标签:
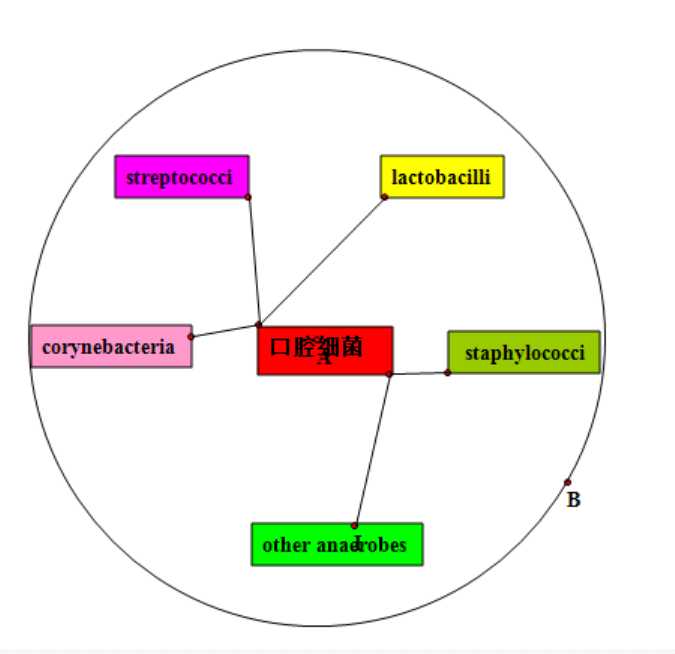
从图中关系可以看出某些细菌在肠胃是益生菌,在口腔是有害菌。
因为不同器官生理机能不同,所以同一细菌可以扮演不同角色。
例如乳酸菌。
Oral microbiology is the study of the microorganisms of the oral cavity(腔) and the interactions(相互作用) between the oral microorganisms(微生物) with each other and with the host. Of particular interest is the role of oral microorganisms in the two major dental(牙科的)diseases: dental caries and periodontal disease.[1]
The mouth harbors a diverse(不同的), abundant(丰富的) and complex(复杂的) microbial(微生物的)community. This highly diverse microflora inhabits(栖息) the various surfaces of the normal mouth.Bacteria accumulate(累积) on both the hard and soft oral tissues(组织) in biofilms. Bacterial adhesion is particularly important for oral bacteria.
细菌在口腔软硬组织累计,形成细菌膜。细菌沾附对于口腔细菌非常重要
Oral bacteria have evolved(发展) mechanisms(机制) to sense their environment and evade(逃避) or modify(修改) the host. Bacteria occupy(占据) the ecological(生态的) niche(生态位) provided by both the tooth surface and gingival epithelium(牙龈上皮细胞). However, a highly efficient(有效率的) innate(先天的)host defense system constantly monitors the bacterial(细菌的) colonization(殖民) and prevents bacterial invasion(入侵) of local tissues. A dynamic(动态的) equilibrium(均衡) exists between dental plaque bacteria and the innate host defense system.
口腔细菌进化了复杂机制,来感应环境,逃避或改变宿主。细菌占据生态位,包括牙齿表面,牙龈上皮细胞。但宿主高效先天防御系统不断监控细菌的繁殖,并阻止细菌入侵局部组织。人体存在一个动态的平衡--宿主免疫系统和牙斑
Oral bacteria include streptococci(链球菌), lactobacilli(乳酸杆菌), staphylococci(葡萄状球菌),corynebacteria(棒状杆菌), and various anaerobes 厌氧菌in particular bacteroides. The oral cavity(腔) of the new-born baby does not contain bacteria but rapidly becomes colonized(移于殖民地) with bacteria such as Streptococcus salivarius. With the appearance of the teeth during the first year colonization(殖民) by Streptococcus mutans and Streptococcus sanguinis occurs as theseorganisms(有机体) colonise(开拓殖民地) the dental(牙科的) surface and gingiva(齿龈). Other strains(系列) of streptococci(链球菌) adhere(坚持) strongly to the gums() and cheeks(脸颊) but not to the teeth. The gingival(齿龈的) crevice(裂缝) area (supporting structures(结构) of the teeth) provides a habitat(栖息地) for a variety of anaerobic(厌氧的) species(种类). Bacteroides and spirochetes(螺旋体) colonize the mouth around puberty(青春期).
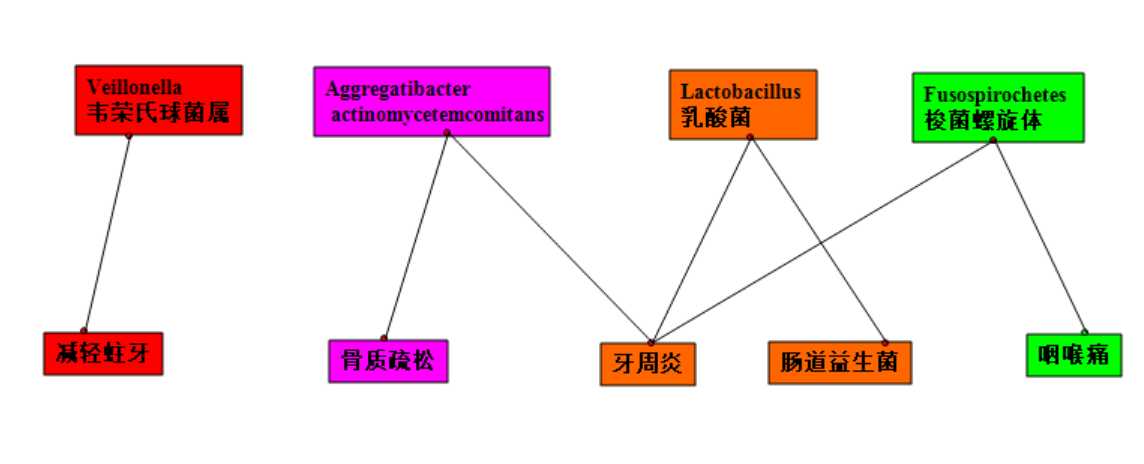
青春期时,细菌大量繁殖在牙龈裂缝区域。口腔出血,容易发生梭菌螺旋体细菌感染。例如牙龈炎,咽喉痛。
Spirochetes螺旋菌 and fusi-form bacilli(杆菌) live as normal flora(植物区系) in the mouth, but in the case of bleeding in the oral cavity, the bacteria can cause infection(感染) and diseases to oral cavity:
Veillonella are gram-negative anaerobic(厌氧的) cocci(球菌). It is thought that this species(物种)thrives(繁荣) in the acidic(酸的) environment of caries(龋齿) and is thought to slow the development of dental(牙科的) caries. It converts(皈依者) the acidic products of other species to less acidic products.
Aggregatibacter actinomycetemcomitans is considered an oral pathogen(病原体) due to its virulence(毒力) factors(因素), its association(协会) with localized(局部的) aggressive periodontitis(牙周炎) in young adolescents(青少年), and studies indicating(表明) that it can cause bone loss.
Some Lactobacillus species(物种) have been associated(交往) with dental(牙科的) caries(龋齿)although these bacteria are normally symbiotic(共生的) in humans and are found in the gut flora(肠道菌群).
一些乳酸菌和龋齿有关,但这些细菌被认为和人共生,属于肠道菌群。
标签:
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/biopy/p/4300369.html