标签:style signed cin search sans linu vmalloc while put
第一次笔试,CVTE,岗位C/C++后台开发实习生,未通过。
笔试有22道题目,其中前20道是单选选择和多选混合,基本五五开的样子,设计的知识点从语言基础,到网络知识还有Linux相关。具体能记住的有字节对齐、TCP/IP协议、用户权限(umask),还有一些特别涉及底层实现(vmalloc和fmalloc功能)。
后2道题目是编程题
题目一:给定一个字符串,里面含有数字字符,请找出这个字符串中最大的数字(不可使用C/C++自带的字符转数字函数)。
示例 str[] = "adasfdsg12dgdrfg789",返回789
我的代码
#include<iostream>
#include<memory.h>
using namespace std;
int func(char str[])
{
if(str==NULL)
return -1;
int max = -1, flag = 0;
for(int i=0; str[i]!=‘\0‘; ++i)//遍历str
{
int tmp = 0;
while(str[i]>=‘0‘ && str[i]<=‘9‘)//发现0~9,提取值保存到tmp
{
flag = 1;
tmp = tmp*10 + (str[i]-‘0‘);
++i;
}
if(tmp>max)//找到较大的数
max = tmp;
}
if(flag)
return max;
return -1;
}
int main()
{
char str[50];
memset(str, ‘\0‘, 50);
while(1)
{
cout<<"please input string include number(0~50):";
cin>>str;
cout<<func(str)<<endl;
memset(str, ‘\0‘, 50);
}
return 0;
}
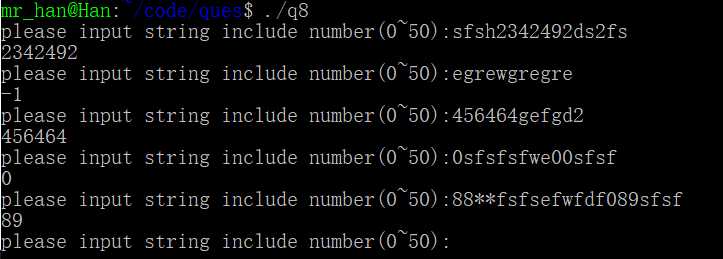
运行结果
题目二:有一个字符串类保存着电脑从开机到现在的毫秒数,有的用户只想看天数,有的用户想看到秒数,有的用户想看到毫秒数。请实现一个函数,它根据用户提供字符来回答当前的时间
函数原型 string func(uint_64 MESL, string str);
例如 func(90061001, "DHMSE"),返回 1天1时1分1秒1毫秒
func(90061001, "D"),返回 1天
func(90061001, "DHM"),返回 1天1时1分
我的代码
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
#include<memory.h>
using namespace std;
typedef unsigned long uint_64;
string fun(uint_64 MS, string str)
{
if(str.size() < 1)
return string("-1");
char ti[50];
memset(ti, ‘\0‘, 50);
int tim[5] = {0};
tim[0] = MS/(24*3600*1000);
tim[1] = (MS-tim[0]*24*3600*1000)/(3600*1000);
tim[2] = (MS-tim[0]*24*3600*1000-tim[1]*3600*1000)/(60*1000);
tim[3] = (MS-tim[0]*24*3600*1000-tim[1]*3600*1000-tim[2]*60*1000)/1000;
tim[4] = MS-tim[0]*24*3600*1000-tim[1]*3600*1000-tim[2]*60*1000-tim[3]*1000;
for(int i=0; str[i]!=‘\0‘; ++i)
{
char tmp[10];
memset(tmp, ‘\0‘, 10);
switch(str[i])
{
case ‘D‘:
cout<<tim[0]<<"天";
//strcat(ti, itoa(tim[0]));
sprintf(tmp, "%d", tim[0]);
strcat(ti, tmp);
strcat(ti, "天");
break;
case ‘H‘:
cout<<tim[1]<<"时";
//strcat(ti, itoa(tim[1]));
sprintf(tmp, "%d", tim[1]);
strcat(ti, tmp);
strcat(ti, "时");
break;
case ‘M‘:
cout<<tim[2]<<"分";
//strcat(ti, itoa(tim[2]));
sprintf(tmp, "%d", tim[2]);
strcat(ti, tmp);
strcat(ti, "分");
break;
case ‘S‘:
cout<<tim[3]<<"秒";
//strcat(ti, itoa(tim[3]));
sprintf(tmp, "%d", tim[3]);
strcat(ti, tmp);
strcat(ti, "秒");
break;
case ‘E‘:
cout<<tim[4]<<"毫秒";
//strcat(ti, itoa(tim[4]));
sprintf(tmp, "%d", tim[4]);
strcat(ti, tmp);
strcat(ti, "毫秒");
break;
default:
break;
}
}
cout<<endl;
return string(ti);
}
int main()
{
uint_64 tim = 0;
char str[5];
while(1)
{
memset(str, ‘\0‘, 5);
cout<<"please input milliscond:";
cin>>tim;
cout<<"please input search tpye:";
cin>>str;
cout<<fun(tim,string(str))<<endl;
tim = 0;
}
return 0;
}
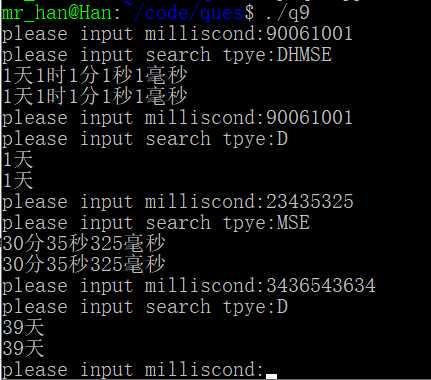
运行结果
标签:style signed cin search sans linu vmalloc while put
原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/area-h-p/p/12059162.html