|
1 |
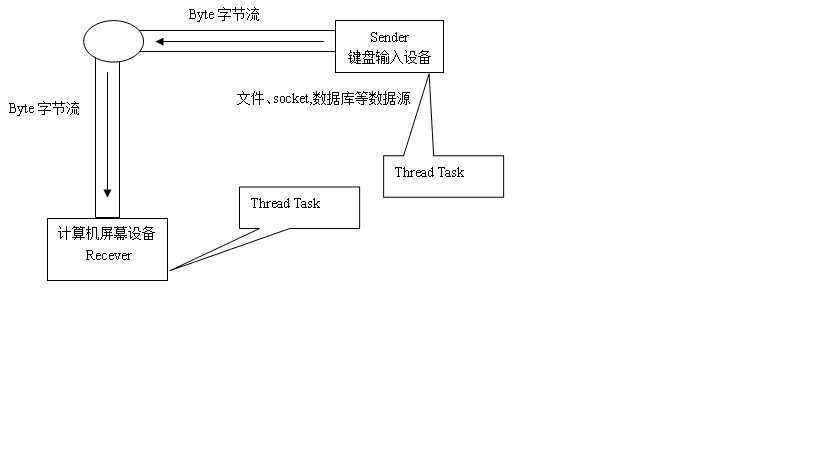
介绍:不同的数据源之间通过建立管道进行数据通信。如图: |
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26 |
<br>class
Recever implements
Runnable { PipedInputStream inputStream; Recever(PipedInputStream inputStream) { this.inputStream = inputStream; } @Override public
void run() { try
{ while
(true) { byte[] buffers = new
byte[512]; int
len = inputStream.read(buffers); String s = new
String(buffers, 0, len); System.out.println("收到:"
+ s); } // inputStream.close(); } catch
(Exception e) { } } } |
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25 |
class Sender implements
Runnable { PipedOutputStream outputStream; Sender(PipedOutputStream outputStream) { this.outputStream = outputStream; } @Override public
void run() { try
{ Scanner scanner = new
Scanner(System.in); while
(scanner.hasNext()) { String msg = scanner.nextLine(); outputStream.write(msg.getBytes()); outputStream.flush(); } } catch
(Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } |
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10 |
public static void main(String[] args) throws
InterruptedException, IOException { PipedInputStream in = new
PipedInputStream(); PipedOutputStream out = new
PipedOutputStream(); in.connect(out); new
Thread(new
Recever(in)).start(); new
Thread(new
Sender(out)).start(); } |
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23 |
//数据流的合并-读取几个文件的内容输入到下一个文件<br>InputStream in1 = new FileInputStream("c:/a1.txt"); InputStream in2 = new
FileInputStream("c:/a2.txt"); InputStream in3 = new
FileInputStream("c:/a3.txt"); Vector<InputStream> inputStreams = new
Vector<InputStream>();inputStreams.add(in1);inputStreams.add(in2);inputStreams.add(in3); Enumeration<? extends
InputStream> enumeration = inputStreams.elements();SequenceInputStream inputStream = new
SequenceInputStream(enumeration ); OutputStream os = new
FileOutputStream("c:/a4.txt"); byte[] buffer = new
byte[512]; int
length = -1; while((length = inputStream.read(buffer))!=-1){ os.write(buffer, 0, length); os.flush(); } os.close(); inputStream.close(); |
|
1
2
3
4
5
6 |
//内存读取<br>ByteArrayOutputStream arrayOutputStream = new ByteArrayOutputStream();arrayOutputStream.write("test".getBytes());arrayOutputStream.flush(); byte[] buffer = arrayOutputStream.toByteArray();ByteArrayInputStream arrayInputStream = new
ByteArrayInputStream(buffer ); |
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/gstsyyb/p/3774599.html