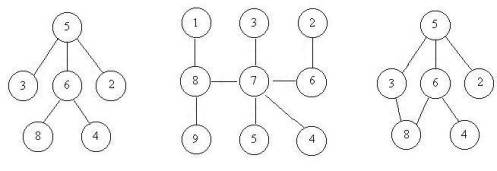
6 8 5 3 5 2 6 4 5 6 0 0 8 1 7 3 6 2 8 9 7 5 7 4 7 8 7 6 0 0 3 8 6 8 6 4 5 3 5 6 5 2 0 0 -1 -1
Yes Yes No
#include<set>
#include<map>
#include<iostream>
#include<string.h>
using namespace std;
const int M=500004;
int F[M];
int cnt[M];
int Find(int x)
{
int r=x;
while(F[r]!=r)
r=F[r];
int k=x;
while(k!=r)
{
int t=F[k];
F[k]=r;
k=t;
}
return r;
}
bool Is_same(int x,int y)
{
return Find(x)==Find(y);
}
void union_set(int x , int y)
{
int tx=Find(x);
int ty=Find(y);
if(tx!=ty)
{
F[tx]=ty;
}
}
int main()
{
int flag1=0;
int a,b;
loop:
for(int j=0; j<M; j++)
F[j]=j;
int aa=0,count=0;
set<int>dict;
int flag2=0;
memset(cnt,0,sizeof(cnt));
int MM=-1,MII=9999999;
cin>>a>>b;
if((a==-1)&&(b==-1))
return 0;
else if(a==0&&b==0)
{
cout<<"Yes"<<endl;
goto loop;
}
else
{
if(!cnt[a])
aa++;
if(!cnt[b])
aa++;
count++;
cnt[a]=1;
cnt[b]=1;
if(a>MM)
MM=a;
if(b>MM)
MM=b;
if(a<MII)
MII=a;
if(b<MII)
MII=b;
union_set(a,b);
}
while(cin>>a>>b,a+b)
{
if(!cnt[a])
aa++;
if(!cnt[b])
aa++;
count++;
cnt[a]=1;
cnt[b]=1;
if(a>MM)
MM=a;
if(b>MM)
MM=b;
if(a<MII)
MII=a;
if(b<MII)
MII=b;
union_set(a,b);
}
for(int t=MII; t<=MM; t++)
{
if(cnt[t]==1)
dict.insert(Find(t));
}
if(dict.size()!=1)
flag2=1;
if(!flag2&&aa==count+1)
cout<<"Yes"<<endl;
else
cout<<"No"<<endl;
dict.clear();
goto loop;
return 0;
}
#include<set>
#include<iostream>
#include<string.h>
using namespace std;
const int M=100004;
int F[M];
int Find(int x)
{
int r=x;
while(F[r]!=r)
r=F[r];
int k=x;
while(k!=r)
{
int t=F[k];
F[k]=r;
k=t;
}
return r;
}
bool Is_same(int x,int y)
{
return Find(x)==Find(y);
}
void union_set(int x , int y)
{
int tx=Find(x);
int ty=Find(y);
if(tx!=ty)
{
F[tx]=ty;
}
}
int main()
{
set<int>dict;
int flag1=0;
for(int j=0; j<M; j++)
F[j]=j;
int a,b,flag=0;
loop:
while(cin>>a>>b,a+b)
{
flag=1;
if((a==-1)&&(b==-1))
return 0;
dict.insert(a);
dict.insert(b);
if(Is_same(a,b))
flag1=1;
union_set(a,b);
}
if(!flag)
{
cout<<"Yes"<<endl;
goto loop;
}
int flag2=0;
set<int> ::iterator it=dict.begin();
int f0=Find(*it);
it++;
for(; it!=dict.end(); it++)
{
if(Find(*it)!=f0)
flag2=1;
}
//cout<<"flag="<<flag1<<" flag2="<<flag2<<endl;
if(flag1||flag2)
cout<<"No"<<endl;
else
cout<<"Yes"<<endl;
dict.clear();
for(int j=0; j<=M; j++)
F[j]=j;
flag=0;
goto loop;
return 0;
}
原文地址:http://blog.csdn.net/lsgqjh/article/details/45973721