标签:源码分析 添加 lin lse guid uid com 修改 点数据
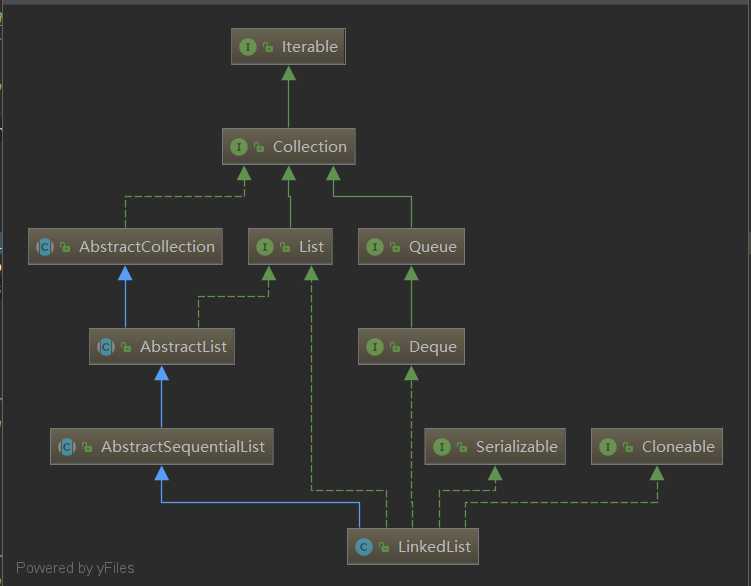
LinkedList 实现List接口,底层是双向链表,非线程安全。LinkedList还可以被当作堆栈、队列或双端队列进行操作。在JDK1.7/8 之后取消了循环,修改为双向链表。
内部类Node,用于存储链表的节点信息
private static class Node<E> {
E item;//节点数据
Node<E> next;//后驱
Node<E> prev;//前驱
Node(Node<E> prev, E element, Node<E> next) {
this.item = element;
this.next = next;
this.prev = prev;
}
}构造方法
//构造一个空的list
public LinkedList() {
}
//用已有的集合创建链表的构造方法
public LinkedList(Collection<? extends E> c) {
this();
addAll(c);
}在首部添加数据
public void addFirst(E e) {
linkFirst(e);
}
private void linkFirst(E e) {
final Node<E> f = first;
final Node<E> newNode = new Node<>(null, e, f);
first = newNode;
if (f == null)
last = newNode;
else
f.prev = newNode;
size++;
modCount++;
}在末尾添加数据,add()方法和addLast()一样
public void addLast(E e) {
linkLast(e);
}
public boolean add(E e) {
linkLast(e);
return true;
}
void linkLast(E e) {
final Node<E> l = last;
final Node<E> newNode = new Node<>(l, e, null);
last = newNode;
if (l == null)
first = newNode;
else
l.next = newNode;
size++;
modCount++;
}根据索引获取数据
public E get(int index) {
checkElementIndex(index);
return node(index).item;
}
Node<E> node(int index) {
// assert isElementIndex(index);
if (index < (size >> 1)) {
Node<E> x = first;
for (int i = 0; i < index; i++)
x = x.next;
return x;
} else {
Node<E> x = last;
for (int i = size - 1; i > index; i--)
x = x.prev;
return x;
}
}上述代码,利用了双向链表的特性,如果index离链表头比较近,就从节点头部遍历。否则就从节点尾部开始遍历。使用空间(双向链表)来换取时间。node()会以O(n/2)的性能去获取一个结点,如果索引值大于链表大小的一半,那么将从尾结点开始遍历。这样的效率是非常低的,特别是当 index 越接近 size 的中间值时。
https://crossoverjie.top/JCSprout/#/collections/LinkedList
标签:源码分析 添加 lin lse guid uid com 修改 点数据
原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/my12/p/10793477.html