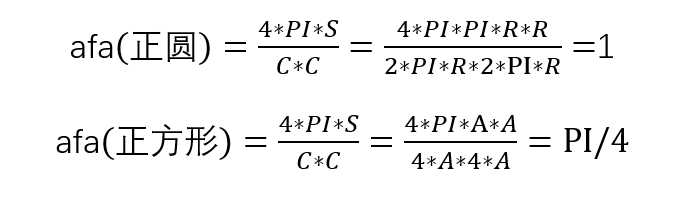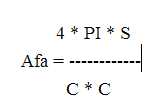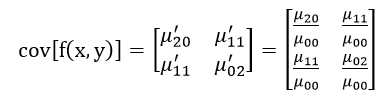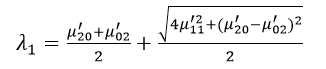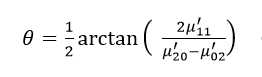标签:阈值处理 word using 相关 点距 more lan erb break

一、blob基础
所谓Blob就是图像中一组具有某些共同属性(例如,灰度值)的连接像素。在上图中,深色连接区域是斑点,斑点检测的目的是识别并标记这些区域。OpenCV提供了一种方便的方法来检测斑点并根据不同的特征对其进行过滤。在OpenCV 3中,使用SimpleBlobDetector :: create方法创建智能指针调用该算法。
Python
Python
# Setup SimpleBlobDetector parameters.
params = cv2.SimpleBlobDetector_Params()
# Change thresholds
params.minThreshold = 10;
params.maxThreshold = 200;
# Filter by Area.
params.filterByArea = True
params.minArea = 1500
# Filter by Circularity
params.filterByCircularity = True
params.minCircularity = 0.1
# Filter by Convexity
params.filterByConvexity = True
params.minConvexity = 0.87
# Filter by Inertia
params.filterByInertia = True
params.minInertiaRatio = 0.01
# Create a detector with the parameters
ver = (cv2.__version__).split(‘.‘)
if int(ver[0]) < 3 :
detector = cv2.SimpleBlobDetector(params)
else :
detector = cv2.SimpleBlobDetector_create(params)
C++
// Setup SimpleBlobDetector parameters.
SimpleBlobDetector::Params params;
// Change thresholds
params.minThreshold = 10;
params.maxThreshold = 200;
// Filter by Area.
params.filterByArea = true;
params.minArea = 1500;
// Filter by Circularity
params.filterByCircularity = true;
params.minCircularity = 0.1;
// Filter by Convexity
params.filterByConvexity = true;
params.minConvexity = 0.87;
// Filter by Inertia
params.filterByInertia = true;
params.minInertiaRatio = 0.01;
#if CV_MAJOR_VERSION < 3 // If you are using OpenCV 2
// Set up detector with params
SimpleBlobDetector detector(params);
// You can use the detector this way
// detector.detect( im, keypoints);
#else
// Set up detector with params
Ptr<SimpleBlobDetector> detector = SimpleBlobDetector::create(params);
// SimpleBlobDetector::create creates a smart pointer.
// So you need to use arrow ( ->) instead of dot ( . )
// detector->detect( im, keypoints);
#endif
二、blob参数设置
在OpenCV中实现的叫做SimpleBlobDetector,它基于以下描述的相当简单的算法,并且进一步由参数控制,具有以下步骤。
SimpleBlobDetector::Params::Params()
{
thresholdStep = 10; //二值化的阈值步长,即公式1的t
minThreshold = 50; //二值化的起始阈值,即公式1的T1
maxThreshold = 220; //二值化的终止阈值,即公式1的T2
//重复的最小次数,只有属于灰度图像斑点的那些二值图像斑点数量大于该值时,该灰度图像斑点才被认为是特征点
minRepeatability = 2;
//最小的斑点距离,不同二值图像的斑点间距离小于该值时,被认为是同一个位置的斑点,否则是不同位置上的斑点
minDistBetweenBlobs = 10;
filterByColor = true; //斑点颜色的限制变量
blobColor = 0; //表示只提取黑色斑点;如果该变量为255,表示只提取白色斑点
filterByArea = true; //斑点面积的限制变量
minArea = 25; //斑点的最小面积
maxArea = 5000; //斑点的最大面积
filterByCircularity = false; //斑点圆度的限制变量,默认是不限制
minCircularity = 0.8f; //斑点的最小圆度
//斑点的最大圆度,所能表示的float类型的最大值
maxCircularity = std::numeric_limits<float>::max();
filterByInertia = true; //斑点惯性率的限制变量
minInertiaRatio = 0.1f; //斑点的最小惯性率
maxInertiaRatio = std::numeric_limits<float>::max(); //斑点的最大惯性率
filterByConvexity = true; //斑点凸度的限制变量
minConvexity = 0.95f; //斑点的最小凸度
maxConvexity = std::numeric_limits<float>::max(); //斑点的最大凸度
}
- 阈值:通过使用以minThreshold开始的阈值对源图像进行阈值处理,将源图像转换为多个二进制图像。这些阈值以thresholdStep递增,直到maxThreshold。因此,第一个阈值为minThreshold,第二个阈值为minThreshold + thresholdStep,第三个阈值为minThreshold + 2 x thresholdStep,依此类推;
- 分组:在每个二进制图像中,连接的白色像素被分组在一起。我们称这些二进制blob;
- 合并:计算二进制图像中二进制斑点的中心,并合并比minDistBetweenBlob更近的斑点;
- 中心和半径计算:计算并返回新合并的Blob的中心和半径。
并且可以进一步设置SimpleBlobDetector的参数来过滤所需的Blob类型。
- 按颜色:首先需要设置filterByColor =True。设置blobColor = 0可选择较暗的blob,blobColor = 255可以选择较浅的blob。
- 按大小:可以通过设置参数filterByArea = 1以及minArea和maxArea的适当值来基于大小过滤blob。例如。设置minArea = 100将滤除所有少于100个像素的斑点。
- 按圆度:这只是测量斑点距圆的距离。例如。正六边形的圆度比正方形高。要按圆度过滤,请设置filterByCircularity =1。然后为minCircularity和maxCircularity设置适当的值。圆度定义为(
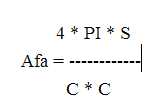 )。圆的为圆度为1,正方形的圆度为PI/4,依此类推。
)。圆的为圆度为1,正方形的圆度为PI/4,依此类推。
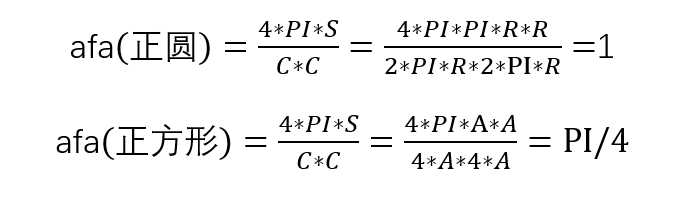
- 按凸性:凸度定义为(斑点的面积/凸包的面积)。现在,形状的“凸包”是最紧密的凸形,它完全包围了该形状,用不严谨的话来讲,给定二维平面上的点集,凸包就是将最外层的点连接起来构成的凸多边形,它能包含点集中所有的点。直观感受上,凸性越高则里面“奇怪的部分”月少。要按凸度过滤,需设置filterByConvexity = true,minConvexity、maxConvexity应该属于[0,1],而且maxConvexity> minConvexity。
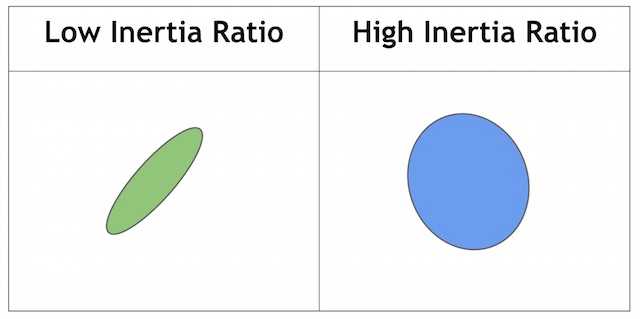
- 按惯性比:这个词汇比较抽象。我们需要知道Ratio可以衡量形状的伸长程度。简单来说。对于圆,此值是1,对于椭圆,它在0到1之间,对于直线,它是0。按惯性比过滤,设置filterByInertia = true,并设置minInertiaRatio、maxInertiaRatio同样属于[0,1]并且maxConvexity> minConvexity。
| 按凸性(左低右高) |
按惯性比(左低右高) |
 |
 |
三、OpenCV的blob代码解析
在它的函数定义部分(feature2d.hpp),详细地说明了该部分代码的使用方法。
单文件构成,结构比较简单,主要函数集中于detect和findBlobs,其他的皆为配合函数。
主要的一个数据结构,包含了中心的位置、半径和确定性。
struct CV_EXPORTS Center
{
Point2d location;
double radius;
double confidence;
};
2.1 findblob函数实现
findblob的主要过程是寻找到当前图片的轮廓,而后根据参数中的相关定义进行筛选。其中值得注意的地方。
std::vector < std::vector<Point> > contours;
findContours(binaryImage, contours, RETR_LIST, CHAIN_APPROX_NONE);
2.1.1在findContours的过程中,使用的是RETR_LIST 和 CHAIN_APPROX_NONE,我们来看下图
RETR_LIST 的方法是将所有的轮廓全部以链表的形式串联起来(反过来说,将丢失轮廓间的树状结构)。
2.1.2注意轮廓遍历的大循环。进入循环后将根据参数中的每一个单项进行逐条筛选。
for (size_t contourIdx = 0; contourIdx < contours.size(); contourIdx++)
{……
2.1.3“面积”筛选通过获得moms.m00来获得面积。
Moments moms = moments(contours[contourIdx]);
if (params.filterByArea)
{
double area = moms.m00;
if (area < params.minArea || area >= params.maxArea)
continue;
}
这个地方调用了moments(),该函数用于计算中心矩。设f(x,y)是一幅数字图像,,我们把像素的坐标看成是一个二维随机变量(X, Y),那么一副灰度图可以用二维灰度图密度函数来表示,因此可以用矩来描述灰度图像的特征。
对于二值图像的来说,零阶矩M00等于它的面积,同时一阶矩计算质心/重心。OpenCV中是这样实现
Moments moments(InputArray array, bool binaryImage=false )
class Moments
{
public:
Moments();
Moments(double m00, double m10, double m01, double m20, double m11,
double m02, double m30, double m21, double m12, double m03 );
Moments( const CvMoments& moments );
operator CvMoments() const;
}
参数说明
- 输入参数:array是一幅单通道,8-bits的图像,或一个二维浮点数组(Point of Point2f)。binaryImage用来指示输出图像是否为一幅二值图像,如果是二值图像,则图像中所有非0像素看作为1进行计算。
- 输出参数:moments是一个类:
2.1.3“圆度”筛选时通过来计算圆度公式,此外自带函数arcLength获得轮廓的周长。
double perimeter = arcLength(contours[contourIdx], true);
double ratio = 4 * CV_PI * area / (perimeter * perimeter);
2.1.3“颜色”筛选,只判断“圆心”的颜色。
if (params.filterByColor)
{
if (binaryImage.at<uchar> (cvRound(center.location.y), cvRound(center.location.x)) != params.blobColor)
continue;
}
这个使用方法值得商榷,在实际使用过程中不采纳。
2.1.4"凸性"筛选,凸图像在0-1之间取值。
if (params.filterByConvexity)
{
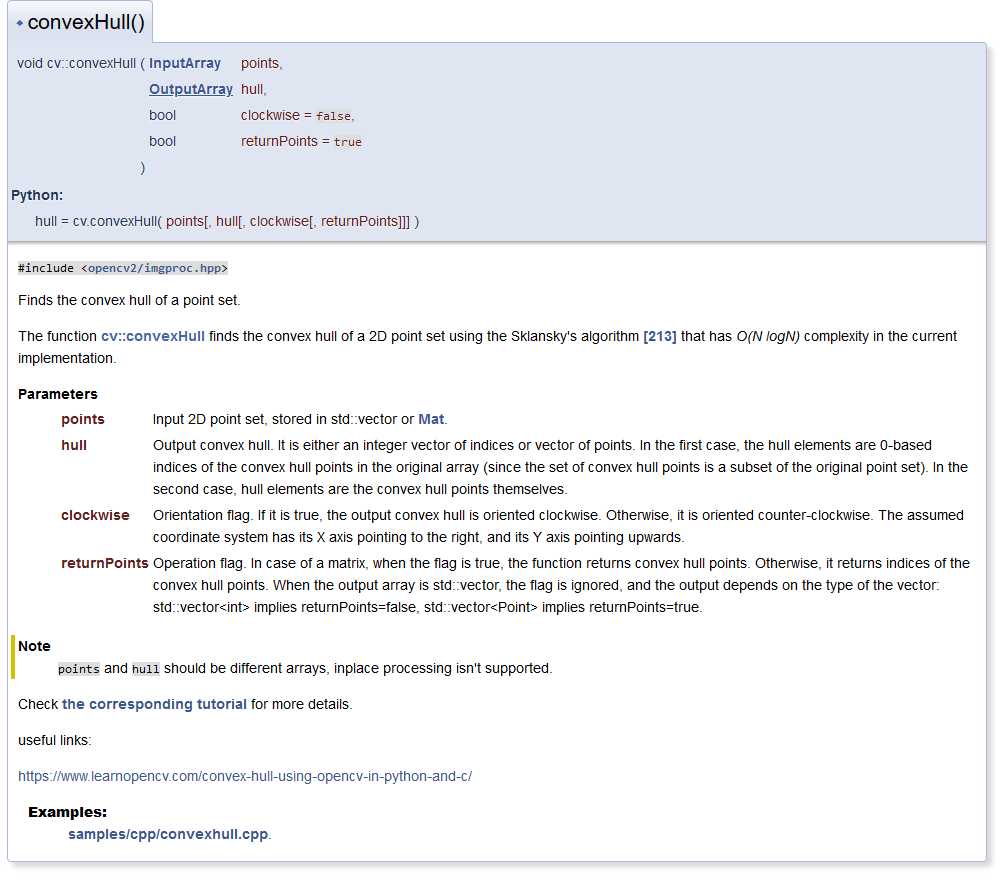
std::vector < Point > hull;
convexHull(contours[contourIdx], hull);
double area = contourArea(contours[contourIdx]);
double hullArea = contourArea(hull);
if (fabs(hullArea) < DBL_EPSILON)
continue;
double ratio = area / hullArea;
if (ratio < params.minConvexity || ratio >= params.maxConvexity)
continue;
}
……
我们可以用凸度来表示斑点凹凸的程度,凸度V的定义为:
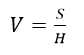
。其中,使用到了内部函数convexHull
2.1.5“惯性比”筛选,简单的来说,就是轮廓“扁”的程度。对于圆,此值是1,对于椭圆,它在0到1之间,对于直线,它是0。基本上就是取值在0-1之间,越扁越小。
if (params.filterByInertia)
{
double denominator = std::sqrt(std::pow(2 * moms.mu11, 2) + std::pow(moms.mu20 - moms.mu02, 2));
const double eps = 1e-2;
double ratio;
if (denominator > eps)
{
double cosmin = (moms.mu20 - moms.mu02) / denominator;
double sinmin = 2 * moms.mu11 / denominator;
double cosmax = -cosmin;
double sinmax = -sinmin;
double imin = 0.5 * (moms.mu20 + moms.mu02) - 0.5 * (moms.mu20 - moms.mu02) * cosmin - moms.mu11 * sinmin;
double imax = 0.5 * (moms.mu20 + moms.mu02) - 0.5 * (moms.mu20 - moms.mu02) * cosmax - moms.mu11 * sinmax;
ratio = imin / imax;
}
else
{
ratio = 1;
}
if (ratio < params.minInertiaRatio || ratio >= params.maxInertiaRatio)
continue;
center.confidence = ratio * ratio;
}
……
二阶中心矩称为惯性矩。如果仅考虑二阶中心矩的话,则图像完全等同于一个具有确定的大小、方向和离心率,以图像质心为中心且具有恒定辐射度的椭圆。图像的协方差矩阵为:
该矩阵的两个特征值λ1和λ2对应于图像强度(即椭圆)的主轴和次轴:
而图像的方向角度θ为:
图像的惯性率I为:
这个函数定义和代码略有不同,没有进一步研究。
2.1.6特别注意“半径”的计算方法
//compute blob radius
{
std::vector<double> dists;
for (size_t pointIdx = 0; pointIdx < contours[contourIdx].size(); pointIdx++)
{
Point2d pt = contours[contourIdx][pointIdx];
dists.push_back(norm(center.location - pt));
}
std::sort(dists.begin(), dists.end());
center.radius = (dists[(dists.size() - 1) / 2] + dists[dists.size() / 2]) / 2.;
}
2.2 detect函数实现
2.2.1对于图像通道的判断,值得借鉴。
Mat grayscaleImage;
if (image.channels() == 3 || image.channels() == 4)
cvtColor(image, grayscaleImage, COLOR_BGR2GRAY);
else
grayscaleImage = image.getMat();
if (grayscaleImage.type() != CV_8UC1) {
CV_Error(Error::StsUnsupportedFormat, "Blob detector only supports 8-bit images!");
}
2.2.2最外层的循环采用的是遍历阈值的方法,该方法非常值得借鉴。
for (double thresh = params.minThreshold; thresh < params.maxThreshold; thresh += params.thresholdStep)
{
Mat binarizedImage;
threshold(grayscaleImage, binarizedImage, thresh, 255, THRESH_BINARY);……
2.2.3通过距离判断新找到的圆是否为新圆,这段绝对是值得复用的。
for (double thresh = params.minThreshold; thresh < params.maxThreshold; thresh += params.thresholdStep)
{
Mat binarizedImage;
threshold(grayscaleImage, binarizedImage, thresh, 255, THRESH_BINARY);
std::vector < Center > curCenters;
findBlobs(grayscaleImage, binarizedImage, curCenters);
std::vector < std::vector<Center> > newCenters;
for (size_t i = 0; i < curCenters.size(); i++)
{
bool isNew = true;
for (size_t j = 0; j < centers.size(); j++)
{
double dist = norm(centers[j][ centers[j].size() / 2 ].location - curCenters[i].location);
isNew = dist >= params.minDistBetweenBlobs && dist >= centers[j][ centers[j].size() / 2 ].radius && dist >= curCenters[i].radius;
if (!isNew)
{
centers[j].push_back(curCenters[i]);
size_t k = centers[j].size() - 1;
while( k > 0 && curCenters[i].radius < centers[j][k-1].radius )
{
centers[j][k] = centers[j][k-1];
k--;
}
centers[j][k] = curCenters[i];
break;
}
}
if (isNew)
newCenters.push_back(std::vector<Center> (1, curCenters[i]));
}
std::copy(newCenters.begin(), newCenters.end(), std::back_inserter(centers));
}
三、blob和contours的区别、对比
blob和contours是高、低配关系。可以通过代码非常明显地看出,blob调用了contours方法,但仅仅是一种方法;blob在轮廓筛选这块更成熟;但contours还有一个重要的信息,那就是“轮廓间关系”。
将来在使用上,应该推广blob方法,但是可能不仅仅是调用其函数,还是需要将其内容掰开来具体研究分析;对于有“轮廓间关系”的情况,应该积极主动使用contours分析。
感谢阅读至此,希望有所帮助。
浅析OpenCV中的BlobDetector
标签:阈值处理 word using 相关 点距 more lan erb break
原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/jsxyhelu/p/13159564.html

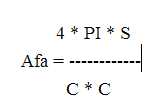 )。圆的为圆度为1,正方形的圆度为PI/4,依此类推。
)。圆的为圆度为1,正方形的圆度为PI/4,依此类推。