch watch2 = new Stopwatch(); 23 watch2.Start(); 24 result = F2(number); 25 watch2.Stop(); 26 Console.WriteLine("F2({0})=" + result + " 耗时:" + watch2.Elapsed, number); 27 28 Stopwatch watch3 = new Stopwatch(); 29 watch3.Start(); 30 result = F3(number); 31 watch3.Stop(); 32 Console.WriteLine("F3({0})=" + result + " 耗时:" + watch3.Elapsed, number); 33 34 Stopwatch watch4 = new Stopwatch(); 35 watch4.Start(); 36 double result4 = F4(number); 37 watch4.Stop(); 38 Console.WriteLine("F4({0})=" + result4 + " 耗时:" + watch4.Elapsed, number); 39 40 Console.WriteLine(); 41 42 Console.WriteLine("结束"); 43 Console.ReadKey(); 44 } 45 46 /// <summary> 47 /// 迭代法 48 /// </summary> 49 /// <param name="number"></param> 50 /// <returns></returns> 51 private static ulong F1(int number) 52 { 53 if (number == 1 || number == 2) 54 { 55 return 1; 56 } 57 else 58 { 59 return F1(number - 1) + F1(number - 2); 60 } 61 62 } 63 64 /// <summary> 65 /// 直接法 66 /// </summary> 67 /// <param name="number"></param> 68 /// <returns></returns> 69 private static ulong F2(int number) 70 { 71 ulong a = 1, b = 1; 72 if (number == 1 || number == 2) 73 { 74 return 1; 75 } 76 else 77 { 78 for (int i = 3; i <= number; i++) 79 { 80 ulong c = a + b; 81 b = a; 82 a = c; 83 } 84 return a; 85 } 86 } 87 88 /// <summary> 89 /// 矩阵法 90 /// </summary> 91 /// <param name="n"></param> 92 /// <returns></returns> 93 static ulong F3(int n) 94 { 95 ulong[,] a = new ulong[2, 2] { { 1, 1 }, { 1, 0 } }; 96 ulong[,] b = MatirxPower(a, n); 97 return b[1, 0]; 98 } 99 100 #region F3 101 static ulong[,] MatirxPower(ulong[,] a, int n) 102 { 103 if (n == 1) { return a; } 104 else if (n == 2) { return MatirxMultiplication(a, a); } 105 else if (n % 2 == 0) 106 { 107 ulong[,] temp = MatirxPower(a, n / 2); 108 return MatirxMultiplication(temp, temp); 109 } 110 else 111 { 112 ulong[,] temp = MatirxPower(a, n / 2); 113 return MatirxMultiplication(MatirxMultiplication(temp, temp), a); 114 } 115 } 116 117 static ulong[,] MatirxMultiplication(ulong[,] a, ulong[,] b) 118 { 119 ulong[,] c = new ulong[2, 2]; 120 for (int i = 0; i < 2; i++) 121 { 122 for (int j = 0; j < 2; j++) 123 { 124 for (int k = 0; k < 2; k++) 125 { 126 c[i, j] += a[i, k] * b[k, j]; 127 } 128 } 129 } 130 return c; 131 } 132 #endregion 133 134 /// <summary> 135 /// 通项公式法 136 /// </summary> 137 /// <param name="n"></param> 138 /// <returns></returns> 139 static double F4(int n) 140 { 141 double sqrt5 = Math.Sqrt(5); 142 return (1/sqrt5*(Math.Pow((1+sqrt5)/2,n)-Math.Pow((1-sqrt5)/2,n))); 143 } 144 } 145 }
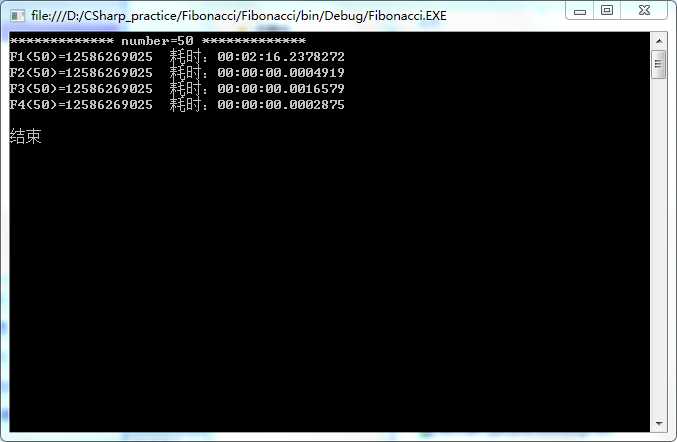
n=50时
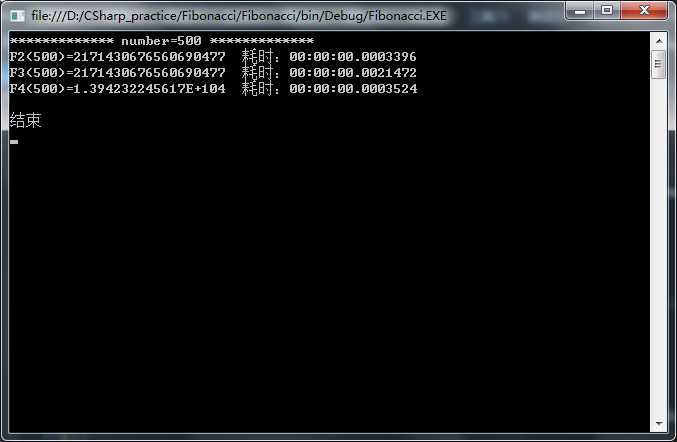
n=500
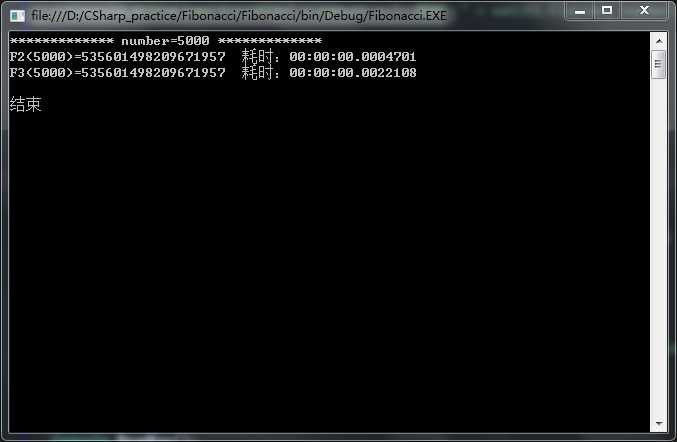
n=5000
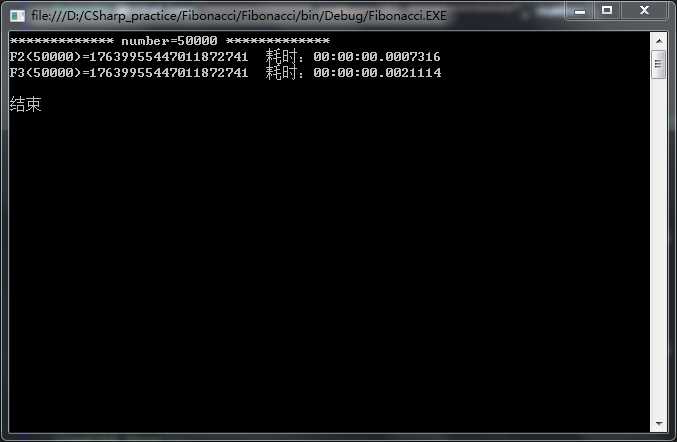
n=50000
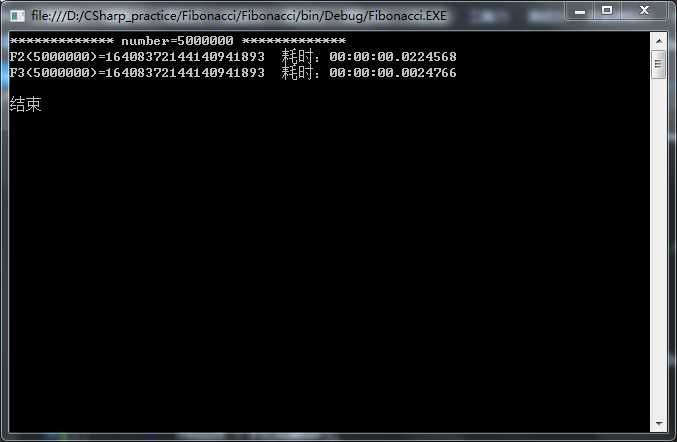
n=5000000
标签:number span com tip stopwatch 精确 void bubuko 5*
原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/zhaoliankun/p/9149555.html