标签:title line fine 语音 选择 root 回声 style amp
1.新建GUI界面

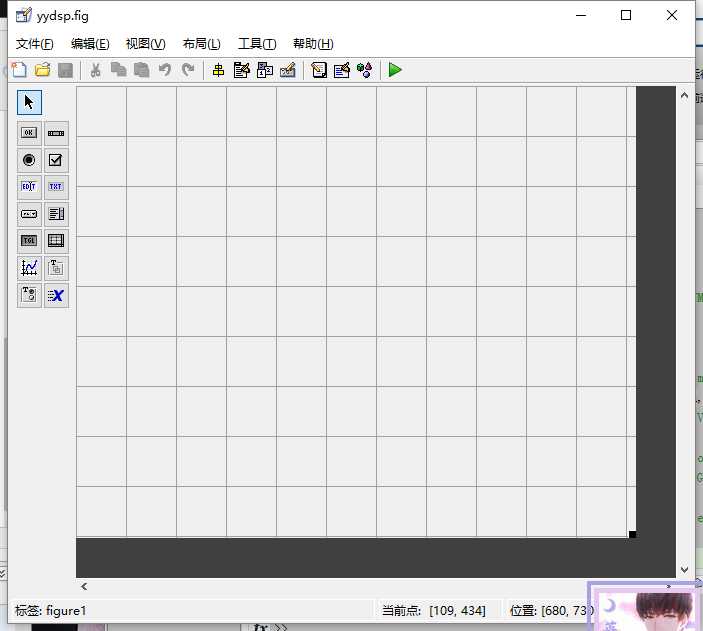

未填写前的代码:
function varargout = yydsp(varargin)
% YYDSP MATLAB code for yydsp.fig
% YYDSP, by itself, creates a new YYDSP or raises the existing
% singleton*.
%
% H = YYDSP returns the handle to a new YYDSP or the handle to
% the existing singleton*.
%
% YYDSP(‘CALLBACK‘,hObject,eventData,handles,...) calls the local
% function named CALLBACK in YYDSP.M with the given input arguments.
%
% YYDSP(‘Property‘,‘Value‘,...) creates a new YYDSP or raises the
% existing singleton*. Starting from the left, property value pairs are
% applied to the GUI before yydsp_OpeningFcn gets called. An
% unrecognized property name or invalid value makes property application
% stop. All inputs are passed to yydsp_OpeningFcn via varargin.
%
% *See GUI Options on GUIDE‘s Tools menu. Choose "GUI allows only one
% instance to run (singleton)".
%
% See also: GUIDE, GUIDATA, GUIHANDLES
% Edit the above text to modify the response to help yydsp
% Last Modified by GUIDE v2.5 27-Oct-2018 13:35:56
% Begin initialization code - DO NOT EDIT
gui_Singleton = 1;
gui_State = struct(‘gui_Name‘, mfilename, ...
‘gui_Singleton‘, gui_Singleton, ...
‘gui_OpeningFcn‘, @yydsp_OpeningFcn, ...
‘gui_OutputFcn‘, @yydsp_OutputFcn, ...
‘gui_LayoutFcn‘, [] , ...
‘gui_Callback‘, []);
if nargin && ischar(varargin{1})
gui_State.gui_Callback = str2func(varargin{1});
end
if nargout
[varargout{1:nargout}] = gui_mainfcn(gui_State, varargin{:});
else
gui_mainfcn(gui_State, varargin{:});
end
% End initialization code - DO NOT EDIT
% --- Executes just before yydsp is made visible.
function yydsp_OpeningFcn(hObject, eventdata, handles, varargin)
% This function has no output args, see OutputFcn.
% hObject handle to figure
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles structure with handles and user data (see GUIDATA)
% varargin command line arguments to yydsp (see VARARGIN)
% Choose default command line output for yydsp
handles.output = hObject;
% Update handles structure
guidata(hObject, handles);
% UIWAIT makes yydsp wait for user response (see UIRESUME)
% uiwait(handles.figure1);
% --- Outputs from this function are returned to the command line.
function varargout = yydsp_OutputFcn(hObject, eventdata, handles)
% varargout cell array for returning output args (see VARARGOUT);
% hObject handle to figure
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles structure with handles and user data (see GUIDATA)
% Get default command line output from handles structure
varargout{1} = handles.output;
% --- Executes on button press in pushbutton1.
function pushbutton1_Callback(hObject, eventdata, handles)
% hObject handle to pushbutton1 (see GCBO)
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles structure with handles and user data (see GUIDATA)
% --- Executes on button press in pushbutton2.
function pushbutton2_Callback(hObject, eventdata, handles)
% hObject handle to pushbutton2 (see GCBO)
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles structure with handles and user data (see GUIDATA)
% --- Executes on button press in pushbutton3.
function pushbutton3_Callback(hObject, eventdata, handles)
% hObject handle to pushbutton3 (see GCBO)
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles structure with handles and user data (see GUIDATA)
% --- Executes on button press in pushbutton4.
function pushbutton4_Callback(hObject, eventdata, handles)
% hObject handle to pushbutton4 (see GCBO)
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles structure with handles and user data (see GUIDATA)
% --- Executes on button press in pushbutton5.
function pushbutton5_Callback(hObject, eventdata, handles)
% hObject handle to pushbutton5 (see GCBO)
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles structure with handles and user data (see GUIDATA)
% --- Executes on button press in pushbutton6.
function pushbutton6_Callback(hObject, eventdata, handles)
% hObject handle to pushbutton6 (see GCBO)
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles structure with handles and user data (see GUIDATA)
% --- Executes on button press in pushbutton7.
function pushbutton7_Callback(hObject, eventdata, handles)
% hObject handle to pushbutton7 (see GCBO)
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles structure with handles and user data (see GUIDATA)
% --- Executes on button press in pushbutton8.
function pushbutton8_Callback(hObject, eventdata, handles)
% hObject handle to pushbutton8 (see GCBO)
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles structure with handles and user data (see GUIDATA)
% --- Executes on button press in pushbutton9.
function pushbutton9_Callback(hObject, eventdata, handles)
% hObject handle to pushbutton9 (see GCBO)
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles structure with handles and user data (see GUIDATA)
% --- Executes on button press in pushbutton10.
function pushbutton10_Callback(hObject, eventdata, handles)
% hObject handle to pushbutton10 (see GCBO)
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles structure with handles and user data (see GUIDATA)
% --- Executes on button press in pushbutton11.
function pushbutton11_Callback(hObject, eventdata, handles)
% hObject handle to pushbutton11 (see GCBO)
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles structure with handles and user data (see GUIDATA)
% --- Executes on button press in pushbutton12.
function pushbutton12_Callback(hObject, eventdata, handles)
% hObject handle to pushbutton12 (see GCBO)
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles structure with handles and user data (see GUIDATA)
% --- Executes on button press in pushbutton13.
function pushbutton13_Callback(hObject, eventdata, handles)
% hObject handle to pushbutton13 (see GCBO)
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles structure with handles and user data (see GUIDATA)
% --- Executes on button press in pushbutton14.
function pushbutton14_Callback(hObject, eventdata, handles)
% hObject handle to pushbutton14 (see GCBO)
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles structure with handles and user data (see GUIDATA)
填写后的代码
1)打开文件部分
[filename,pathname]=uigetfile({‘*.*‘,‘ALL FILES‘},‘选择声音‘);%显示模态对话框,
%列出当前文件夹中的文件,如果文件有效,点击打开时会返回文件名,如果点击取消,返回0
if isequal([filename pathname],[0,0])
return;
end
str=[pathname filename];%合成路径+文件名
[temp,Fs]=audioread(str);%读取音频声音
temp=temp(:,1); %取一行提取矩阵
temp1=resample(temp,80,441);%信号降采样处理
handles.y=temp1;%降采样的句柄
handles.y1=temp;%y1为原声
handles.Fs=Fs;%采样频率
guidata(hObject,handles);%存储或检索 UI 数据
程序中,resample为信号降采样处理,理解如下:
B=resample(x,90,250); %
采样从250Hz降到90Hz,如果250在前,就是插值从90到250,可以看B的长度,250Hz采样4000个数据等于90hz采样1440个数据,这就是降采样。
2)播放原声,画时频图
fs=handles.Fs;
Y=handles.y1;
Y=Y(:,1);%取单声道
t1=1:length(Y);
t=t1/fs;
sound(Y,fs); %播放原声
F = fft(Y);%快速傅里叶变换
freq = linspace(-fs/2,fs/2,length(Y)+1);
freq(end) = [];
plot(handles.axes1,t,Y)
xlabel(handles.axes1,‘时间‘);
ylabel(handles.axes1,‘幅度‘);
title(handles.axes1,‘原声音的波形‘);
y1=fft(Y);
plot(handles.axes4,abs(y1));
xlabel(handles.axes4,‘圆频率‘);
ylabel(handles.axes4,‘幅度‘);
title(handles.axes4,‘未改变坐标轴的频率特性‘);
plot(handles.axes2,freq,abs(fftshift(F)));
title(handles.axes2,‘原声音的真实频响‘);
xlabel(handles.axes2,‘圆频率‘);
ylabel(handles.axes2,‘幅度‘);
title(handles.axes2,‘频率特性‘);
3)男声变女声
FL = 80 ; % 帧移
WL = 240 ; % 窗长
P = 10 ; %预测系数个数
s = handles.y;
fs = handles.Fs;
% 定义常数
s = s/max(s); % 归一化
L = length(s); % 读入语音长度
FN = floor(L/FL)-2; % 计算帧长,floor;向负无穷方向
% 预测和重建滤波器
exc = zeros(L,1); % 激励信号,double类零矩阵L行1列
zi_pre = zeros(P,1); % 预测滤波器状态
s_rec = zeros(L,1); % 重建语音
zi_rec = zeros(P,1);
% 变调滤波器
exc_syn_t = zeros(L,1); % 合成的激励信号,创建一个L行1列的0脉冲
s_syn_t = zeros(L,1); % 合成语音
last_syn_t = 0; % 存储上一个段的最后一个脉冲的下标
zi_syn_t = zeros(P,1); % 合成滤波器
hw = hamming(WL); %汉明窗
%滤波器
% 依次处理每帧语音
for n = 3:FN %从第三个子数组开始
% 计算预测系数
s_w = s(n*FL-WL+1:n*FL).*hw; %汉明窗加权
[A,E]=lpc(s_w,P); %线性预测计算预测系数
% A是预测系数,E会被用来计算合成激励的能量
s_f=s((n-1)*FL+1:n*FL); % 本帧语音
%利用filter函数重建语音
[exc1,zi_pre] = filter(A,1,s_f,zi_pre);
exc((n-1)*FL+1:n*FL) = exc1; %计算激励
%利用filter函数重建语音
[s_rec1,zi_rec] = filter(1,A,exc1,zi_rec);
s_rec((n-1)*FL+1:n*FL) = s_rec1; %重建语音
% 下面只有得到exc后才可以
s_Pitch = exc(n*FL-222:n*FL);
PT(n) = findpitch(s_Pitch); %计算基音周期pt
G = sqrt(E*PT(n)); %计算合成激励的能量G
PT1 =floor(PT(n)/2); %减小基音周期
poles = roots(A);
deltaOMG =100*2*pi/fs;
for p=1:10 %增加共振峰
if imag(poles(p))>0
poles(p) = poles(p)*exp(1j*deltaOMG);
elseif imag(poles(p))<0
poles(p) = poles(p)*exp(-1j*deltaOMG);
end
end
A1=poly(poles);
tempn_syn_t=(1:n*FL-last_syn_t);
exc_syn1_t = zeros(length(tempn_syn_t),1);
exc_syn1_t(mod(tempn_syn_t,PT1)==0) = G;
exc_syn1_t = exc_syn1_t((n-1)*FL-last_syn_t+1:n*FL-last_syn_t);
[s_syn1_t,zi_syn_t] = filter(1,A1,exc_syn1_t,zi_syn_t);
exc_syn_t((n-1)*FL+1:n*FL) = exc_syn1_t; %合成激励
s_syn_t((n-1)*FL+1:n*FL) = s_syn1_t; %合成语音
last_syn_t = last_syn_t+PT1*floor((n*FL-last_syn_t)/PT1);
end
Y = s_syn_t;
F = fft(Y);
freq = linspace(-fs/2,fs/2,length(Y)+1);
freq(end) = [];
plot(handles.axes4,freq,abs(fftshift(F)));
xlabel(handles.axes4,‘圆频率‘);
ylabel(handles.axes4,‘幅度‘);
title(handles.axes4,‘频率特性‘);
handles.y=s_syn_t;
guidata(hObject,handles);
plot(handles.axes3,s_syn_t);
t1=1:length(s_syn_t);
t=t1/8000;
plot(handles.axes3,t,s_syn_t);
title(handles.axes3,‘时域图‘);
xlabel(handles.axes3,‘时间‘);
ylabel(handles.axes3,‘幅度‘);
sound(handles.y,8000);
4)退出
delete(handles.figure1);
5)快放
fs=handles.Fs;
Y=handles.y1;
Y=Y(:,1);
F = fft(Y);
freq = linspace(-fs/2,fs/2,length(Y)+1);
freq(end) = [];
sound(Y,2*fs);
t1=1:length(Y);
t=t1/(2*fs);
plot(handles.axes3,t,Y)
title(handles.axes3,‘时域图‘);
xlabel(handles.axes3,‘时间‘);
ylabel(handles.axes3,‘幅度‘);
plot(handles.axes4,freq,abs(fftshift(F)));
xlabel(handles.axes4,‘圆频率‘);
ylabel(handles.axes4,‘幅度‘);
title(handles.axes4,‘频率特性‘);
6)慢放
fs=handles.Fs;
Y=handles.y1;
Y=Y(:,1);
sound(Y,0.5*fs);
F = fft(Y);
freq = linspace(-fs/2,fs/2,length(Y)+1);
freq(end) = [];%
t1=1:length(Y);
t=t1/(0.5*fs);
plot(handles.axes3,t,Y)
title(handles.axes3,‘时域图‘);
xlabel(handles.axes3,‘时间‘);
ylabel(handles.axes3,‘幅度‘);
plot(handles.axes4,freq,abs(fftshift(F)));
xlabel(handles.axes4,‘圆频率‘);
ylabel(handles.axes4,‘幅度‘);
title(handles.axes4,‘频率特性‘);
7)制造回音
fs=handles.Fs;
N=length(handles.y1);
x1=handles.y1(1:N);
x2=handles.y1(1:N);
x1=[x1,zeros(1,5000)];
x2=[zeros(1,4000),0.4*x2,zeros(1,1000)];
z=x1+x2;
F = fft(z);
freq = linspace(-fs/2,fs/2,length(z)+1);
freq(end) = [];
t1=1:length(z);
t=t1/fs;
plot(handles.axes3,t,z)
title(handles.axes3,‘含回音波形‘);
xlabel(handles.axes3,‘时间‘);
ylabel(handles.axes3,‘幅度‘);
plot(handles.axes4,freq,abs(fftshift(F)));
xlabel(handles.axes4,‘圆频率‘);
ylabel(handles.axes4,‘幅度‘);
title(handles.axes4,‘频率特性‘);
sound(z,fs);
8)回音还原
fs=handles.Fs;
N=length(handles.y1);
x1=handles.y1(1:N);
x2=handles.y1(1:N);
x3=handles.y1(1:N);
x1=[x1,zeros(1,5000)];
x2=[zeros(1,4000),0.4*x2,zeros(1,1000)];
z=x1+x2;
b=1;
a=zeros(1,N);
a(1)=1;
a(4001)=0.4;
z2=filter(b,a,z);
F = fft(z2);
freq = linspace(-fs/2,fs/2,length(z2)+1);
freq(end) = [];
t1=1:length(z2);
t=t1/fs;
plot(handles.axes3,t,z2)
title(handles.axes3,‘滤除回声的波形‘);
xlabel(handles.axes3,‘时间‘);
ylabel(handles.axes3,‘幅度‘);
plot(handles.axes4,freq,abs(fftshift(F)));
xlabel(handles.axes4,‘圆频率‘);
ylabel(handles.axes4,‘幅度‘);
title(handles.axes4,‘频率特性‘);
sound(z2,fs);
9)制造噪声
fs=handles.Fs;
x=handles.y1;
y=x(:,1); %取一行提取矩阵
noise=0.2*sin(pi*20000*(1:length(y))/fs)+0.3*sin(pi*21000*(1:length(y))/fs)...
+0.4*sin(pi*22000*(1:length(y))/fs);%噪声 10000rad/s+10500+11000
VNnoise=y+noise‘;%向量维度一致
F = fft(VNnoise);
freq = linspace(-fs/2,fs/2,length(VNnoise)+1);
freq(end) = [];
t1=1:length(VNnoise);
t=t1/fs;
plot(handles.axes3,t,VNnoise)
xlabel(handles.axes3,‘时间‘);
ylabel(handles.axes3,‘幅度‘);
title(handles.axes3,‘添加噪声的波形‘);
plot(handles.axes4,freq,abs(fftshift(F)));
xlabel(handles.axes4,‘圆频率‘);
ylabel(handles.axes4,‘幅度‘);
title(handles.axes4,‘频率特性‘);
sound(VNnoise,fs);
10)滤除噪声
fs=handles.Fs;
x=handles.y1;
y=x(:,1); %取一行提取矩阵
noise=0.2*sin(pi*20000*(1:length(y))/fs)+0.3*sin(pi*21000*(1:length(y))/fs)...
+0.4*sin(pi*22000*(1:length(y))/fs);%噪声 10000rad/s+10500+11000
VNnoise=y+noise‘;%向量维度一致
%[b,a] = butter(8,5000*2/fs,‘LOW‘) ; %巴特沃斯滤波器
%result=filter(b,a,VNnoise);
Hd = ditong1;%Fdatool滤波
result=filter(Hd,x);
result=result(:,1);
sound(result,fs);
F = fft(result);
freq = linspace(-fs/2,fs/2,length(result)+1);
freq(end) = [];
t1=1:length(result);
t=t1/fs;
plot(handles.axes3,t,result)
xlabel(handles.axes3,‘时间‘);
ylabel(handles.axes3,‘幅度‘);
title(handles.axes3,‘添加噪声的波形‘);
plot(handles.axes4,freq,abs(fftshift(F)));
xlabel(handles.axes4,‘圆频率‘);
ylabel(handles.axes4,‘幅度‘);
title(handles.axes4,‘频率特性‘);
11)左右声道合唱
fs=handles.Fs;
sound(original,fs);
a1=1;
a2=-1;
b1=1;
b2=-1;
Soundleft=original(:,1);%左声道
Soundright=original(:,2);%右声道
newleft=Soundleft+Soundright; %新的左声道为原来的全部声道
newright=b1*Soundleft+b2*Soundright; %新的右声道为原来的左声道-原来的右
Sound(:,1)=newleft;
Sound(:,2)=newright;
bp=fir1(300,[500,2000]/(fs/2));
cutdown=filter(bp,1,Sound);
Sound_final=Sound-0.6*abs(cutdown);
sound(Sound_final,fs)
F = fft(Sound_final);
freq = linspace(-fs/2,fs/2,length(Sound_final)+1);
freq(end) = [];
t1=1:length(Sound_final);
t=t1/fs;
plot(handles.axes3,t,Sound_final)
xlabel(handles.axes3,‘时间‘);
ylabel(handles.axes3,‘幅度‘);
title(handles.axes3,‘时域波形‘);
plot(handles.axes4,freq,abs(fftshift(F)));
xlabel(handles.axes4,‘圆频率‘);
ylabel(handles.axes4,‘幅度‘);
title(handles.axes4,‘频率特性‘);
12)反放
fs=handles.Fs;
y=handles.y1;
M=length(y):-1:1;
rever=y(M);
sound(rever,fs);%反播
F = fft(rever);
freq = linspace(-fs/2,fs/2,length(rever)+1);
freq(end) = [];
t1=1:length(rever);
t=t1/fs;
plot(handles.axes3,t,rever)
xlabel(handles.axes3,‘时间‘);
ylabel(handles.axes3,‘幅度‘);
title(handles.axes3,‘反播的波形‘);
plot(handles.axes4,freq,abs(fftshift(F)));
xlabel(handles.axes4,‘圆频率‘);
ylabel(handles.axes4,‘幅度‘);
title(handles.axes4,‘频率特性‘);
标签:title line fine 语音 选择 root 回声 style amp
原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/Sonny-xby/p/9860999.html