标签:code cin 波特率 variable 相关 echo some monit util
1、前言
Uboot启动后,会进入到一个倒计时,在倒计时结束之前,如果此时我们按下键盘的回车键,将进入到uboot的命令行模式,有点类似Linux系统终端模式,如果没有按下回车键的话,将直接启动Linux内核,本篇文章将介绍uboot中的一些常用命令,熟悉这些命令后,以后在适配调试uboot的时候会得心应手。
如下所示,倒计时的时候按下回车键后,进入到uboot的命令行模式:
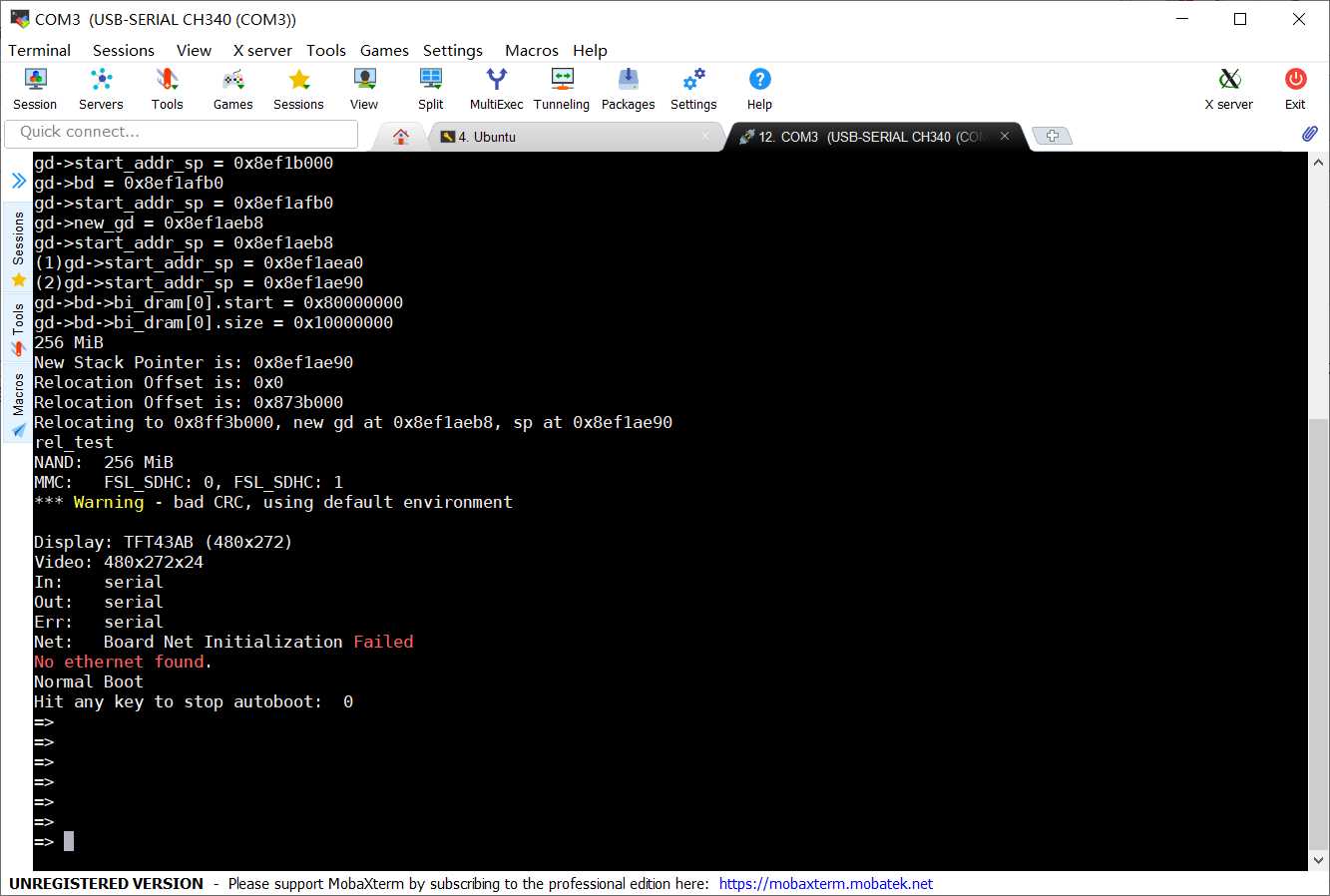
在行的前面多了"=>"字符串,说明此时已经进入uboot的命令行模式了,接下来就可以进行一些命令输入。
2、查看uboot支持的命令
在使用uboot命令之前,我们先来看看当前的uboot版本所支持的命令有哪些,可以在当前的命令函数输入:
=> help
or
=> ?
该命令用于查看当前uboot版本所支持的所有命令,输入后按回车即可,在我当前使用的uboot版本中所支持的命令如下:
? - alias for ‘help‘ base - print or set address offset bdinfo - print Board Info structure bmode - sd1|sd2|qspi1|normal|usb|sata|ecspi1:0|ecspi1:1|ecspi1:2|ecspi1:3|esdhc1|esdhc2|esdhc3|esdhc4 [noreset] bmp - manipulate BMP image data boot - boot default, i.e., run ‘bootcmd‘ bootd - boot default, i.e., run ‘bootcmd‘ bootelf - Boot from an ELF image in memory bootm - boot application image from memory bootp - boot image via network using BOOTP/TFTP protocol bootvx - Boot vxWorks from an ELF image bootz - boot Linux zImage image from memory clocks - display clocks clrlogo - fill the boot logo area with black cmp - memory compare coninfo - print console devices and information cp - memory copy crc32 - checksum calculation dcache - enable or disable data cache dhcp - boot image via network using DHCP/TFTP protocol dm - Driver model low level access echo - echo args to console editenv - edit environment variable env - environment handling commands erase - erase FLASH memory exit - exit script ext2load- load binary file from a Ext2 filesystem ext2ls - list files in a directory (default /) ext4load- load binary file from a Ext4 filesystem ext4ls - list files in a directory (default /) ext4size- determine a file‘s size ext4write- create a file in the root directory false - do nothing, unsuccessfully fatinfo - print information about filesystem fatload - load binary file from a dos filesystem fatls - list files in a directory (default /) fatsize - determine a file‘s size fdt - flattened device tree utility commands flinfo - print FLASH memory information fstype - Look up a filesystem type fuse - Fuse sub-system go - start application at address ‘addr‘ gpio - query and control gpio pins help - print command description/usage i2c - I2C sub-system icache - enable or disable instruction cache iminfo - print header information for application image imxtract- extract a part of a multi-image itest - return true/false on integer compare load - load binary file from a filesystem loadb - load binary file over serial line (kermit mode) loads - load S-Record file over serial line loadx - load binary file over serial line (xmodem mode) loady - load binary file over serial line (ymodem mode) loop - infinite loop on address range ls - list files in a directory (default /) md - memory display mm - memory modify (auto-incrementing address) mmc - MMC sub system mmcinfo - display MMC info mw - memory write (fill) nand - NAND sub-system nboot - boot from NAND device nfs - boot image via network using NFS protocol nm - memory modify (constant address) ping - send ICMP ECHO_REQUEST to network host pmic - PMIC printenv- print environment variables protect - enable or disable FLASH write protection reset - Perform RESET of the CPU run - run commands in an environment variable save - save file to a filesystem saveenv - save environment variables to persistent storage setenv - set environment variables setexpr - set environment variable as the result of eval expression showvar - print local hushshell variables size - determine a file‘s size sleep - delay execution for some time source - run script from memory test - minimal test like /bin/sh tftpboot- boot image via network using TFTP protocol true - do nothing, successfully usb - USB sub-system usbboot - boot from USB device version - print monitor, compiler and linker version
对于上面的命令列表中的命令,并不是所有都能运行的,如果该命令并没有在板级文件中使能配置的话,哪么直接在命令行中输入后按回车键,将会直接提示运行不了,也就是说上面列出的命令,并没有全部都使能了。
上面列出的命令,后面都描述了命令的功能,例如,最后一个version命令,它的功能就是用来输出uboot编译和链接的相关版本信息,除此之外,如果我们想查看某个命令的详细用法的话,可以输入:
=> help command_name
or
=> ? command_name
例如,我们查看bootz命令的用法,输入如下,然后回车:
=> help bootz
or
=> ? bootz
回车后,输出如下:
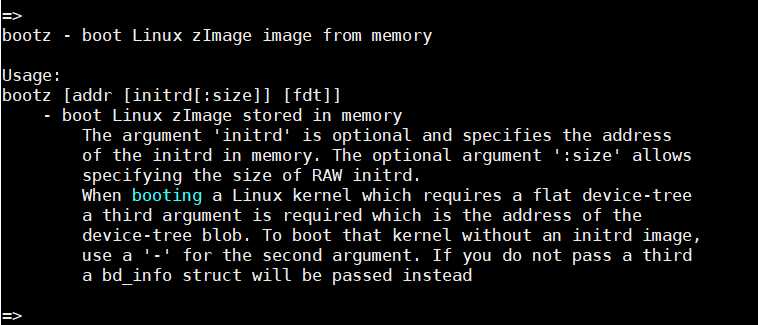
从输出的结果可以看到,bootz命令的用法被详细的列出来了,该命令就是用来在内存中启动Linux内核的,对于其它命令的详细用法,我们也可以使用这个方式进行命令的详细使用方式进行查询,接下来,我们了解一些常用的uboot命令用法。
3、信息查询相关命令
在uboot的命令中,常用的信息查询命令主要有3个,分别是bdinfo、printenv和version命令。
首先是bdinfo命令,该命令用来查询当前板子的相关信息,在命令行模式下,直接输入bdinfo,然后回车即可,输出如下:
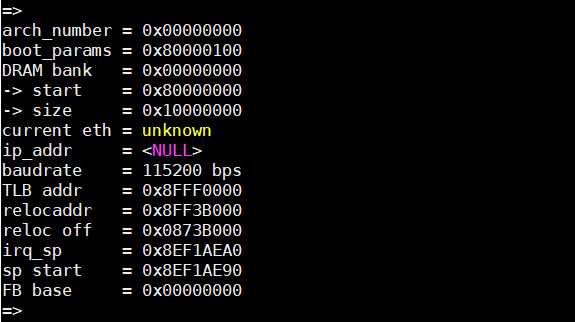
如上所示,通过该命令可以查看板子的DRAM的大小以及DRAM的起始地址、当前使用的网络接口以及IP地址、波特率和uboot偏移地址以及偏移量等相关信息。
接下来是printenv命令,该命令用于查询当前板子的一些相关环境变量,同样,在命令行模式下输入printenv并回车,输出如下:
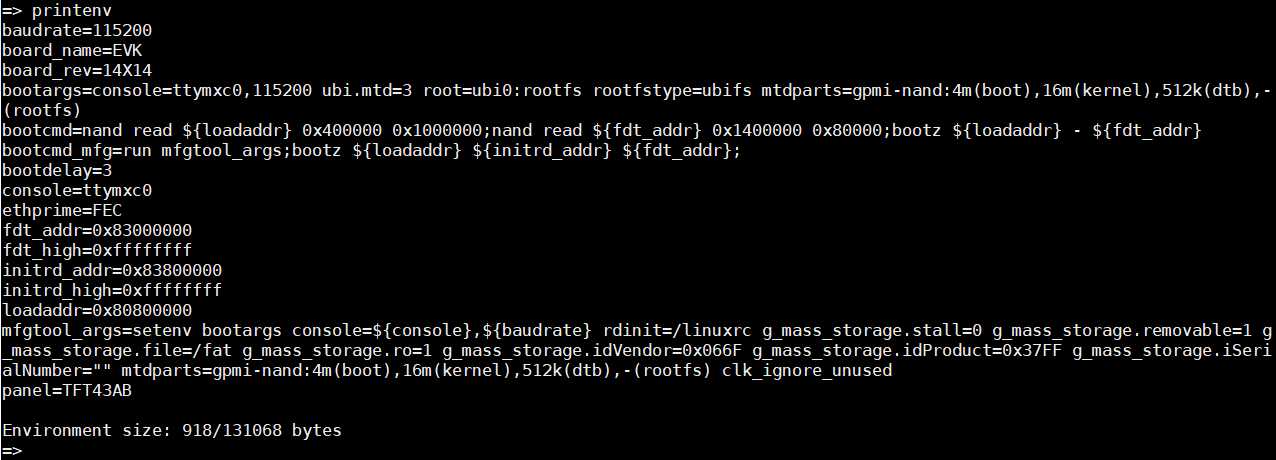
从上图可以看到,命令输入后,将会输出一堆的环境变量,例如:当前串口的波特率baudrate、启动参数bootargs以及启动命令bootcmd等,这些环境变量都是字符串,能对其进行修改。
最后则是version命令,该命令用于查询uboot版本和交叉编译工具的相关信息,在命令模式下输入version后并回车,输出如下:
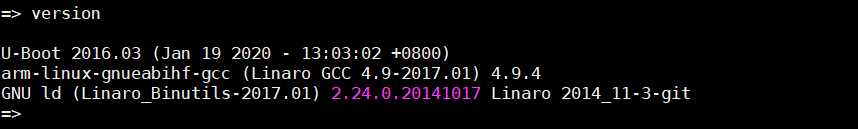
从输出的信息可以看到,当前的uboot版本号为2016.03,后面接的是编译时间,交叉编译工具链为arm-linux-gnueabihf-gcc,版本号为4.9.4。
4、环境变量相关命令
5、内存操作相关命令
标签:code cin 波特率 variable 相关 echo some monit util
原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/Cqlismy/p/12214305.html