标签:style class blog code http tar
给定一个非负整数序列{dn},若存在一个无向图使得图中各点的度与此序列一一对应,则称此序列可图化。进一步,若图为简单图,则称此序列可简单图化。
此题因为是无自环无重边,所以是简单图。用判定简单图可图化的Havel-Hakimi定理。
Havel-Hakimi定理:
一个度序列:
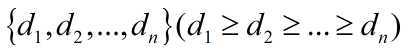
是简单图度序列当且仅当:
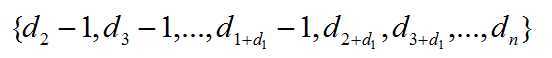
是简单图的度序列。
简单来讲,算法流程如下:
设度序列为d1,d2,d3....dn
1.如果度序列中元素有负数或者度序列和不为偶数,则肯定不可图。
2.每次取度序列中最大元素,设为M,如果M>n-1(n为此时的元素数),则不可图。否则取次大的M个元素,将他们都减1,再次加入到度序列中,元素数减1,如此往复,直到:
(1)度序列出现负数元素,则不可图,退出。
(2)度序列全为0,则可图,退出。
回到题目,这题由于n过大(10^5),所以不能每次都排序来找前M大的数,所以考虑用优先队列来实现高效的插入,排序,取最大元素等操作。
(优先队列的复杂度)
代码:

#include <iostream> #include <cstdio> #include <cstring> #include <cmath> #include <algorithm> #include <vector> #include <queue> #include <functional> using namespace std; #define N 100007 priority_queue<int,vector<int>,less<int> > que; queue<int> tmp; int check(int n) { int dmax,k,i; while(1) { dmax = que.top(); que.pop(); if(dmax > n-1) return 0; while(dmax--) { k = que.top(); que.pop(); k--; if(k < 0) return 0; tmp.push(k); } while(!tmp.empty()) { k = tmp.front(); tmp.pop(); que.push(k); } dmax = que.top(); if(dmax == 0 || n == 1) break; n--; } return 1; } int main() { int t,n,i,x; scanf("%d",&t); while(t--) { while(!que.empty()) que.pop(); while(!tmp.empty()) tmp.pop(); scanf("%d",&n); int flag = 1; int sum = 0; for(i=0;i<n;i++) { scanf("%d",&x); if(x < 0) flag = 0; que.push(x); sum += x; } if(!flag || sum%2) { puts("NO"); continue; } flag = check(n); if(flag) puts("YES"); else puts("NO"); } return 0; }
UESTC 913 握手 Havel定理+优先队列,布布扣,bubuko.com
标签:style class blog code http tar
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/whatbeg/p/3765392.html