前言
现在,我们已经了解了如何建立索引和搜索数据了。
那么,是时候来探索背后的故事了!当数据传递到elasticsearch后,到底发生了什么?
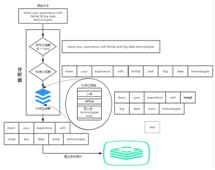
分析过程
当数据被发送到elasticsearch后并加入到倒排索引之前,elasticsearch会对该文档的进行一系列的处理步骤:
- 字符过滤:使用字符过滤器转变字符。
- 文本切分为分词:将文本(档)分为单个或多个分词。
- 分词过滤:使用分词过滤器转变每个分词。
- 分词索引:最终将分词存储在Lucene倒排索引中。
整体流程如下图所示:
接下来,我们简要的介绍elasticsearch中的分析器、分词器和分词过滤器。它们配置简单,灵活好用,我们可以通过不同的组合来获取我们想要的分词!
是的,无论多么复杂的分析过程,都是为了获取更加人性化的分词!
接下来,我们来看看其中,在整个分析过程的各个组件吧。
分析器
在elasticsearch中,一个分析器可以包括:
- 可选的字符过滤器
- 一个分词器
- 0个或多个分词过滤器
接下来简要的介绍各内置分词的大致情况。在介绍之前,为了方便演示。如果你已经按照之前的教程安装了ik analysis,现在请暂时将该插件移出plugins目录。
标准分析器:standard analyzer
标准分析器(standard analyzer):是elasticsearch的默认分析器,该分析器综合了大多数欧洲语言来说合理的默认模块,包括标准分词器、标准分词过滤器、小写转换分词过滤器和停用词分词过滤器。
POST _analyze
{
"analyzer": "standard",
"text":"To be or not to be, That is a question ———— 莎士比亚"
}
分词结果如下:
{
"tokens" : [
{
"token" : "to",
"start_offset" : 0,
"end_offset" : 2,
"type" : "<ALPHANUM>",
"position" : 0
},
{
"token" : "be",
"start_offset" : 3,
"end_offset" : 5,
"type" : "<ALPHANUM>",
"position" : 1
},
{
"token" : "or",
"start_offset" : 6,
"end_offset" : 8,
"type" : "<ALPHANUM>",
"position" : 2
},
{
"token" : "not",
"start_offset" : 9,
"end_offset" : 12,
"type" : "<ALPHANUM>",
"position" : 3
},
{
"token" : "to",
"start_offset" : 13,
"end_offset" : 15,
"type" : "<ALPHANUM>",
"position" : 4
},
{
"token" : "be",
"start_offset" : 16,
"end_offset" : 18,
"type" : "<ALPHANUM>",
"position" : 5
},
{
"token" : "that",
"start_offset" : 21,
"end_offset" : 25,
"type" : "<ALPHANUM>",
"position" : 6
},
{
"token" : "is",
"start_offset" : 26,
"end_offset" : 28,
"type" : "<ALPHANUM>",
"position" : 7
},
{
"token" : "a",
"start_offset" : 29,
"end_offset" : 30,
"type" : "<ALPHANUM>",
"position" : 8
},
{
"token" : "question",
"start_offset" : 31,
"end_offset" : 39,
"type" : "<ALPHANUM>",
"position" : 9
},
{
"token" : "莎",
"start_offset" : 45,
"end_offset" : 46,
"type" : "<IDEOGRAPHIC>",
"position" : 10
},
{
"token" : "士",
"start_offset" : 46,
"end_offset" : 47,
"type" : "<IDEOGRAPHIC>",
"position" : 11
},
{
"token" : "比",
"start_offset" : 47,
"end_offset" : 48,
"type" : "<IDEOGRAPHIC>",
"position" : 12
},
{
"token" : "亚",
"start_offset" : 48,
"end_offset" : 49,
"type" : "<IDEOGRAPHIC>",
"position" : 13
}
]
}
简单分析器:simple analyzer
简单分析器(simple analyzer):简单分析器仅使用了小写转换分词,这意味着在非字母处进行分词,并将分词自动转换为小写。这个分词器对于亚种语言来说效果不佳,因为亚洲语言不是根据空白来分词的,所以一般用于欧洲言中。
POST _analyze
{
"analyzer": "simple",
"text":"To be or not to be, That is a question ———— 莎士比亚"
}
分词结果如下:
{
"tokens" : [
{
"token" : "to",
"start_offset" : 0,
"end_offset" : 2,
"type" : "word",
"position" : 0
},
{
"token" : "be",
"start_offset" : 3,
"end_offset" : 5,
"type" : "word",
"position" : 1
},
{
"token" : "or",
"start_offset" : 6,
"end_offset" : 8,
"type" : "word",
"position" : 2
},
{
"token" : "not",
"start_offset" : 9,
"end_offset" : 12,
"type" : "word",
"position" : 3
},
{
"token" : "to",
"start_offset" : 13,
"end_offset" : 15,
"type" : "word",
"position" : 4
},
{
"token" : "be",
"start_offset" : 16,
"end_offset" : 18,
"type" : "word",
"position" : 5
},
{
"token" : "that",
"start_offset" : 21,
"end_offset" : 25,
"type" : "word",
"position" : 6
},
{
"token" : "is",
"start_offset" : 26,
"end_offset" : 28,
"type" : "word",
"position" : 7
},
{
"token" : "a",
"start_offset" : 29,
"end_offset" : 30,
"type" : "word",
"position" : 8
},
{
"token" : "question",
"start_offset" : 31,
"end_offset" : 39,
"type" : "word",
"position" : 9
},
{
"token" : "莎士比亚",
"start_offset" : 45,
"end_offset" : 49,
"type" : "word",
"position" : 10
}
]
}
空白分析器:whitespace analyzer
空白(格)分析器(whitespace analyzer):这玩意儿只是根据空白将文本切分为若干分词,真是有够偷懒!
POST _analyze
{
"analyzer": "whitespace",
"text":"To be or not to be, That is a question ———— 莎士比亚"
}
分词结果如下:
{
"tokens" : [
{
"token" : "To",
"start_offset" : 0,
"end_offset" : 2,
"type" : "word",
"position" : 0
},
{
"token" : "be",
"start_offset" : 3,
"end_offset" : 5,
"type" : "word",
"position" : 1
},
{
"token" : "or",
"start_offset" : 6,
"end_offset" : 8,
"type" : "word",
"position" : 2
},
{
"token" : "not",
"start_offset" : 9,
"end_offset" : 12,
"type" : "word",
"position" : 3
},
{
"token" : "to",
"start_offset" : 13,
"end_offset" : 15,
"type" : "word",
"position" : 4
},
{
"token" : "be,",
"start_offset" : 16,
"end_offset" : 19,
"type" : "word",
"position" : 5
},
{
"token" : "That",
"start_offset" : 21,
"end_offset" : 25,
"type" : "word",
"position" : 6
},
{
"token" : "is",
"start_offset" : 26,
"end_offset" : 28,
"type" : "word",
"position" : 7
},
{
"token" : "a",
"start_offset" : 29,
"end_offset" : 30,
"type" : "word",
"position" : 8
},
{
"token" : "question",
"start_offset" : 31,
"end_offset" : 39,
"type" : "word",
"position" : 9
},
{
"token" : "————",
"start_offset" : 40,
"end_offset" : 44,
"type" : "word",
"position" : 10
},
{
"token" : "莎士比亚",
"start_offset" : 45,
"end_offset" : 49,
"type" : "word",
"position" : 11
}
]
}
停用词分析器:stop analyzer
停用词分析(stop analyzer)和简单分析器的行为很像,只是在分词流中额外的过滤了停用词。
POST _analyze
{
"analyzer": "stop",
"text":"To be or not to be, That is a question ———— 莎士比亚"
}
结果也很简单:
{
"tokens" : [
{
"token" : "question",
"start_offset" : 31,
"end_offset" : 39,
"type" : "word",
"position" : 9
},
{
"token" : "莎士比亚",
"start_offset" : 45,
"end_offset" : 49,
"type" : "word",
"position" : 10
}
]
}
关键词分析器:keyword analyzer
关键词分析器(keyword analyzer)将整个字段当做单独的分词,如无必要,我们不在映射中使用关键词分析器。
POST _analyze
{
"analyzer": "keyword",
"text":"To be or not to be, That is a question ———— 莎士比亚"
}
结果如下:
{
"tokens" : [
{
"token" : "To be or not to be, That is a question ———— 莎士比亚",
"start_offset" : 0,
"end_offset" : 49,
"type" : "word",
"position" : 0
}
]
}
说的一点没错,分析结果是将整段当做单独的分词。
模式分析器:pattern analyzer
模式分析器(pattern analyzer)允许我们指定一个分词切分模式。但是通常更佳的方案是使用定制的分析器,组合现有的模式分词器和所需要的分词过滤器更加合适。
POST _analyze
{
"analyzer": "pattern",
"explain": false,
"text":"To be or not to be, That is a question ———— 莎士比亚"
}
结果如下:
{
"tokens" : [
{
"token" : "to",
"start_offset" : 0,
"end_offset" : 2,
"type" : "word",
"position" : 0
},
{
"token" : "be",
"start_offset" : 3,
"end_offset" : 5,
"type" : "word",
"position" : 1
},
{
"token" : "or",
"start_offset" : 6,
"end_offset" : 8,
"type" : "word",
"position" : 2
},
{
"token" : "not",
"start_offset" : 9,
"end_offset" : 12,
"type" : "word",
"position" : 3
},
{
"token" : "to",
"start_offset" : 13,
"end_offset" : 15,
"type" : "word",
"position" : 4
},
{
"token" : "be",
"start_offset" : 16,
"end_offset" : 18,
"type" : "word",
"position" : 5
},
{
"token" : "that",
"start_offset" : 21,
"end_offset" : 25,
"type" : "word",
"position" : 6
},
{
"token" : "is",
"start_offset" : 26,
"end_offset" : 28,
"type" : "word",
"position" : 7
},
{
"token" : "a",
"start_offset" : 29,
"end_offset" : 30,
"type" : "word",
"position" : 8
},
{
"token" : "question",
"start_offset" : 31,
"end_offset" : 39,
"type" : "word",
"position" : 9
}
]
}
我们来自定制一个模式分析器,比如我们写匹配邮箱的正则。
PUT pattern_test
{
"settings": {
"analysis": {
"analyzer": {
"my_email_analyzer":{
"type":"pattern",
"pattern":"\\W|_",
"lowercase":true
}
}
}
}
}
上例中,我们在创建一条索引的时候,配置分析器为自定义的分析器。
需要注意的是,在json字符串中,正则的斜杠需要转义。
我们使用自定义的分析器来查询。
POST pattern_test/_analyze
{
"analyzer": "my_email_analyzer",
"text": "John_Smith@foo-bar.com"
}
结果如下:
{
"tokens" : [
{
"token" : "john",
"start_offset" : 0,
"end_offset" : 4,
"type" : "word",
"position" : 0
},
{
"token" : "smith",
"start_offset" : 5,
"end_offset" : 10,
"type" : "word",
"position" : 1
},
{
"token" : "foo",
"start_offset" : 11,
"end_offset" : 14,
"type" : "word",
"position" : 2
},
{
"token" : "bar",
"start_offset" : 15,
"end_offset" : 18,
"type" : "word",
"position" : 3
},
{
"token" : "com",
"start_offset" : 19,
"end_offset" : 22,
"type" : "word",
"position" : 4
}
]
}
语言和多语言分析器:chinese
elasticsearch为很多世界流行语言提供良好的、简单的、开箱即用的语言分析器集合:阿拉伯语、亚美尼亚语、巴斯克语、巴西语、保加利亚语、加泰罗尼亚语、中文、捷克语、丹麦、荷兰语、英语、芬兰语、法语、加里西亚语、德语、希腊语、北印度语、匈牙利语、印度尼西亚、爱尔兰语、意大利语、日语、韩国语、库尔德语、挪威语、波斯语、葡萄牙语、罗马尼亚语、俄语、西班牙语、瑞典语、土耳其语和泰语。
我们可以指定其中之一的语言来指定特定的语言分析器,但必须是小写的名字!如果你要分析的语言不在上述集合中,可能还需要搭配相应的插件支持。
POST _analyze
{
"analyzer": "chinese",
"text":"To be or not to be, That is a question ———— 莎士比亚"
}
结果如下:
{
"tokens" : [
{
"token" : "question",
"start_offset" : 31,
"end_offset" : 39,
"type" : "<ALPHANUM>",
"position" : 9
},
{
"token" : "莎",
"start_offset" : 45,
"end_offset" : 46,
"type" : "<IDEOGRAPHIC>",
"position" : 10
},
{
"token" : "士",
"start_offset" : 46,
"end_offset" : 47,
"type" : "<IDEOGRAPHIC>",
"position" : 11
},
{
"token" : "比",
"start_offset" : 47,
"end_offset" : 48,
"type" : "<IDEOGRAPHIC>",
"position" : 12
},
{
"token" : "亚",
"start_offset" : 48,
"end_offset" : 49,
"type" : "<IDEOGRAPHIC>",
"position" : 13
}
]
}
也可以是别语言:
POST _analyze
{
"analyzer": "french",
"text":"Je suis ton père"
}
POST _analyze
{
"analyzer": "german",
"text":"Ich bin dein vater"
}
雪球分析器:snowball analyzer
雪球分析器(snowball analyzer)除了使用标准的分词和分词过滤器(和标准分析器一样)也是用了小写分词过滤器和停用词过滤器,除此之外,它还是用了雪球词干器对文本进行词干提取。
POST _analyze
{
"analyzer": "snowball",
"text":"To be or not to be, That is a question ———— 莎士比亚"
}
结果如下:
{
"tokens" : [
{
"token" : "question",
"start_offset" : 31,
"end_offset" : 39,
"type" : "<ALPHANUM>",
"position" : 9
},
{
"token" : "莎",
"start_offset" : 45,
"end_offset" : 46,
"type" : "<IDEOGRAPHIC>",
"position" : 10
},
{
"token" : "士",
"start_offset" : 46,
"end_offset" : 47,
"type" : "<IDEOGRAPHIC>",
"position" : 11
},
{
"token" : "比",
"start_offset" : 47,
"end_offset" : 48,
"type" : "<IDEOGRAPHIC>",
"position" : 12
},
{
"token" : "亚",
"start_offset" : 48,
"end_offset" : 49,
"type" : "<IDEOGRAPHIC>",
"position" : 13
}
]
}
字符过滤器
字符过滤器在<charFilter>属性中定义,它是对字符流进行处理。字符过滤器种类不多。elasticearch只提供了三种字符过滤器:
- HTML字符过滤器(HTML Strip Char Filter)
- 映射字符过滤器(Mapping Char Filter)
- 模式替换过滤器(Pattern Replace Char Filter)
我们来分别看看都是怎么玩的吧!
HTML字符过滤器
HTML字符过滤器(HTML Strip Char Filter)从文本中去除HTML元素。
POST _analyze
{
"tokenizer": "keyword",
"char_filter": ["html_strip"],
"text":"<p>I'm so <b>happy</b>!</p>"
}
结果如下:
{
"tokens" : [
{
"token" : """
I‘m so happy!
""",
"start_offset" : 0,
"end_offset" : 32,
"type" : "word",
"position" : 0
}
]
}
映射字符过滤器
映射字符过滤器(Mapping Char Filter)接收键值的映射,每当遇到与键相同的字符串时,它就用该键关联的值替换它们。
PUT pattern_test4
{
"settings": {
"analysis": {
"analyzer": {
"my_analyzer":{
"tokenizer":"keyword",
"char_filter":["my_char_filter"]
}
},
"char_filter":{
"my_char_filter":{
"type":"mapping",
"mappings":["苍井空 => 666","武藤兰 => 888"]
}
}
}
}
}
上例中,我们自定义了一个分析器,其内的分词器使用关键字分词器,字符过滤器则是自定制的,将字符中的苍井空替换为666,武藤兰替换为888。
POST pattern_test4/_analyze
{
"analyzer": "my_analyzer",
"text": "苍井空热爱武藤兰,可惜后来苍井空结婚了"
}
结果如下:
{
"tokens" : [
{
"token" : "666热爱888,可惜后来666结婚了",
"start_offset" : 0,
"end_offset" : 19,
"type" : "word",
"position" : 0
}
]
}
模式替换过滤器
模式替换过滤器(Pattern Replace Char Filter)使用正则表达式匹配并替换字符串中的字符。但要小心你写的抠脚的正则表达式。因为这可能导致性能变慢!
PUT pattern_test5
{
"settings": {
"analysis": {
"analyzer": {
"my_analyzer": {
"tokenizer": "standard",
"char_filter": [
"my_char_filter"
]
}
},
"char_filter": {
"my_char_filter": {
"type": "pattern_replace",
"pattern": "(\\d+)-(?=\\d)",
"replacement": "$1_"
}
}
}
}
}
上例中,我们自定义了一个正则规则。
POST pattern_test5/_analyze
{
"analyzer": "my_analyzer",
"text": "My credit card is 123-456-789"
}
结果如下:
{
"tokens" : [
{
"token" : "My",
"start_offset" : 0,
"end_offset" : 2,
"type" : "<ALPHANUM>",
"position" : 0
},
{
"token" : "credit",
"start_offset" : 3,
"end_offset" : 9,
"type" : "<ALPHANUM>",
"position" : 1
},
{
"token" : "card",
"start_offset" : 10,
"end_offset" : 14,
"type" : "<ALPHANUM>",
"position" : 2
},
{
"token" : "is",
"start_offset" : 15,
"end_offset" : 17,
"type" : "<ALPHANUM>",
"position" : 3
},
{
"token" : "123_456_789",
"start_offset" : 18,
"end_offset" : 29,
"type" : "<NUM>",
"position" : 4
}
]
}
我们大致的了解elasticsearch分析处理数据的流程。但可以看到的是,我们极少地在例子中演示中文处理。因为elasticsearch内置的分析器处理起来中文不是很好。所以,后续会介绍一个重量级的插件就是elasticsearch analysis ik(一般习惯称呼为ik分词器)。
分词器
由于elasticsearch内置了分析器,它同样也包含了分词器。分词器,顾名思义,主要的操作是将文本字符串分解为小块,而这些小块这被称为分词token。
标准分词器:standard tokenizer
标准分词器(standard tokenizer)是一个基于语法的分词器,对于大多数欧洲语言来说还是不错的,它同时还处理了Unicode文本的分词,但分词默认的最大长度是255字节,它也移除了逗号和句号这样的标点符号。
POST _analyze
{
"tokenizer": "standard",
"text":"To be or not to be, That is a question ———— 莎士比亚"
}
结果如下:
{
"tokens" : [
{
"token" : "To",
"start_offset" : 0,
"end_offset" : 2,
"type" : "<ALPHANUM>",
"position" : 0
},
{
"token" : "be",
"start_offset" : 3,
"end_offset" : 5,
"type" : "<ALPHANUM>",
"position" : 1
},
{
"token" : "or",
"start_offset" : 6,
"end_offset" : 8,
"type" : "<ALPHANUM>",
"position" : 2
},
{
"token" : "not",
"start_offset" : 9,
"end_offset" : 12,
"type" : "<ALPHANUM>",
"position" : 3
},
{
"token" : "to",
"start_offset" : 13,
"end_offset" : 15,
"type" : "<ALPHANUM>",
"position" : 4
},
{
"token" : "be",
"start_offset" : 16,
"end_offset" : 18,
"type" : "<ALPHANUM>",
"position" : 5
},
{
"token" : "That",
"start_offset" : 21,
"end_offset" : 25,
"type" : "<ALPHANUM>",
"position" : 6
},
{
"token" : "is",
"start_offset" : 26,
"end_offset" : 28,
"type" : "<ALPHANUM>",
"position" : 7
},
{
"token" : "a",
"start_offset" : 29,
"end_offset" : 30,
"type" : "<ALPHANUM>",
"position" : 8
},
{
"token" : "question",
"start_offset" : 31,
"end_offset" : 39,
"type" : "<ALPHANUM>",
"position" : 9
},
{
"token" : "莎",
"start_offset" : 45,
"end_offset" : 46,
"type" : "<IDEOGRAPHIC>",
"position" : 10
},
{
"token" : "士",
"start_offset" : 46,
"end_offset" : 47,
"type" : "<IDEOGRAPHIC>",
"position" : 11
},
{
"token" : "比",
"start_offset" : 47,
"end_offset" : 48,
"type" : "<IDEOGRAPHIC>",
"position" : 12
},
{
"token" : "亚",
"start_offset" : 48,
"end_offset" : 49,
"type" : "<IDEOGRAPHIC>",
"position" : 13
}
]
}
关键词分词器:keyword tokenizer
关键词分词器(keyword tokenizer)是一种简单的分词器,将整个文本作为单个的分词,提供给分词过滤器,当你只想用分词过滤器,而不做分词操作时,它是不错的选择。
POST _analyze
{
"tokenizer": "keyword",
"text":"To be or not to be, That is a question ———— 莎士比亚"
}
结果如下:
{
"tokens" : [
{
"token" : "To be or not to be, That is a question ———— 莎士比亚",
"start_offset" : 0,
"end_offset" : 49,
"type" : "word",
"position" : 0
}
]
}
字母分词器:letter tokenizer
字母分词器(letter tokenizer)根据非字母的符号,将文本切分成分词。
POST _analyze
{
"tokenizer": "letter",
"text":"To be or not to be, That is a question ———— 莎士比亚"
}
结果如下:
{
"tokens" : [
{
"token" : "To",
"start_offset" : 0,
"end_offset" : 2,
"type" : "word",
"position" : 0
},
{
"token" : "be",
"start_offset" : 3,
"end_offset" : 5,
"type" : "word",
"position" : 1
},
{
"token" : "or",
"start_offset" : 6,
"end_offset" : 8,
"type" : "word",
"position" : 2
},
{
"token" : "not",
"start_offset" : 9,
"end_offset" : 12,
"type" : "word",
"position" : 3
},
{
"token" : "to",
"start_offset" : 13,
"end_offset" : 15,
"type" : "word",
"position" : 4
},
{
"token" : "be",
"start_offset" : 16,
"end_offset" : 18,
"type" : "word",
"position" : 5
},
{
"token" : "That",
"start_offset" : 21,
"end_offset" : 25,
"type" : "word",
"position" : 6
},
{
"token" : "is",
"start_offset" : 26,
"end_offset" : 28,
"type" : "word",
"position" : 7
},
{
"token" : "a",
"start_offset" : 29,
"end_offset" : 30,
"type" : "word",
"position" : 8
},
{
"token" : "question",
"start_offset" : 31,
"end_offset" : 39,
"type" : "word",
"position" : 9
},
{
"token" : "莎士比亚",
"start_offset" : 45,
"end_offset" : 49,
"type" : "word",
"position" : 10
}
]
}
小写分词器:lowercase tokenizer
小写分词器(lowercase tokenizer)结合了常规的字母分词器和小写分词过滤器(跟你想的一样,就是将所有的分词转化为小写)的行为。通过一个单独的分词器来实现的主要原因是,一次进行两项操作会获得更好的性能。
POST _analyze
{
"tokenizer": "lowercase",
"text":"To be or not to be, That is a question ———— 莎士比亚"
}
结果如下:
{
"tokens" : [
{
"token" : "to",
"start_offset" : 0,
"end_offset" : 2,
"type" : "word",
"position" : 0
},
{
"token" : "be",
"start_offset" : 3,
"end_offset" : 5,
"type" : "word",
"position" : 1
},
{
"token" : "or",
"start_offset" : 6,
"end_offset" : 8,
"type" : "word",
"position" : 2
},
{
"token" : "not",
"start_offset" : 9,
"end_offset" : 12,
"type" : "word",
"position" : 3
},
{
"token" : "to",
"start_offset" : 13,
"end_offset" : 15,
"type" : "word",
"position" : 4
},
{
"token" : "be",
"start_offset" : 16,
"end_offset" : 18,
"type" : "word",
"position" : 5
},
{
"token" : "that",
"start_offset" : 21,
"end_offset" : 25,
"type" : "word",
"position" : 6
},
{
"token" : "is",
"start_offset" : 26,
"end_offset" : 28,
"type" : "word",
"position" : 7
},
{
"token" : "a",
"start_offset" : 29,
"end_offset" : 30,
"type" : "word",
"position" : 8
},
{
"token" : "question",
"start_offset" : 31,
"end_offset" : 39,
"type" : "word",
"position" : 9
},
{
"token" : "莎士比亚",
"start_offset" : 45,
"end_offset" : 49,
"type" : "word",
"position" : 10
}
]
}
空白分词器:whitespace tokenizer
空白分词器(whitespace tokenizer)通过空白来分隔不同的分词,空白包括空格、制表符、换行等。但是,我们需要注意的是,空白分词器不会删除任何标点符号。
POST _analyze
{
"tokenizer": "whitespace",
"text":"To be or not to be, That is a question ———— 莎士比亚"
}
结果如下:
{
"tokens" : [
{
"token" : "To",
"start_offset" : 0,
"end_offset" : 2,
"type" : "word",
"position" : 0
},
{
"token" : "be",
"start_offset" : 3,
"end_offset" : 5,
"type" : "word",
"position" : 1
},
{
"token" : "or",
"start_offset" : 6,
"end_offset" : 8,
"type" : "word",
"position" : 2
},
{
"token" : "not",
"start_offset" : 9,
"end_offset" : 12,
"type" : "word",
"position" : 3
},
{
"token" : "to",
"start_offset" : 13,
"end_offset" : 15,
"type" : "word",
"position" : 4
},
{
"token" : "be,",
"start_offset" : 16,
"end_offset" : 19,
"type" : "word",
"position" : 5
},
{
"token" : "That",
"start_offset" : 21,
"end_offset" : 25,
"type" : "word",
"position" : 6
},
{
"token" : "is",
"start_offset" : 26,
"end_offset" : 28,
"type" : "word",
"position" : 7
},
{
"token" : "a",
"start_offset" : 29,
"end_offset" : 30,
"type" : "word",
"position" : 8
},
{
"token" : "question",
"start_offset" : 31,
"end_offset" : 39,
"type" : "word",
"position" : 9
},
{
"token" : "————",
"start_offset" : 40,
"end_offset" : 44,
"type" : "word",
"position" : 10
},
{
"token" : "莎士比亚",
"start_offset" : 45,
"end_offset" : 49,
"type" : "word",
"position" : 11
}
]
}
模式分词器:pattern tokenizer
模式分词器(pattern tokenizer)允许指定一个任意的模式,将文本切分为分词。
POST _analyze
{
"tokenizer": "pattern",
"text":"To be or not to be, That is a question ———— 莎士比亚"
}
现在让我们手动定制一个以逗号分隔的分词器。
PUT pattern_test2
{
"settings": {
"analysis": {
"analyzer": {
"my_analyzer":{
"tokenizer":"my_tokenizer"
}
},
"tokenizer": {
"my_tokenizer":{
"type":"pattern",
"pattern":","
}
}
}
}
}
上例中,在settings下的自定义分析器my_analyzer中,自定义的模式分词器名叫my_tokenizer;在与自定义分析器同级,为新建的自定义模式分词器设置一些属性,比如以逗号分隔。
POST pattern_test2/_analyze
{
"tokenizer": "my_tokenizer",
"text":"To be or not to be, That is a question ———— 莎士比亚"
}
结果如下:
{
"tokens" : [
{
"token" : "To be or not to be",
"start_offset" : 0,
"end_offset" : 18,
"type" : "word",
"position" : 0
},
{
"token" : " That is a question ———— 莎士比亚",
"start_offset" : 19,
"end_offset" : 49,
"type" : "word",
"position" : 1
}
]
}
根据结果可以看到,文档被逗号分割为两部分。
UAX URL电子邮件分词器:UAX RUL email tokenizer
在处理单个的英文单词的情况下,标准分词器是个非常好的选择,但是现在很多的网站以网址或电子邮件作为结尾,比如我们现在有这样的一个文本:
作者:张开
来源:未知
原文:https://www.cnblogs.com/Neeo/articles/10402742.html
邮箱:xxxxxxx@xx.com
版权声明:本文为博主原创文章,转载请附上博文链接!
现在让我们使用标准分词器查看一下:
POST _analyze
{
"tokenizer": "standard",
"text":"作者:张开来源:未知原文:https://www.cnblogs.com/Neeo/articles/10402742.html邮箱:xxxxxxx@xx.com版权声明:本文为博主原创文章,转载请附上博文链接!"
}
结果很长:
{
"tokens" : [
{
"token" : "作",
"start_offset" : 0,
"end_offset" : 1,
"type" : "<IDEOGRAPHIC>",
"position" : 0
},
{
"token" : "者",
"start_offset" : 1,
"end_offset" : 2,
"type" : "<IDEOGRAPHIC>",
"position" : 1
},
{
"token" : "张",
"start_offset" : 3,
"end_offset" : 4,
"type" : "<IDEOGRAPHIC>",
"position" : 2
},
{
"token" : "开",
"start_offset" : 4,
"end_offset" : 5,
"type" : "<IDEOGRAPHIC>",
"position" : 3
},
{
"token" : "来",
"start_offset" : 5,
"end_offset" : 6,
"type" : "<IDEOGRAPHIC>",
"position" : 4
},
{
"token" : "源",
"start_offset" : 6,
"end_offset" : 7,
"type" : "<IDEOGRAPHIC>",
"position" : 5
},
{
"token" : "未",
"start_offset" : 8,
"end_offset" : 9,
"type" : "<IDEOGRAPHIC>",
"position" : 6
},
{
"token" : "知",
"start_offset" : 9,
"end_offset" : 10,
"type" : "<IDEOGRAPHIC>",
"position" : 7
},
{
"token" : "原",
"start_offset" : 10,
"end_offset" : 11,
"type" : "<IDEOGRAPHIC>",
"position" : 8
},
{
"token" : "文",
"start_offset" : 11,
"end_offset" : 12,
"type" : "<IDEOGRAPHIC>",
"position" : 9
},
{
"token" : "https",
"start_offset" : 13,
"end_offset" : 18,
"type" : "<ALPHANUM>",
"position" : 10
},
{
"token" : "www.cnblogs.com",
"start_offset" : 21,
"end_offset" : 36,
"type" : "<ALPHANUM>",
"position" : 11
},
{
"token" : "Neeo",
"start_offset" : 37,
"end_offset" : 41,
"type" : "<ALPHANUM>",
"position" : 12
},
{
"token" : "articles",
"start_offset" : 42,
"end_offset" : 50,
"type" : "<ALPHANUM>",
"position" : 13
},
{
"token" : "10402742",
"start_offset" : 51,
"end_offset" : 59,
"type" : "<NUM>",
"position" : 14
},
{
"token" : "html",
"start_offset" : 60,
"end_offset" : 64,
"type" : "<ALPHANUM>",
"position" : 15
},
{
"token" : "邮",
"start_offset" : 64,
"end_offset" : 65,
"type" : "<IDEOGRAPHIC>",
"position" : 16
},
{
"token" : "箱",
"start_offset" : 65,
"end_offset" : 66,
"type" : "<IDEOGRAPHIC>",
"position" : 17
},
{
"token" : "xxxxxxx",
"start_offset" : 67,
"end_offset" : 74,
"type" : "<ALPHANUM>",
"position" : 18
},
{
"token" : "xx.com",
"start_offset" : 75,
"end_offset" : 81,
"type" : "<ALPHANUM>",
"position" : 19
},
{
"token" : "版",
"start_offset" : 81,
"end_offset" : 82,
"type" : "<IDEOGRAPHIC>",
"position" : 20
},
{
"token" : "权",
"start_offset" : 82,
"end_offset" : 83,
"type" : "<IDEOGRAPHIC>",
"position" : 21
},
{
"token" : "声",
"start_offset" : 83,
"end_offset" : 84,
"type" : "<IDEOGRAPHIC>",
"position" : 22
},
{
"token" : "明",
"start_offset" : 84,
"end_offset" : 85,
"type" : "<IDEOGRAPHIC>",
"position" : 23
},
{
"token" : "本",
"start_offset" : 86,
"end_offset" : 87,
"type" : "<IDEOGRAPHIC>",
"position" : 24
},
{
"token" : "文",
"start_offset" : 87,
"end_offset" : 88,
"type" : "<IDEOGRAPHIC>",
"position" : 25
},
{
"token" : "为",
"start_offset" : 88,
"end_offset" : 89,
"type" : "<IDEOGRAPHIC>",
"position" : 26
},
{
"token" : "博",
"start_offset" : 89,
"end_offset" : 90,
"type" : "<IDEOGRAPHIC>",
"position" : 27
},
{
"token" : "主",
"start_offset" : 90,
"end_offset" : 91,
"type" : "<IDEOGRAPHIC>",
"position" : 28
},
{
"token" : "原",
"start_offset" : 91,
"end_offset" : 92,
"type" : "<IDEOGRAPHIC>",
"position" : 29
},
{
"token" : "创",
"start_offset" : 92,
"end_offset" : 93,
"type" : "<IDEOGRAPHIC>",
"position" : 30
},
{
"token" : "文",
"start_offset" : 93,
"end_offset" : 94,
"type" : "<IDEOGRAPHIC>",
"position" : 31
},
{
"token" : "章",
"start_offset" : 94,
"end_offset" : 95,
"type" : "<IDEOGRAPHIC>",
"position" : 32
},
{
"token" : "转",
"start_offset" : 96,
"end_offset" : 97,
"type" : "<IDEOGRAPHIC>",
"position" : 33
},
{
"token" : "载",
"start_offset" : 97,
"end_offset" : 98,
"type" : "<IDEOGRAPHIC>",
"position" : 34
},
{
"token" : "请",
"start_offset" : 98,
"end_offset" : 99,
"type" : "<IDEOGRAPHIC>",
"position" : 35
},
{
"token" : "附",
"start_offset" : 99,
"end_offset" : 100,
"type" : "<IDEOGRAPHIC>",
"position" : 36
},
{
"token" : "上",
"start_offset" : 100,
"end_offset" : 101,
"type" : "<IDEOGRAPHIC>",
"position" : 37
},
{
"token" : "博",
"start_offset" : 101,
"end_offset" : 102,
"type" : "<IDEOGRAPHIC>",
"position" : 38
},
{
"token" : "文",
"start_offset" : 102,
"end_offset" : 103,
"type" : "<IDEOGRAPHIC>",
"position" : 39
},
{
"token" : "链",
"start_offset" : 103,
"end_offset" : 104,
"type" : "<IDEOGRAPHIC>",
"position" : 40
},
{
"token" : "接",
"start_offset" : 104,
"end_offset" : 105,
"type" : "<IDEOGRAPHIC>",
"position" : 41
}
]
}
无论如何,这个结果不符合我们的预期,因为把我们的邮箱和网址分的乱七八糟!那么针对这种情况,我们应该使用UAX URL电子邮件分词器(UAX RUL email tokenizer),该分词器将电子邮件和URL都作为单独的分词进行保留。
POST _analyze
{
"tokenizer": "uax_url_email",
"text":"作者:张开来源:未知原文:https://www.cnblogs.com/Neeo/articles/10402742.html邮箱:xxxxxxx@xx.com版权声明:本文为博主原创文章,转载请附上博文链接!"
}
结果如下:
{
"tokens" : [
{
"token" : "作",
"start_offset" : 0,
"end_offset" : 1,
"type" : "<IDEOGRAPHIC>",
"position" : 0
},
{
"token" : "者",
"start_offset" : 1,
"end_offset" : 2,
"type" : "<IDEOGRAPHIC>",
"position" : 1
},
{
"token" : "张",
"start_offset" : 3,
"end_offset" : 4,
"type" : "<IDEOGRAPHIC>",
"position" : 2
},
{
"token" : "开",
"start_offset" : 4,
"end_offset" : 5,
"type" : "<IDEOGRAPHIC>",
"position" : 3
},
{
"token" : "来",
"start_offset" : 5,
"end_offset" : 6,
"type" : "<IDEOGRAPHIC>",
"position" : 4
},
{
"token" : "源",
"start_offset" : 6,
"end_offset" : 7,
"type" : "<IDEOGRAPHIC>",
"position" : 5
},
{
"token" : "未",
"start_offset" : 8,
"end_offset" : 9,
"type" : "<IDEOGRAPHIC>",
"position" : 6
},
{
"token" : "知",
"start_offset" : 9,
"end_offset" : 10,
"type" : "<IDEOGRAPHIC>",
"position" : 7
},
{
"token" : "原",
"start_offset" : 10,
"end_offset" : 11,
"type" : "<IDEOGRAPHIC>",
"position" : 8
},
{
"token" : "文",
"start_offset" : 11,
"end_offset" : 12,
"type" : "<IDEOGRAPHIC>",
"position" : 9
},
{
"token" : "https://www.cnblogs.com/Neeo/articles/10402742.html",
"start_offset" : 13,
"end_offset" : 64,
"type" : "<URL>",
"position" : 10
},
{
"token" : "邮",
"start_offset" : 64,
"end_offset" : 65,
"type" : "<IDEOGRAPHIC>",
"position" : 11
},
{
"token" : "箱",
"start_offset" : 65,
"end_offset" : 66,
"type" : "<IDEOGRAPHIC>",
"position" : 12
},
{
"token" : "xxxxxxx@xx.com",
"start_offset" : 67,
"end_offset" : 81,
"type" : "<EMAIL>",
"position" : 13
},
{
"token" : "版",
"start_offset" : 81,
"end_offset" : 82,
"type" : "<IDEOGRAPHIC>",
"position" : 14
},
{
"token" : "权",
"start_offset" : 82,
"end_offset" : 83,
"type" : "<IDEOGRAPHIC>",
"position" : 15
},
{
"token" : "声",
"start_offset" : 83,
"end_offset" : 84,
"type" : "<IDEOGRAPHIC>",
"position" : 16
},
{
"token" : "明",
"start_offset" : 84,
"end_offset" : 85,
"type" : "<IDEOGRAPHIC>",
"position" : 17
},
{
"token" : "本",
"start_offset" : 86,
"end_offset" : 87,
"type" : "<IDEOGRAPHIC>",
"position" : 18
},
{
"token" : "文",
"start_offset" : 87,
"end_offset" : 88,
"type" : "<IDEOGRAPHIC>",
"position" : 19
},
{
"token" : "为",
"start_offset" : 88,
"end_offset" : 89,
"type" : "<IDEOGRAPHIC>",
"position" : 20
},
{
"token" : "博",
"start_offset" : 89,
"end_offset" : 90,
"type" : "<IDEOGRAPHIC>",
"position" : 21
},
{
"token" : "主",
"start_offset" : 90,
"end_offset" : 91,
"type" : "<IDEOGRAPHIC>",
"position" : 22
},
{
"token" : "原",
"start_offset" : 91,
"end_offset" : 92,
"type" : "<IDEOGRAPHIC>",
"position" : 23
},
{
"token" : "创",
"start_offset" : 92,
"end_offset" : 93,
"type" : "<IDEOGRAPHIC>",
"position" : 24
},
{
"token" : "文",
"start_offset" : 93,
"end_offset" : 94,
"type" : "<IDEOGRAPHIC>",
"position" : 25
},
{
"token" : "章",
"start_offset" : 94,
"end_offset" : 95,
"type" : "<IDEOGRAPHIC>",
"position" : 26
},
{
"token" : "转",
"start_offset" : 96,
"end_offset" : 97,
"type" : "<IDEOGRAPHIC>",
"position" : 27
},
{
"token" : "载",
"start_offset" : 97,
"end_offset" : 98,
"type" : "<IDEOGRAPHIC>",
"position" : 28
},
{
"token" : "请",
"start_offset" : 98,
"end_offset" : 99,
"type" : "<IDEOGRAPHIC>",
"position" : 29
},
{
"token" : "附",
"start_offset" : 99,
"end_offset" : 100,
"type" : "<IDEOGRAPHIC>",
"position" : 30
},
{
"token" : "上",
"start_offset" : 100,
"end_offset" : 101,
"type" : "<IDEOGRAPHIC>",
"position" : 31
},
{
"token" : "博",
"start_offset" : 101,
"end_offset" : 102,
"type" : "<IDEOGRAPHIC>",
"position" : 32
},
{
"token" : "文",
"start_offset" : 102,
"end_offset" : 103,
"type" : "<IDEOGRAPHIC>",
"position" : 33
},
{
"token" : "链",
"start_offset" : 103,
"end_offset" : 104,
"type" : "<IDEOGRAPHIC>",
"position" : 34
},
{
"token" : "接",
"start_offset" : 104,
"end_offset" : 105,
"type" : "<IDEOGRAPHIC>",
"position" : 35
}
]
}
路径层次分词器:path hierarchy tokenizer
路径层次分词器(path hierarchy tokenizer)允许以特定的方式索引文件系统的路径,这样在搜索时,共享同样路径的文件将被作为结果返回。
POST _analyze
{
"tokenizer": "path_hierarchy",
"text":"/usr/local/python/python2.7"
}
返回结果如下:
{
"tokens" : [
{
"token" : "/usr",
"start_offset" : 0,
"end_offset" : 4,
"type" : "word",
"position" : 0
},
{
"token" : "/usr/local",
"start_offset" : 0,
"end_offset" : 10,
"type" : "word",
"position" : 0
},
{
"token" : "/usr/local/python",
"start_offset" : 0,
"end_offset" : 17,
"type" : "word",
"position" : 0
},
{
"token" : "/usr/local/python/python2.7",
"start_offset" : 0,
"end_offset" : 27,
"type" : "word",
"position" : 0
}
]
}
分词过滤器
asticsearch内置很多(真是变态多啊!但一般用不到,美滋滋!!!)的分词过滤器。其中包含分词过滤器和字符过滤器。
常见分词过滤器
这里仅列举几个常见的分词过滤器(token filter)包括:
- 标准分词过滤器(Standard Token Filter)在6.5.0版本弃用。此筛选器已被弃用,将在下一个主要版本中删除。在之前的版本中其实也没干啥,甚至在更老版本的
Lucene中,它用于去除单词结尾的s字符,还有不必要的句点字符,但是现在, 连这些小功能都被其他的分词器和分词过滤器顺手干了,真可怜! - ASCII折叠分词过滤器(ASCII Folding Token Filter)将前127个ASCII字符(基本拉丁语的Unicode块)中不包含的字母、数字和符号Unicode字符转换为对应的ASCII字符(如果存在的话)。
- 扁平图形分词过滤器(Flatten Graph Token Filter)接受任意图形标记流。例如由同义词图形标记过滤器生成的标记流,并将其展平为适合索引的单个线性标记链。这是一个有损的过程,因为单独的侧路径被压扁在彼此之上,但是如果在索引期间使用图形令牌流是必要的,因为Lucene索引当前不能表示图形。 出于这个原因,最好只在搜索时应用图形分析器,因为这样可以保留完整的图形结构,并为邻近查询提供正确的匹配。该功能在Lucene中为实验性功能。
- 长度标记过滤器(Length Token Filter)会移除分词流中太长或者太短的标记,它是可配置的,我们可以在settings中设置。
- 小写分词过滤器(Lowercase Token Filter)将分词规范化为小写,它通过
language参数支持希腊语、爱尔兰语和土耳其语小写标记过滤器。 - 大写分词过滤器(Uppercase Token Filter)将分词规范为大写。
其余分词过滤器不一一列举。详情参见官网。
自定义分词过滤器
接下来我们简单的来学习自定义两个分词过滤器。首先是长度分词过滤器。
PUT pattern_test3
{
"settings": {
"analysis": {
"filter": {
"my_test_length":{
"type":"length",
"max":8,
"min":2
}
}
}
}
}
上例中,我们自定义了一个长度过滤器,过滤掉长度大于8和小于2的分词。
需要补充的是,max参数表示最大分词长度。默认为Integer.MAX_VALUE,就是2147483647(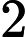


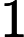 231?1),而min则表示最小长度,默认为0。
231?1),而min则表示最小长度,默认为0。
POST pattern_test3/_analyze
{
"tokenizer": "standard",
"filter": ["my_test_length"],
"text":"a Small word and a longerword"
}
结果如下:
{
"tokens" : [
{
"token" : "Small",
"start_offset" : 2,
"end_offset" : 7,
"type" : "<ALPHANUM>",
"position" : 1
},
{
"token" : "word",
"start_offset" : 8,
"end_offset" : 12,
"type" : "<ALPHANUM>",
"position" : 2
},
{
"token" : "and",
"start_offset" : 13,
"end_offset" : 16,
"type" : "<ALPHANUM>",
"position" : 3
}
]
}
自定义小写分词过滤器
自定义一个小写分词过滤器,过滤希腊文:
PUT lowercase_example
{
"settings": {
"analysis": {
"analyzer": {
"standard_lowercase_example": {
"type": "custom",
"tokenizer": "standard",
"filter": ["lowercase"]
},
"greek_lowercase_example": {
"type": "custom",
"tokenizer": "standard",
"filter": ["greek_lowercase"]
}
},
"filter": {
"greek_lowercase": {
"type": "lowercase",
"language": "greek"
}
}
}
}
}
过滤内容是:
POST lowercase_example/_analyze
{
"tokenizer": "standard",
"filter": ["greek_lowercase"],
"text":"?να φ?λτρο διακριτικο? τ?που πεζ? s ομαλοποιε? το κε?μενο διακριτικο? σε χαμηλ?τερη θ?κη"
}
结果如下:
{
"tokens" : [
{
"token" : "ενα",
"start_offset" : 0,
"end_offset" : 3,
"type" : "<ALPHANUM>",
"position" : 0
},
{
"token" : "φιλτρο",
"start_offset" : 4,
"end_offset" : 10,
"type" : "<ALPHANUM>",
"position" : 1
},
{
"token" : "διακριτικου",
"start_offset" : 11,
"end_offset" : 22,
"type" : "<ALPHANUM>",
"position" : 2
},
{
"token" : "τυπου",
"start_offset" : 23,
"end_offset" : 28,
"type" : "<ALPHANUM>",
"position" : 3
},
{
"token" : "πεζα",
"start_offset" : 29,
"end_offset" : 33,
"type" : "<ALPHANUM>",
"position" : 4
},
{
"token" : "s",
"start_offset" : 34,
"end_offset" : 35,
"type" : "<ALPHANUM>",
"position" : 5
},
{
"token" : "ομαλοποιει",
"start_offset" : 36,
"end_offset" : 46,
"type" : "<ALPHANUM>",
"position" : 6
},
{
"token" : "το",
"start_offset" : 47,
"end_offset" : 49,
"type" : "<ALPHANUM>",
"position" : 7
},
{
"token" : "κειμενο",
"start_offset" : 50,
"end_offset" : 57,
"type" : "<ALPHANUM>",
"position" : 8
},
{
"token" : "διακριτικου",
"start_offset" : 58,
"end_offset" : 69,
"type" : "<ALPHANUM>",
"position" : 9
},
{
"token" : "σε",
"start_offset" : 70,
"end_offset" : 72,
"type" : "<ALPHANUM>",
"position" : 10
},
{
"token" : "χαμηλοτερη",
"start_offset" : 73,
"end_offset" : 83,
"type" : "<ALPHANUM>",
"position" : 11
},
{
"token" : "θηκη",
"start_offset" : 84,
"end_offset" : 88,
"type" : "<ALPHANUM>",
"position" : 12
}
]
}
多个分词过滤器
除此之外,我们可以使用多个分词过滤器。例如我们在使用长度过滤器时,可以同时使用小写分词过滤器或者更多。
POST _analyze
{
"tokenizer": "standard",
"filter": ["length","lowercase"],
"text":"a Small word and a longerword"
}
上例中,我们用列表来管理多个分词过滤器。
结果如下:
{
"tokens" : [
{
"token" : "a",
"start_offset" : 0,
"end_offset" : 1,
"type" : "<ALPHANUM>",
"position" : 0
},
{
"token" : "small",
"start_offset" : 2,
"end_offset" : 7,
"type" : "<ALPHANUM>",
"position" : 1
},
{
"token" : "word",
"start_offset" : 8,
"end_offset" : 12,
"type" : "<ALPHANUM>",
"position" : 2
},
{
"token" : "and",
"start_offset" : 13,
"end_offset" : 16,
"type" : "<ALPHANUM>",
"position" : 3
},
{
"token" : "a",
"start_offset" : 17,
"end_offset" : 18,
"type" : "<ALPHANUM>",
"position" : 4
},
{
"token" : "longerword",
"start_offset" : 19,
"end_offset" : 29,
"type" : "<ALPHANUM>",
"position" : 5
}
]
}