标签:图形 透明 依赖关系 type mmap ace pac 里氏替换原则 程序实现
在我们的称后续的编写过程中,我们会面临着来自耦合。内聚性以及可维护性,可扩展性,重用性,灵活性等多方面的挑战,设计模式为了让程序具有更好的:
不要问为什么设计模式要这么去设计,这个只是设计模式的一个开发规范,你不遵守也没关系,但是我们应该去遵守这个规范,方便你我他。
简单的理解就是:一个类只负责一项职责,就像笔者一样,一生只够爱一人,虽然目前还是单身。
简单的理解就是:一个类对另一个类的依赖应该建立在最小的接口上。比如说,我是安徽的,安徽是中国的一个省,是依赖于中国的,我是依赖于安徽的,但是这个时候,虽然可以说,我是依赖于中国的,但是,我们不能这么说,因为安徽是我们的依赖关系中最小的那个依赖接口,所以说,我们依赖于安徽(大致是这个意思),看个图:
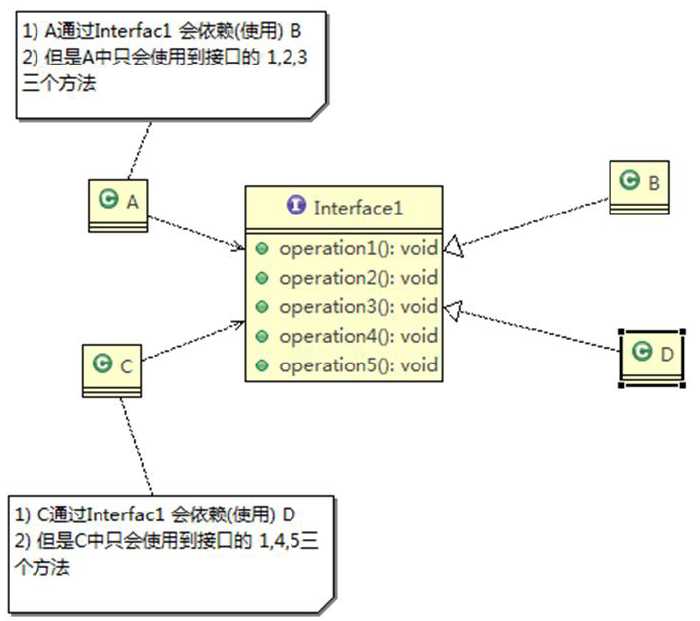
A会通过接口依赖类B,C会通过接口依赖D,如果接口对于A,C来说不是最小接口的,那么B和D就要去实现他们不需要的方法;
按照隔离原则,A,C分别于他们需要的接口建立依赖关系,也就是采用依赖隔离。
存在的问题以及改进思路
1) 类A通过接口依赖于类B,类C通过接口依赖于D,如果接口对于AC不是最小的接口,那么BD就必须要去实现他们不需要的方法;
2) 将接口拆分为独立的几个接口,AC分别于他们需要的接口建立依赖关系,也就是采用依赖隔离。
3) 效果图如下
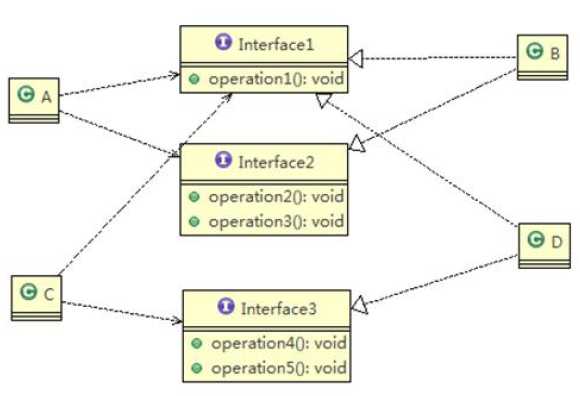
依赖倒转原则是指:
看个实例:
package com.ci123.dependence;
/**
* Copyright (c) 2018-2028 Corp-ci All Rights Reserved
* <p> 依赖倒转(倒置)原则
* Project: design-pattern
* Package: com.ci123.dependence
* Version: 1.0
* <p>
* Created by SunYang on 2019/11/7 10:14
*/
public class DependenceInversionPrinciple {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Person person = new Person();
person.receive(new EmailIR());
person.receive(new WeiXinIR());
}
}
class Email {
public String getInfo() {
return "电子邮件信息:Hello,World";
}
}
/**
* 完成Person接收消息的功能
* 方式1 分析:
* 1. 简单,比较容易想到的
* 2. 如果我们获取的对象是 微信,短信等,则新增类,同时Person也要增加相应的接收方法
* 3. 解决思路: 引入一个抽象的接口 IReceiver ,表示接收者 , 这样Person类与接口IReceiver发生依赖
* 因为Email,WeiXin等属于接收的范围,他们各自实现IReceiver接口就OK,这样我们就符合依赖倒转原则
*/
class Person {
public void receive(IRceiver iRceiver) {
System.out.println(iRceiver.getInfo());
}
}
interface IRceiver {
String getInfo();
}
class EmailIR implements IRceiver {
@Override
public String getInfo() {
return "电子邮件信息(IReceiver):Hello,World";
}
}
class WeiXinIR implements IRceiver {
@Override
public String getInfo() {
return "微信信息(IReceiver):Hello,World";
}
}依赖关系的三种传递
这里我们看个例子:
package com.ci123.base.liskov;
/**
* Copyright (c) 2018-2028 Corp-ci All Rights Reserved
* <p>
* Project: design-pattern
* Package: com.ci123.base.liskov
* Version: 1.0
* <p> 这里可以看到,我们的B重写了A的func1(int num1,int num2)方法,无意中将减法改成了加法,但是我们的整个继承体系
* 是已经被破坏了的,会导致继承体系的复用性会比较差,特别是运行多态比较繁琐的时候
* <p>
* 改进:
* 通用的做法是:原来的父类和子类都继承一个更通俗的基类,原有的继承关系去掉,采用依赖,聚合,组合等关系替代。
* 即:
* base <- A
* base <- B
* B <<- A
* <p>
* Created by SunYang on 2019/11/7 10:55
*/
public class Liskov {
public static void main(String[] args) {
A a = new A();
System.out.println("5-3=" + a.func1(5, 3));
B b = new B();
System.out.println("5-3=" + b.func1(5, 3)); // 这里原本是要输出 5-3 的
System.out.println("/************************************************/");
AA aa = new AA();
System.out.println("5-3=" + aa.func1(5, 3));
BB bb = new BB();
System.out.println("5-3=" + bb.func(5, 3)); // 这里原本是要输出 5-3 的
}
}
class Base {
// 这里放很基础的方法和成员
}
/********************************************************************************************/
class A {
// 返回两个数的差
public int func1(int num1, int num2) {
return num1 - num2;
}
}
// B 继承A
// 增加一个新的功能,完成两个数相加
class B extends A {
// 这里重写 A类方法
@Override
public int func1(int num1, int num2) {
// 这里是无意识的重写,是我们不需要的重写,我们本意是要求 减法的
return num1 + num2;
}
public int func2(int num1, int num2) {
return func1(num1, num2) * 8;
}
}
/********************************************************************************************/
class AA {
public int func1(int num1, int num2) {
return num1 - num2;
}
}
class BB extends Base {
// 这里重写 A类方法
public int func1(int num1, int num2) {
// 这里是无意识的重写,是我们不需要的重写,我们本意是要求 减法的
return num1 + num2;
}
public int func2(int num1, int num2) {
return func1(num1, num2) * 8;
}
private AA aa = new AA();
// 这里想要用AA方法
public int func(int num1 , int num2){
return this.aa.func1(num1 , num2) ;
}
}package com.ci123.base.ocp;
/**
* Copyright (c) 2018-2028 Corp-ci All Rights Reserved
* <p>
* Project: design-pattern
* Package: com.ci123.base.ocp
* Version: 1.0
* <p> 1. 优点比较好理解,简单易操作
* 2. 缺点是违反了设计模式的OCP原则,即对扩展开放(提供方),对修改关闭(使用方)。即当我们给类增加新功能的时候,尽量不要修改代码,或者尽量少修改代码
* 3. 如果我们要增加一个新的图形种类,我们要做的修改还是挺多的
* Created by SunYang on 2019/11/7 11:20
*/
public class OCPDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 使用看看存在的问题
GraphicEditor graphicEditor = new GraphicEditor();
graphicEditor.drawShape(new Rectangle());
graphicEditor.drawShape(new Circle());
graphicEditor.drawShape(new Triangle());
}
}
// 使用方,绘图
class GraphicEditor{
public void drawShape(Shape shape){
switch (shape.m_type){
case 1:
drawRectangle(shape);
break;
case 2:
drawCircle(shape);
break;
case 3:
drawTriangle(shape);
break;
default:
break;
}
}
private void drawRectangle(Shape shape){
System.out.println("矩形");
}
private void drawCircle(Shape shape){
System.out.println("圆");
}
private void drawTriangle(Shape shape){
System.out.println("三角形");
}
}
// 基类
class Shape{
int m_type ;
}
class Rectangle extends Shape{
Rectangle(){
super.m_type = 1 ;
}
}
class Circle extends Shape{
Circle(){
super.m_type = 2 ;
}
}
// 新增三角形
class Triangle extends Shape{
Triangle(){
super.m_type = 3 ;
}
}在看看修改后的:
public class OCPDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 使用看看存在的问题
GraphicEditor graphicEditor = new GraphicEditor();
graphicEditor.drawShape(new Rectangle());
graphicEditor.drawShape(new Circle());
graphicEditor.drawShape(new Triangle());
graphicEditor.drawShape(new Other());
}
}
// 使用方,绘图
class GraphicEditor {
public void drawShape(Shape shape) {
shape.draw();
}
}
// 基类
abstract class Shape {
int m_type;
abstract void draw();
}
class Rectangle extends Shape {
Rectangle() {
super.m_type = 1;
}
@Override
void draw() {
System.out.println("矩形");
}
}
class Circle extends Shape {
Circle() {
super.m_type = 2;
}
@Override
void draw() {
System.out.println("圆");
}
}
// 新增三角形
class Triangle extends Shape {
Triangle() {
super.m_type = 3;
}
@Override
void draw() {
System.out.println("三角形");
}
}
class Other extends Shape {
Other() {
super.m_type = 4;
}
@Override
void draw() {
System.out.println("其他的");
}
}package com.ci123.base.dp;
import com.sun.org.apache.bcel.internal.generic.NEW;
import com.sun.org.apache.xpath.internal.SourceTree;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.EnumMap;
import java.util.List;
/**
* Copyright (c) 2018-2028 Corp-ci All Rights Reserved
* <p> 迪米特法则
* Project: design-pattern
* Package: com.ci123.base.dp
* Version: 1.0
* <p>
* Created by SunYang on 2019/11/7 11:50
*/
// 有一个学校,下属有各个学院和总部,现要求打印出学校总部员工ID和学院员工ID
public class DemeterDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 先创建一个 SchoolManager 对象
SchoolManager schoolManager = new SchoolManager();
// 输出学院的员工 ID 和 学校总部的员工信息
schoolManager.printAllEmployee(new CollegeManager());
}
}
// 学校总部的员工类
class Employee{
private String id ;
public void setId(String id){
this.id = id ;
}
public String getId(){
return id ;
}
}
// 学院员工类
class CollegeEmployee{
private String id ;
public String getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(String id) {
this.id = id;
}
}
// 管理学院员工的管理类
class CollegeManager{
// 返回学院的所有员工
public List<CollegeEmployee> geAllEmployee(){
List<CollegeEmployee> list = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
CollegeEmployee employee = new CollegeEmployee();
employee.setId("学院员工ID=" + i);
list.add(employee) ;
}
return list ;
}
}
// 分析SchoolManager类的直接朋友有哪些,Employee,CollegeManager
// CollegeEmployee 不是直接朋友关系,而是一个陌生类,这样违背了 迪米特法则
class SchoolManager{
// 返回学校的总员工
public List<Employee> getAllEmployees(){
List<Employee> list = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < 20; i++) {
Employee employee = new Employee();
employee.setId("学校ID=" + i);
list.add(employee) ;
}
return list ;
}
// 该方法完成输出学校总部和学院员工信息 ID
void printAllEmployee(CollegeManager manager){
// 分析问题
// 1. 这里的 CollegeEmployee 不是SchoolManager 的直接朋友
// 2. CollegeEmployee 是以局部变量方式出现在SchoolManager
// 3. 违反了 迪米特 法则
// 获取到学院员工
List<CollegeEmployee> list = manager.geAllEmployee();
System.out.println("========== 学院员工 ============");
for (CollegeEmployee employee : list) {
System.out.println(employee.getId());
}
// 获取到学校员工
List<Employee> allEmployee = this.getAllEmployees();
System.out.println("========== 学校员工 ============");
for (Employee employee : allEmployee) {
System.out.println(employee.getId());
}
}
}改进如下:
// 管理学院员工的管理类
class CollegeManager{
// 返回学院的所有员工
public List<CollegeEmployee> geAllEmployee(){
List<CollegeEmployee> list = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
CollegeEmployee employee = new CollegeEmployee();
employee.setId("学院员工ID=" + i);
list.add(employee) ;
}
return list ;
}
public void printEmployee(){
// 获取到学院员工
List<CollegeEmployee> list = this.geAllEmployee();
System.out.println("========== 学院员工 ============");
for (CollegeEmployee employee : list) {
System.out.println(employee.getId());
}
}
}
class SchoolManager{
// 返回学校的总员工
public List<Employee> getAllEmployees(){
List<Employee> list = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < 20; i++) {
Employee employee = new Employee();
employee.setId("学校ID=" + i);
list.add(employee) ;
}
return list ;
}
// 该方法完成输出学校总部和学院员工信息 ID
void printAllEmployee(CollegeManager manager){
// 封装到 CollegeManager 里面
manager.printEmployee();
// 获取到学校员工
List<Employee> allEmployee = this.getAllEmployees();
System.out.println("========== 学校员工 ============");
for (Employee employee : allEmployee) {
System.out.println(employee.getId());
}
}
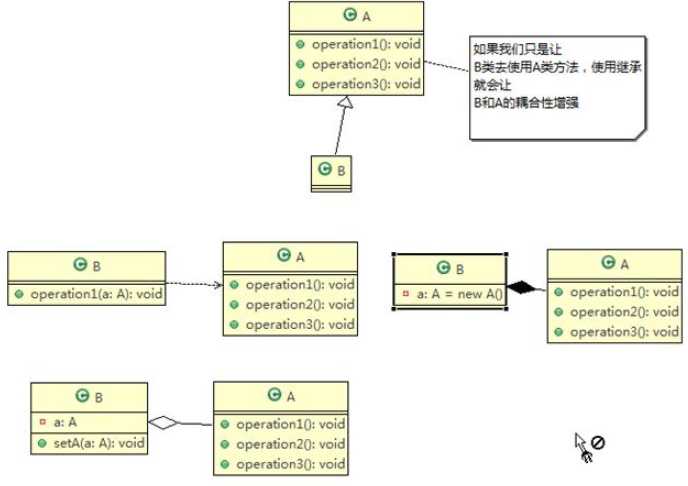
}注意点
一句话:尽量使用合成 / 聚合的方式 , 而不是使用继承
标签:图形 透明 依赖关系 type mmap ace pac 里氏替换原则 程序实现
原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/sun-iot/p/12198051.html