标签:intval cal png image param 手动 span 接口 构造方法
1.TestInherits.java
public class TestInherits
{
public static void main(String args[])
{
Child c = new Child();
}
}
输出结果: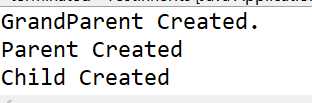
修改代码:

输出结果: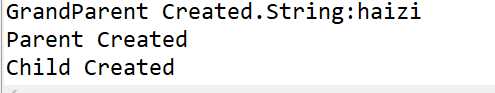
结论:通过 super 调用基类构造方法,必须是子类构造方法中的第一个语句。
2. 为什么子类的构造方法在运行之前,必须调用父类的构造方法?能不能反过来?为什么不能反过来?
构造方法用于对基类的初始化。当构造一个对象时,先调用构造函数对成员函数和成员变量进行初始化,。子类继承了父类的成员函数和成员变量,若不进行调用,则不会对父类的初始化。
3.ExplorationJDKSource.java
public class ExplorationJDKSource {
/**
* @param args
*/
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println(new A());
}
}
class A{}
在编译源码时,当遇到没有父类的类时,编译器会定义的默认的父类(一般为Object),public void println(Object x),这一方法内部调用了String类的valueOf方法。valueOf方法内部又调用Object.toString方法:
public String toString() {
return getClass().getName() +"@" +
Integer.toHexString(hashCode());
}
4.
public class Fruit
{
public String toString()
{
return "Fruit toString.";
}
public static void main(String args[])
{
Fruit f=new Fruit();
System.out.println("f="+f);
// System.out.println("f="+f.toString());
}
}
输出结果: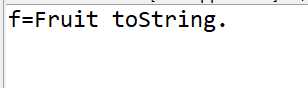
结论:在“+”运算中,当任何一个对象与一个String对象,连接时,会隐式地调用其toString()方法,默认情况下,此方法返回“类名 @ + hashCode”。为了返回有意义的信息,子类可以重写toString()方法。
5. 方法覆盖
public class parents {
public void parents(){
System.out.println("parent!");
}
public void parent1(){
System.out.println("parent1!");
}
}
public class child extends parents {
public void child(){
super.parents();
}
public void parents(){
System.out.println("child");
}
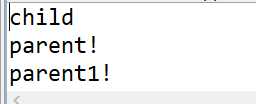
public static void main(String[]args){
child ch=new child();
ch.parents();
ch.child();
ch.parent1();
}
}
输出结果:
6. TestInstanceof.Java
public class TestInstanceof
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
//声明hello时使用Object类,则hello的编译类型是Object,Object是所有类的父类
//但hello变量的实际类型是String
Object hello = "Hello";
//String是Object类的子类,所以返回true。
System.out.println("字符串是否是Object类的实例:" + (hello instanceof Object));
//返回true。
System.out.println("字符串是否是String类的实例:" + (hello instanceof String));
//返回false。
System.out.println("字符串是否是Math类的实例:" + (hello instanceof Math));
//String实现了Comparable接口,所以返回true。
System.out.println("字符串是否是Comparable接口的实例:" + (hello instanceof Comparable));
String a = "Hello";
//String类既不是Math类,也不是Math类的父类,所以下面代码编译无法通过
//System.out.println("字符串是否是Math类的实例:" + (a instanceof Math));
}
}
输出结果:
7. 类型转换
class Mammal{}
class Dog extends Mammal {}
class Cat extends Mammal{}
public class TestCast
{
public static void main(String args[])
{
Mammal m;
Dog d=new Dog();
Cat c=new Cat();
m=d;
//d=m;
d=(Dog)m;
//d=c;
//c=(Cat)m;
}
}
结果:d=m; d=c;有错误,c=(Cat)m正确
结论:在继承中,子类可以自动转换成父类,但父类转换成子类只有引用类型真正身份才会转换成功,否则会失败。
8.
public class ParentChildTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Parent parent=new Parent();
parent.printValue();
Child child=new Child();
child.printValue();
parent=child;
parent.printValue();
parent.myValue++;
parent.printValue();
((Child)parent).myValue++;
parent.printValue();
}
}

结论:由此可得Java的一些语法特性(多态):
当子类与父类拥有一样的方法,并且让一个父类变量引用一个子类对象时,到底调用哪个方法,由对象自己的“真实”类型所决定,这就是说:对象是子类型的,它就调用子类型的方法,是父类型的,它就调用父类型的方法。
如果子类与父类有相同的字段,则子类中的字段会代替或隐藏父类的字段,子类方法中访问的是子类中的字段(而不是父类中的字段)。如果子类方法确实想访问父类中被隐藏的同名字段,可以用super关键字来访问它。 如果子类被当作父类使用,则通过子类访问的字段是父类的。
因此,我们进行程序设计时应避免子类与父类同名的字段!
9.
public class TestPolymorphism
{
public static void main(String args[])
{
Parent p=new Parent();
p.Introduce();
System.out.println(p.value);
p=new Son();
p.Introduce();
System.out.println(p.value);
p=new Daughter();
p.Introduce();
System.out.println(p.value);
}
多态代码:当多个类实现同一接口(或派生自同一抽象类)时,针对这些类所创建的对象调用接口所定义的方法时,会分别调用相应的类的具体实现代码。
标签:intval cal png image param 手动 span 接口 构造方法
原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/NCLONG/p/9903877.html