标签:cto 留空 调整 prot style war lse 维护 细节
vector是动态空间,随着元素的加入,它的内部机制会自行扩充空间以容纳新元素。
vector类中主要有三根指针start, finish和end_of_storage
1 template <typename T> 2 class vector 3 { 4 public: 5 typedef T value_type; 6 typedef value_type* iterator; 7 ... 8 protected: 9 iterator start; 10 iterator finish; 11 iterator end_of_storage; 12 ... 13 };
其中start是指向当前使用空间的起始位置
finish是指向当前使用空间末尾元素的下一个位置
end_of_storage是指向当前分配的可使用空间的最后一个位置的下一个位置
vector维护的是一个连续空间,所以不论其元素的类型是什么,普通指针都可以作为vector的迭代器,可以满足vector迭代器所需要的所有操作行为,vector支持随机存取,而普通指针正有着这样的能力,所以vector的迭代器是一个Random Access Iterator
当vector的预留空间无法满足时,vector就会扩张空间,将重新分配两倍的当前空间大小,将现有空间的所有对象移动到新的空间里,在释放掉原空间,如下图
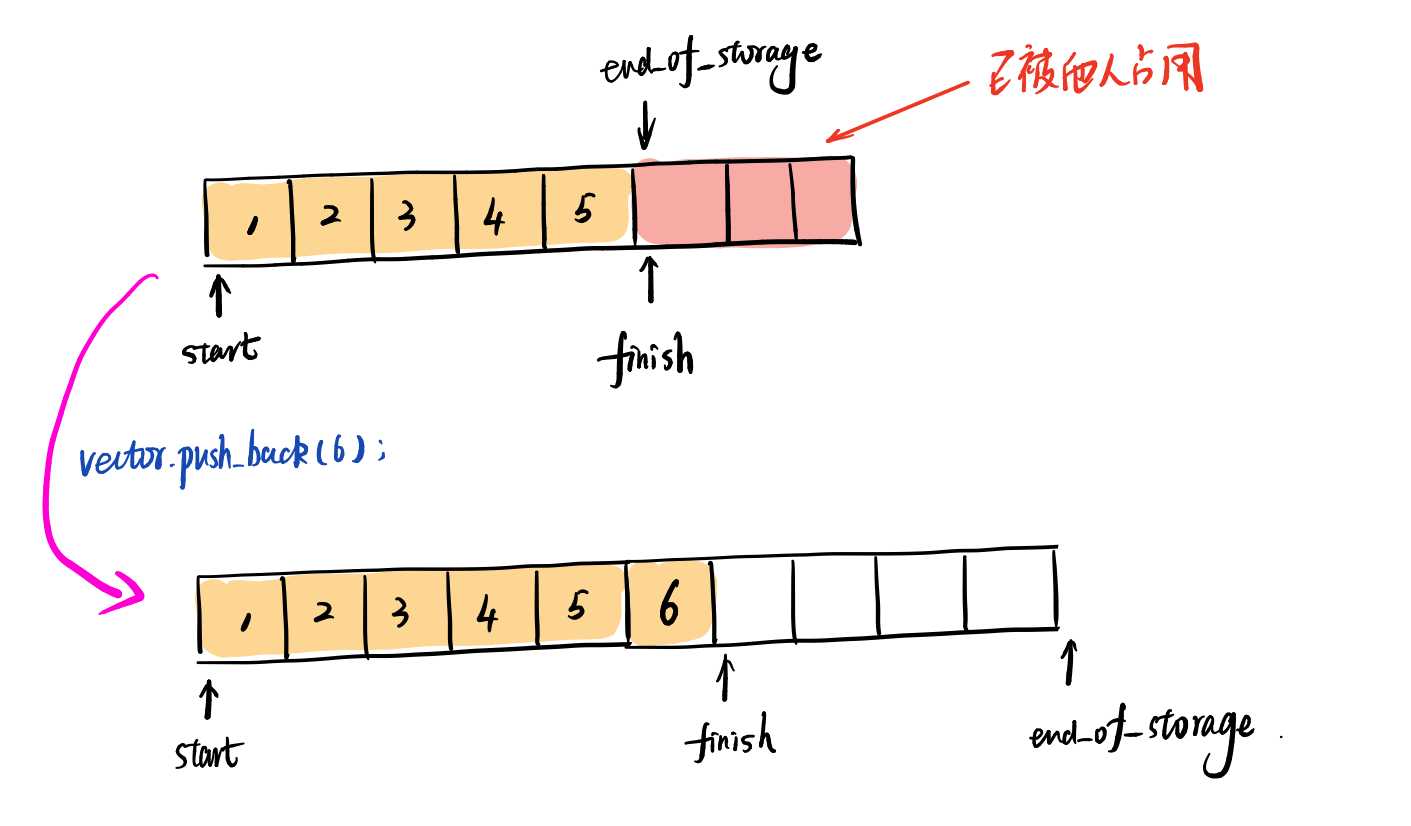
下面是vector的成员函数push_back的实现
1 void push_back(const T& x) { 2 //拥有预留空间 3 if (finish != end_of_storage) { 4 std::allocator<T>().construct(finish, x); 5 ++finish; 6 } 7 //没有预留空间 8 else 9 inset_axu(end(), x); 10 }
可以看出动态分配空间技巧的实现落在了insert_axu()身上
1 template<typename T> 2 void Vector<T>::insert_axu(Vector::iterator position, const T &x) { 3 //Vector拥有备用空间 4 if (finish != end_of_storage) { 5 std::allocator<T>().construct(finish, *(finish-1)); 6 ++finish; 7 T x_copy = x; 8 std::copy_backward(position, finish-2, finish-1); 9 *position = x_copy; 10 11 } 12 //Vector没有备用空间 13 else { 14 const size_type old_size = size(); 15 //当原来空间大小不为零时分配原来空间大小二倍的空间 16 const size_type len = old_size == 0 ? 1 : 2 * old_size; 17 iterator new_start = std::allocator<T>().allocate(len); 18 iterator new_finish = new_start; 19 try { 20 //将原vector插入位置之前的内容拷贝到新vector 21 new_finish = std::uninitialized_copy(start, position, new_start); 22 //在新配置空间的finish位置设定要插入的对象 23 std::allocator<T>().construct(new_finish, x); 24 //更新新finish指向的位置 25 ++new_finish; 26 //将原vector插入位置之后的内容拷贝到新vector 27 new_finish = std::uninitialized_copy(position, finish, new_finish); 28 } 29 //若分配新空间时出现异常,则析构并释放新空间 30 catch(...) { 31 auto iter = new_start; 32 for (; iter != new_finish; ++iter) 33 std::allocator<T>().destroy(iter); 34 std::allocator<T>().deallocate(new_start, len); 35 throw; 36 } 37 //析构并释放原vector 38 auto iter = begin(); 39 for (; iter != end(); ++iter) 40 std::allocator<T>().destroy(iter); 41 deallocate(); 42 //调整迭代器 43 start = new_start; 44 finish = new_finish; 45 end_of_storage = new_finish + len; 46 47 } 48 }
标签:cto 留空 调整 prot style war lse 维护 细节
原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/swenwen/p/12526804.html