标签:over name -- tag dex new net .net 一起
在讲解深拷贝与浅拷贝讲解之前,需要先弄懂拷贝的分类:引用拷贝和对象拷贝。
注:深拷贝和浅拷贝都是对象拷贝
(1)引用拷贝
创建一个指向对象的引用变量的拷贝。
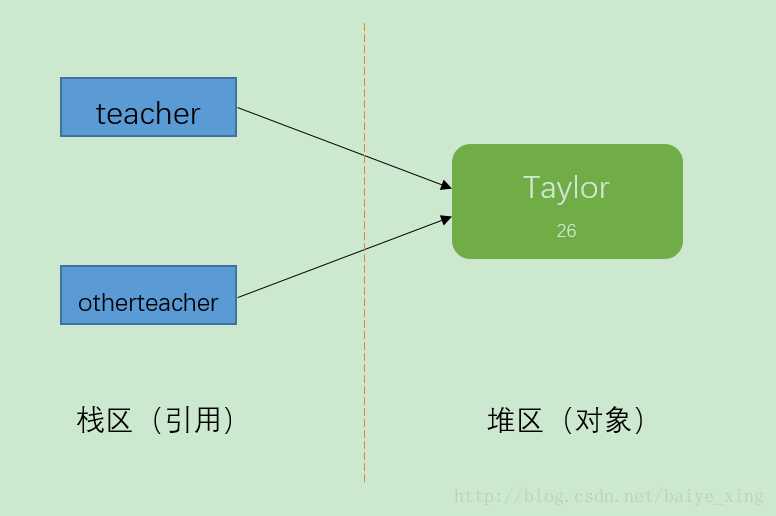
例1:
Teacher teacher = new Teacher("Taylor",26);
Teacher otherteacher = teacher;
System.out.println(teacher);
System.out.println(otherteacher);输出结果:
blog.Teacher@355da254
blog.Teacher@355da254结果分析:由输出结果可以看出,它们的地址值是相同的,那么它们肯定是同一个对象。teacher和otherteacher的只是引用而已,他们都指向了一个相同的对象Teacher(“Taylor”,26)。 这就叫做引用拷贝。
创建对象本身的一个副本。
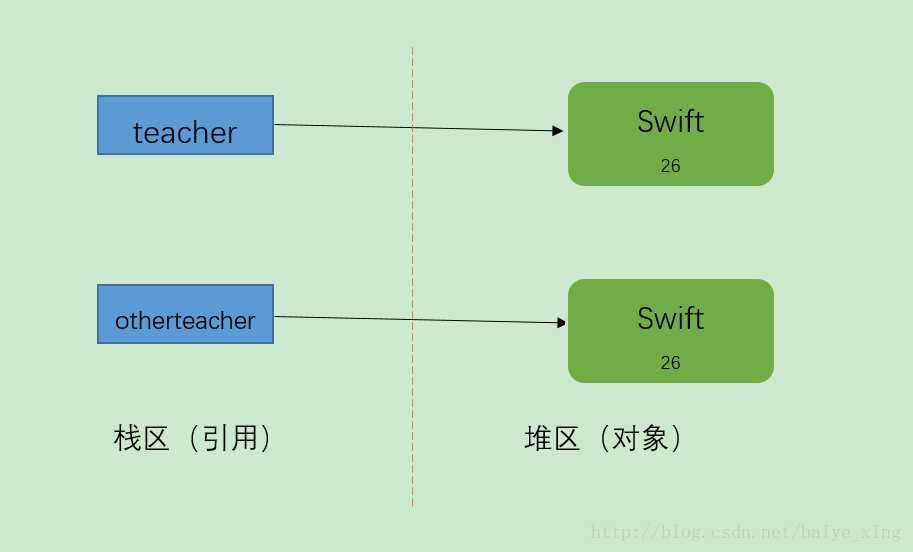
例2:
Teacher teacher = new Teacher("Swift",26);
Teacher otherteacher = (Teacher)teacher.clone();
System.out.println(teacher);
System.out.println(otherteacher);输出结果:
blog.Teacher@355da254
blog.Teacher@4dc63996结果分析:由输出结果可以看出,它们的地址是不同的,也就是说创建了新的对象, 而不是把原对象的地址赋给了一个新的引用变量,这就叫做对象拷贝。
(1)定义:
被复制对象的所有变量都含有与原来的对象相同的值,而所有的对其他对象的引用仍然指向原来的对象。即对象的浅拷贝会对“主”对象进行拷贝,但不会复制主对象里面的对象。”里面的对象“会在原来的对象和它的副本之间共享。
简而言之,浅拷贝仅仅复制所考虑的对象,而不复制它所引用的对象
(2)浅拷贝实例:
例3:
public class ShallowCopy {
public static void main(String[] args) throws CloneNotSupportedException {
Teacher teacher = new Teacher();
teacher.setName("Delacey");
teacher.setAge(29);
Student2 student1 = new Student2();
student1.setName("Dream");
student1.setAge(18);
student1.setTeacher(teacher);
Student2 student2 = (Student2) student1.clone();
System.out.println("拷贝后");
System.out.println(student2.getName());
System.out.println(student2.getAge());
System.out.println(student2.getTeacher().getName());
System.out.println(student2.getTeacher().getAge());
System.out.println("修改老师的信息后-------------");
// 修改老师的信息
teacher.setName("Jam");
System.out.println(student1.getTeacher().getName());
System.out.println(student2.getTeacher().getName());
}
}
class Teacher implements Cloneable
{
private String name;
private int age;
public String getName()
{
return name;
}
public void setName(String name)
{
this.name = name;
}
public int getAge()
{
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age)
{
this.age = age;
}
}
class Student2 implements Cloneable
{
private String name;
private int age;
private Teacher teacher;
public String getName()
{
return name;
}
public void setName(String name)
{
this.name = name;
}
public int getAge()
{
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age)
{
this.age = age;
}
public Teacher getTeacher()
{
return teacher;
}
public void setTeacher(Teacher teacher)
{
this.teacher = teacher;
}
@Override
public Object clone() throws CloneNotSupportedException
{
Object object = super.clone();
return object;
}
}输出结果:
拷贝后
Dream
18
Delacey
29
修改老师的信息后-------------
Jam
Jam结果分析: 两个引用student1和student2指向不同的两个对象,但是两个引用student1和student2中的两个teacher引用指向的是同一个对象,所以说明是浅拷贝。
例3 图解:
(1)定义:
深拷贝是一个整个独立的对象拷贝,深拷贝会拷贝所有的属性,并拷贝属性指向的动态分配的内存。当对象和它所引用的对象一起拷贝时即发生深拷贝。深拷贝相比于浅拷贝速度较慢并且花销较大。
简而言之,深拷贝把要复制的对象所引用的对象都复制了一遍。
(2)实现深拷贝(实例1):
例4:
public class DeepCopy {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception
{
Teacher2 teacher = new Teacher2();
teacher.setName("Delacey");
teacher.setAge(29);
Student3 student1 = new Student3();
student1.setName("Dream");
student1.setAge(18);
student1.setTeacher(teacher);
Student3 student2 = (Student3) student1.clone();
System.out.println("拷贝后");
System.out.println(student2.getName());
System.out.println(student2.getAge());
System.out.println(student2.getTeacher().getName());
System.out.println(student2.getTeacher().getAge());
System.out.println("修改老师的信息后-------------");
// 修改老师的信息
teacher.setName("Jam");
System.out.println(student1.getTeacher().getName());
System.out.println(student2.getTeacher().getName());
}
}
class Teacher2 implements Cloneable {
private String name;
private int age;
public String getName()
{
return name;
}
public void setName(String name)
{
this.name = name;
}
public int getAge()
{
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age)
{
this.age = age;
}
@Override
public Object clone() throws CloneNotSupportedException
{
return super.clone();
}
}
class Student3 implements Cloneable {
private String name;
private int age;
private Teacher2 teacher;
public String getName()
{
return name;
}
public void setName(String name)
{
this.name = name;
}
public int getAge()
{
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age)
{
this.age = age;
}
public Teacher2 getTeacher()
{
return teacher;
}
public void setTeacher(Teacher2 teacher)
{
this.teacher = teacher;
}
@Override
public Object clone() throws CloneNotSupportedException
{
// 浅复制时:
// Object object = super.clone();
// return object;
// 改为深复制:
Student3 student = (Student3) super.clone();
// 本来是浅复制,现在将Teacher对象复制一份并重新set进来
student.setTeacher((Teacher2) student.getTeacher().clone());
return student;
}
}输出结果:
拷贝后
Dream
18
Delacey
29
修改老师的信息后-------------
Jam
Delacey结果分析:
两个引用student1和student2指向不同的两个对象,两个引用student1和student2中的两个teacher引用指向的是两个对象,但对teacher对象的修改只能影响student1对象,所以说是深拷贝。
例4 图解1(teacher姓名Delacey更改前):
例4 图解2(teacher姓名Jam更改后):
标签:over name -- tag dex new net .net 一起
原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/hobby0524/p/9460808.html